Three researchers from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency make some predictions for the future.
Category: military – Page 276
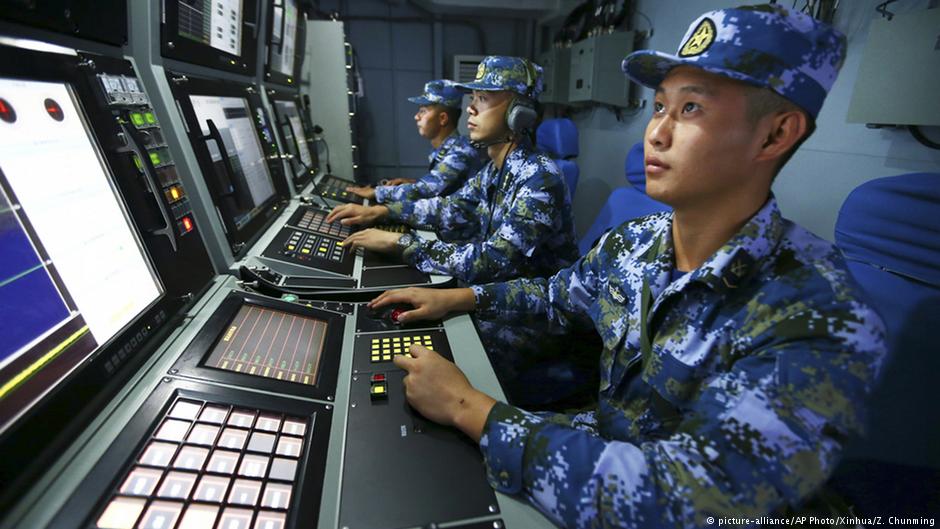

China’s military progress challenges Western dominance, says IISS
Chinese military technology is reaching “near-parity” with the West, a new report from the London-based think tank IISS has found. Western dominance in advanced military systems can no longer be taken for granted.
China accounted for a third of Asia’s military spending in 2016 and was looking to sell more arms abroad, the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) said in a report on Tuesday.
China’s overall defense budget last year was $145 billion (137 billion euros), 1.8 times higher than South Korea and Japan combined. China’s spending was topped only by the United States which spent $604.5 billion (572 billion euros) on defense in 2016.

Gov’t Sued For Taking US Company’s Business Plan And Giving It To Foreigners
Hmmmm.
A private space company is suing the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) for allegedly taking an idea and giving it to a foreign-owned competitor.
Orbital ATK accused DARPA, which develops military technology, of giving its business plan to repair satellites to Space Systems Loral (SSL), a company-based in California but registered as foreign-owned. Orbital ATK says handing business plans to SSL violates U.S. policy.
DARPA entered into a commercial partnership with Space Systems Loral (SSL) to take advantage of its Robotic Servicing of Geosynchronous Satellites (RSGS) program to capture, re-position, and repair satellites in orbit. DARPA plans to buy future RSGS services from SSL, despite it being a Bermuda-based company.

