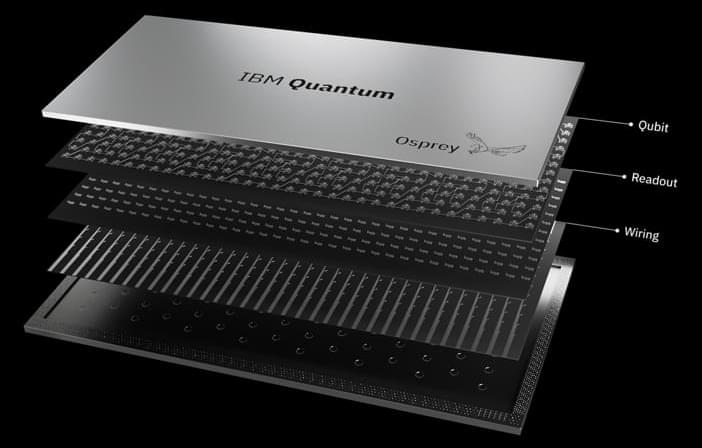
I’ve funded Ukraine media, the Ukraine army, and now I just funded the Ukraine navy. The navy part is extra interesting because it is “the world’s first naval fleet of drones”. That is pretty futuristic!
As Elon Musk said, “Future wars are all about the drones.”
Small and fast unmanned ships 3 russian vessels were damaged, including the Admiral Makarov, flagship of the russian Black Sea Fleet. This is the first case in history where the attack was carried out exclusively by unmanned vessels.
The result of this daring operation was incredible — russia has lost its undeniable advantage on the water. The killers of Ukrainian civilians — warships armed with missiles — became targets themselves.
Today, Ukraine starts assembling the world’s first Naval Fleet of Drones!