A new theory proposes that the quantum properties of an object extend into an “atmosphere” that surrounds the material.
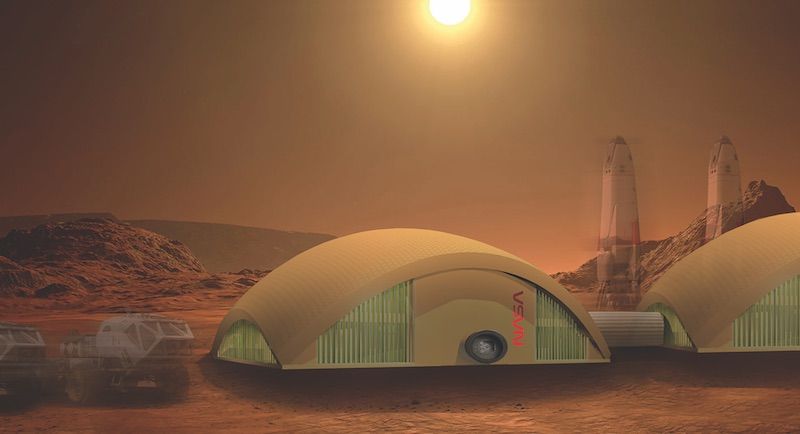



The thought of colonizing Mars has science fiction aficionados, scientists, and billionaire entrepreneurs staring up at the night sky with renewed wonder and inspiration. But the key to achieving the lofty goal of colonizing and building extensively on a new planet may not exist out among the stars, but under our feet right here on Earth.
Christopher Maurer, an architect and Founder of Cleveland-based Redhouse Studio, and Lynn Rothschild, a NASA Ames researcher, believe algae and mycelium (the vegetative part of a fungus that consists of a network of fine white filaments) may make the perfect building material on Mars.

Researchers from Drexel University’s College of Engineering invented a material called MXene, that they say perform as well as those currently used in mobile devices.
MXene titanium carbide can be dissolved in water to create an ink or paint and the exceptional conductivity of the material enables it to transmit and direct radio waves, even when it’s applied in a very thin coating.
It would allow antennas to easily applied to wide variety of objects and surfaces without adding additional weight or circuitry or requiring a certain level of rigidity.
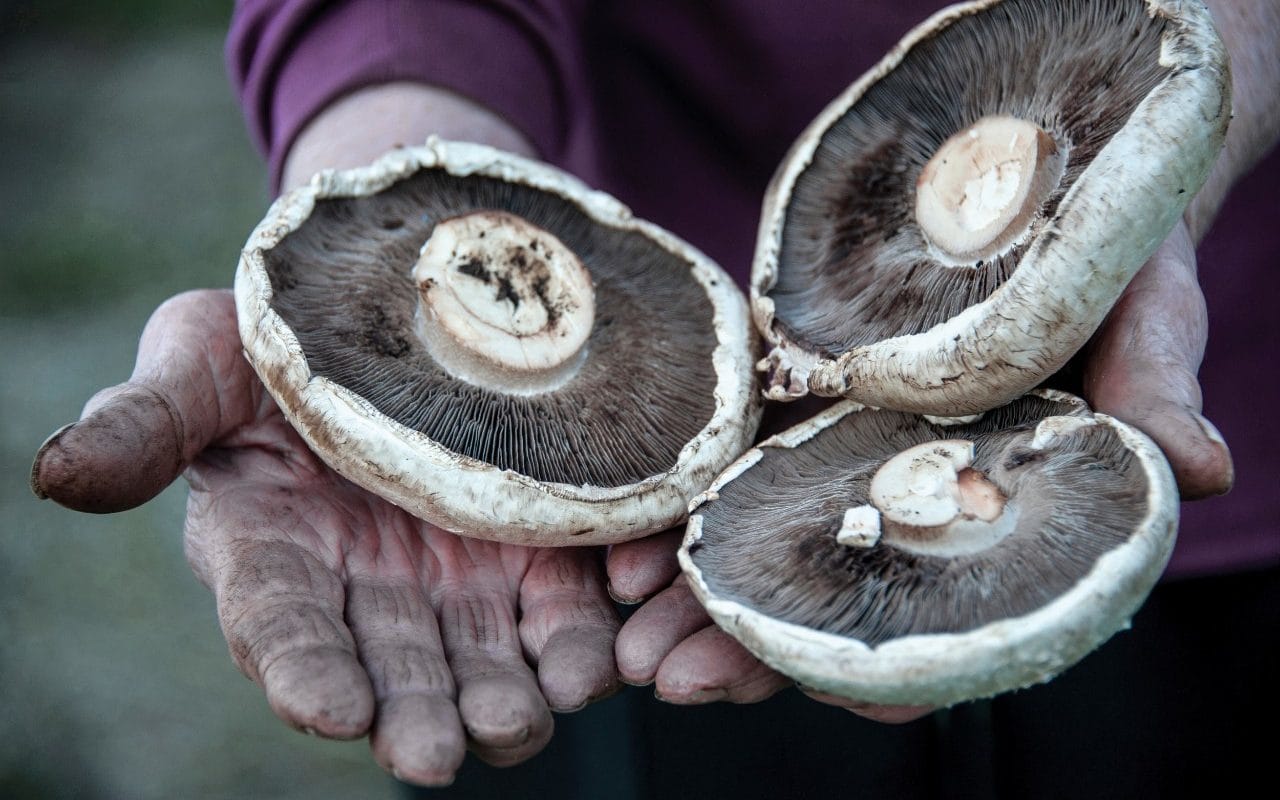


Fungi could be the key to winning the war on plastic, leading scientists at Kew Gardens has said.
The first ever report on the state of the world’s fungi has today revealed that if the natural properties of fungus can be harnessed and developed, plastic could be broken down naturally in weeks rather than years.
Kew Gardens and a team of over 100 scientists from 18 countries have compiled the paper, which shows how different organisms can decompose plastics, clean up radioactive material and even speed up the production of biodiesel.
TRULY SUPER. There’s a reason researchers call graphene a “super material.” Even though it’s just a single layer of carbon atoms thick, it’s super strong, super flexible, and super light. It also conducts electricity, and is biodegradable. Now an international team of researchers has found a way to use the super material: to create artificial retinas.
They presented their work Monday at a meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS).
ARTIFICIAL RETINAS. The retina is the layer of light-sensitive cells at the back of the eye responsible for converting images into impulses that the brain can interpret. And without a functional one, a person simply can’t see.
Graphene — an ultrathin material consisting of a single layer of interlinked carbon atoms — is considered a promising candidate for the nanoelectronics of the future. In theory, it should allow clock rates up to a thousand times faster than today’s silicon-based electronics. Scientists from the Helmholtz Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) and the University of Duisburg-Essen (UDE), in cooperation with the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research (MPI-P), have now shown for the first time that graphene can actually convert electronic signals with frequencies in the gigahertz range — which correspond to today’s clock rates — extremely efficiently into signals with several times higher frequency. The researchers present their results in the scientific journal Nature.
Gatebox’s Boku no Yome (“My Wife”) has been released in mass production for 150,000 yen (US$1,352). The holographic character stands about 8 inches tall and talks to her husband from behind a cylindrical plastic barrier. In addition to the upfront cost for Boku no Yome, husbands must pay a subscription fee of 1,500 yen (US$13.52) per month to keep their wife from getting outdated.