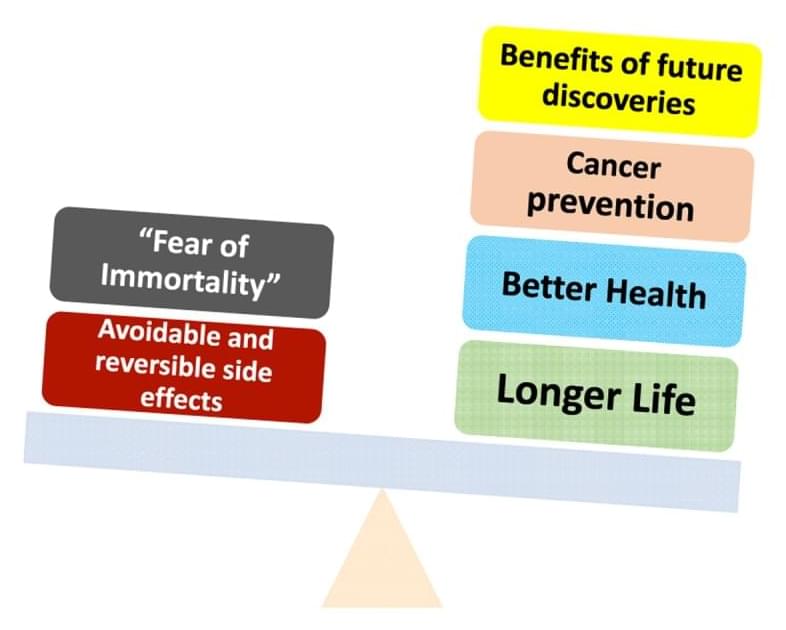
On the one hand, from the dawn of civilization humans have dreamed of immortality. On the other hand, from the dawn of civilization a myriad of anti-aging remedies turned out to be empty promises. Even worse, they often shorten lifespan. Two notable examples are antioxidants and human growth hormone. The idea that free radicals, or reactive oxygen species (ROS), cause aging was based on a “wild guess,” as Harman, a father of the ROS theory, acknowledged when he titled his paper, “I thought, thought, thought for four months in vain and suddenly the idea came” [116]. The idea is simple and intuitive, and it was widely accepted based on circumstantial evidence. In fact, ROS are inevitable products of metabolism, and they do damage biomolecules. Moreover, excessive ROS can shorten lifespan. Similarly, the atomic bomb can shorten life span. Yet this does not mean that either atomic bombs or oxidants are the cause of normal aging as we know it.
Numerous experiments support the ROS theory. However, key experiments ruled the ROS theory out (see for references [2, 117 – 122]. To make a long story short, antioxidants could in theory prolong lifespan if mTOR-driven (quasi-programmed) aging were suppressed and we lived long enough to die from ROS-induced post-aging syndrome (I will discuss the nuances in the forthcoming article “ROS and aging revisited”). Indeed, ROS will kill any organism eventually. However, organisms normally die from mTOR-driven, age-related diseases (aging as we know it) before ROS can kill them (see for discussion [2]). As an analogy, consider most of the passengers on the Titanic. Would antioxidant treatment have been useful to them for life extension? The best way to extend life for members of that group would have been to carry more life boats. Only after their safe rescue could one expect antioxidants to potentially increase their life further. Similarly, only after rescue from the quasi-program of aging may antioxidants potentially have an impact.