Nice.
When you think of diamonds, rings and anniversaries generally come to mind. But one day, the first thing that will come to mind may be bone surgery. By carefully designing modified diamonds at the nano-scale level, a Missouri University of Science and Technology researcher hopes to create multifunctional diamond-based materials for applications ranging from advanced composites to drug delivery platforms and biomedical imaging agents.
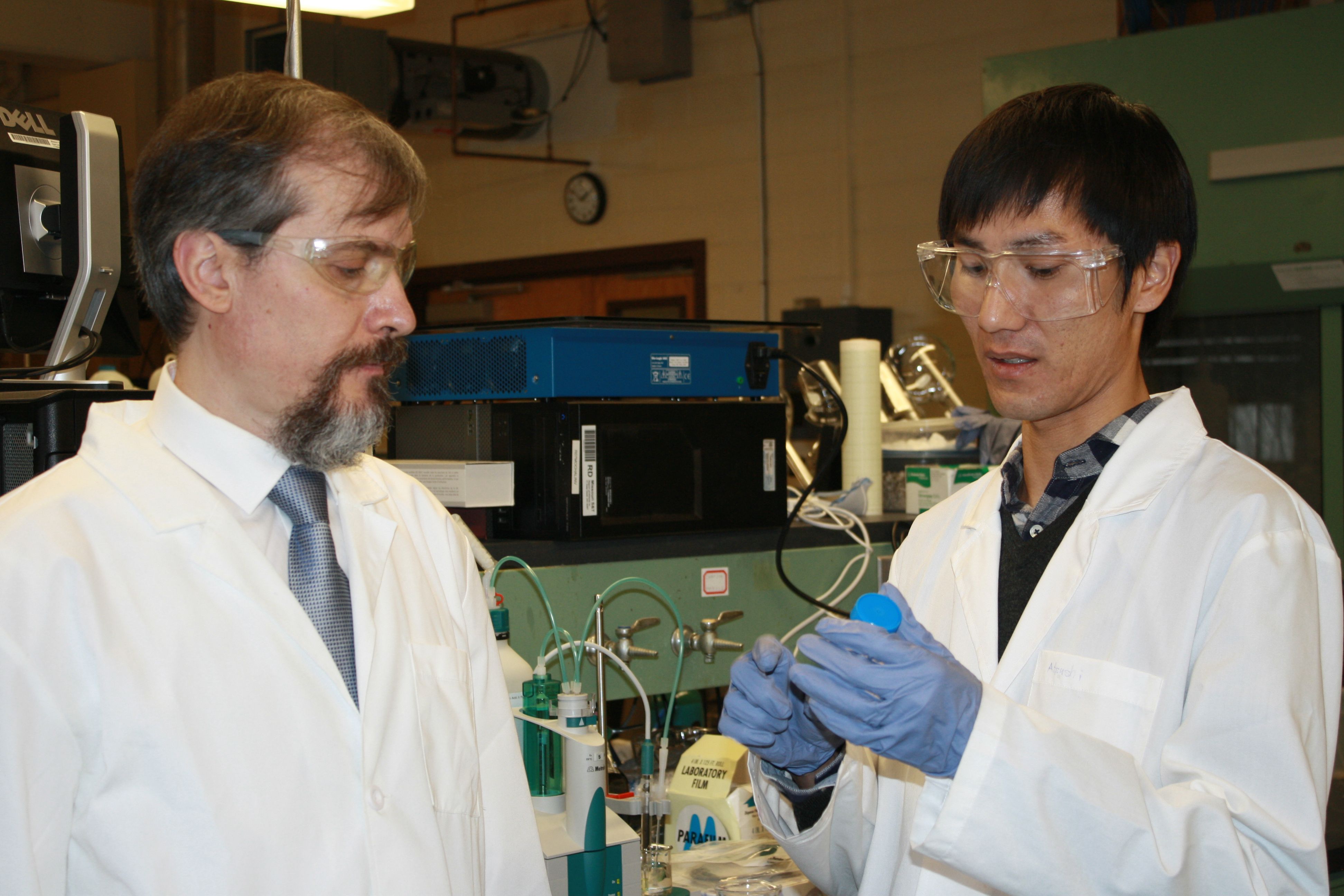
Dr. Vadym Mochalin, an associate professor of chemistry and materials science and engineering at Missouri S&T, is characterizing and modifying 5-nanometer nanodiamond particles produced from expired military grade explosives so that they can be developed to perform specific tasks. His current research studies their use as a filler in various types of composites.
Mochalin hopes to develop a way to uniformly incorporate the nanodiamonds and form strong chemical bonds between them to help design composite structures that can be used in medical applications, oil drilling bits, polishing and lubricating compositions, and even energy storage systems. Nanodiamonds are the ideal choice for such applications because they are mechanically strong, chemically stable and non-toxic. They can also form bonds with many other materials due to their tailorable surface chemistry.



 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)


 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)