DARPA to brief industry on RadioBio program to communicate biologically using radio waves
While everyone is worried over Robots and other AI systems taking our jobs and do we need universal income; I want to use my energy to change the world and the people in it to be better, stronger, and smarter.
Definitely Quantum (Quantum Bio) at work here due to the experiment program write up for the RFP targeted cell to cell communications and leveraging electromagnetisms to do so. And, that is Quantum Mechanics at work.
ARLINGTON, Va. – ARLINGTON, Va. U.S. military researchers will use an online Webcast to brief industry later this month on a new initiative to determine if humans and other living things can communicate with one another biologically with radio waves without the use of conventional antennas or RF transmitting equipment.
Google Test Of AI’s Killer Instinct Shows We Should Be Very Careful
If climate change, nuclear weapons or Donald Trump don’t kill us first, there’s always artificial intelligence just waiting in the wings. It’s been a long time worry that when AI gains a certain level of autonomy it will see no use for humans or even perceive them as a threat. A new study by Google’s DeepMind lab may or may not ease those fears.
YK Bae can now amplify photonic laser thrust
Young Bae of Advanced Space and Energy Technologies in Tustin, California, has improved his photonic laser thruster. was developed with NASA funding. His thruster works because light exerts pressure when it hits something. In theory, it is possible to move an object like a CubeSat by nudging it with a laser beam. In practice, however, the pressure which light exerts is so small that a device able to do a useful amount of nudging would require a laser of unfeasibly large power.
Dr Bae has overcome this limitation by bouncing light repeatedly between the source laser and the satellite, to multiply the thrust. In his latest experiments, Dr Bae has managed to amplify the thrust imparted by a single nudge of the laser by a factor of 1,500, which is big enough to manoeuvre a CubeSat as well as a conventional thruster would. This brings two advantages. First, since no on-board propellant is required, there is more room for instruments. Second, there being no fuel to run out, a CubeSat’s orbit can be boosted as many times as is desired, and its working life prolonged indefinitely.
A suitable laser is required to provide the thrust. Dr Bae thinks it could be in orbit as well. The laser would be powered by solar cells and shepherd a veritable flock of CubeSats, providing the propulsion needed to move and arrange them as required.
Future Warfare: Meet The Electromagnetic Railgun
At the U.S. Army’s annual Maneuver and Fires Integration Experiment (MFIX), the Blitzer railgun performed successfully during eleven test firings. The test projectiles contained a Guidance Electronics Unit (GEU), which beamed back telemetry indicating the shells achieved an acceleration of over 30,000 gravities, and that all components survived the multi-Tesla magnetic field that powers the launcher.
“We continue to perform risk reduction and technology maturation of projectile designs and components to culminate in an integrated demonstration of a maneuvering railgun launched projectile,” says Nick Bucci, vice president of Missile Defense and Space Systems at General Atomics Electromagnetic Systems.
The next step is to integrate the system into a mobile, truck-based platform.
RadioBio: What role does electromagnetic signaling have in biological systems?
Many have asked me what does this DARPA announcement on their project (RadioBio) mean. Well, imagine a world in the next 10 to 15 years where you no longer need any devices (no smartphone, no AR contacts, no smartwatch, no wearables, no external BMIs or invasive implants, etc.) of any kind as Quantum Bio technology uses (in DARPA’s case) connected cell technology to connect people to people and information online (private and publically available. This approach is the least invasive method of turning cells into connected technology.
Military will mean no more lugging of devices and certain types of equipment around on the battlefield plus lower risk of stolen intelligence as no device or equipment left behind or stolen.
What does it mean to consumers? Means no more losing phones and other devices as well as broken down equipment be replaced every 2years and no more insurance and extra-warranty payments for devices; and no more devices stolen with your information on it. And, it means my doctors and body (AI and non-AI methods) can monitor my health and activate pain relief, etc. through biosystem treatments such as pain can be suppressed via the readings or before the pain is felt. It also empowers the immune system to proactively prevent diseases as the biosystem technology will monitor and treat as needed.
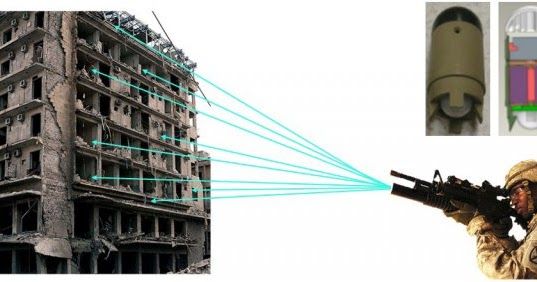
Smaller and smarter MEMS and electronics for bullets that can monitor a building during urban warfare
Engineers at the U.S. Army Armament Research, Development and Engineering Center, or ARDEC, have been making advancements in an initiative called “Component Miniaturization.”
Its mission focuses on making armament systems more precise, energy efficient, scalable and effective by reducing the size of critical components in sub-systems such as safe and arm devices, electronics packages, power supplies and inertial measurement systems. Size reductions in one sub-system can have a positive effect on another. For example, a smaller and more efficient electronics package design can reduce power supply demands as well as reduce the need for heavier supporting structures. The space savings and mass savings could then be used to add a larger explosive warhead or increase control surfaces for additional maneuverability. The reduced size and mass could also allow for additional portability to smaller calibers or to systems with greater launch velocities.
The initiative involves several discrete projects, some of which are described below:
China’s Intelligent Weaponry Gets Smarter
The Pentagon’s plan to bring A.I. to the military is taking shape as Chinese researchers assert themselves in the nascent technology field. And that shift is reflected in surprising commercial advances in artificial intelligence among Chinese companies.
Robert O. Work, the veteran defense official retained as deputy secretary by President Trump, calls them his “A.I. dudes.” The breezy moniker belies their serious task: The dudes have been a kitchen cabinet of sorts, and have advised Mr. Work as he has sought to reshape warfare by bringing artificial intelligence to the battlefield.
Last spring, he asked, “O.K., you guys are the smartest guys in A.I., right?”
No, the dudes told him, “the smartest guys are at Facebook and Google,” Mr. Work recalled in an interview.