Lore et al. explore how biological and synthetic replacement therapies, from engineered tissues to advanced prosthetics, could restore aging cells and organs, offering strategies to extend healthy human lifespan and combat age-related decline.



Developmental time (or time to maturity) strongly correlates with an animal’s maximum lifespan, with late-maturing individuals often living longer. However, the genetic mechanisms underlying this phenomenon remain largely unknown. This may be because most previously identified longevity genes regulate growth rate rather than developmental time. To address this gap, we genetically manipulated prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH), the primary regulator of developmental timing in Drosophila, to explore the genetic link between developmental time and longevity. Loss of PTTH delays developmental timing without altering the growth rate. Intriguingly, PTTH mutants exhibit extended lifespan despite their larger body size. This lifespan extension depends on ecdysone signaling, as feeding 20-hydroxyecdysone to PTTH mutants reverses the effect. Mechanistically, loss of PTTH blunts age-dependent chronic inflammation, specifically in fly hepatocytes (oenocytes). Developmental transcriptomics reveal that NF-κB signaling activates during larva-to-adult transition, with PTTH inducing this signaling via ecdysone. Notably, time-restricted and oenocyte-specific silencing of Relish (an NF-κB homolog) at early 3rd instar larval stages significantly prolongs adult lifespan while delaying pupariation. Our study establishes an aging model that uncouples developmental time from growth rate, highlighting NF-κB signaling as a key developmental program in linking developmental time to adult lifespan.
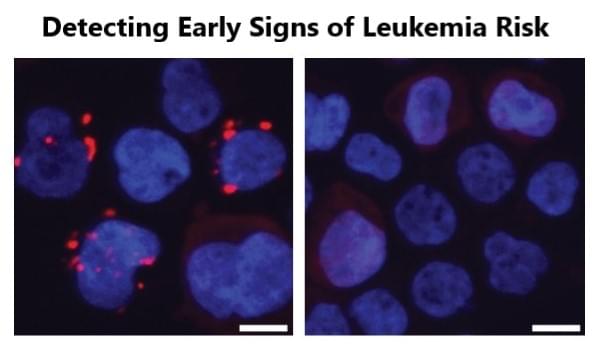
New findings in Nature reveal how age-related gut changes fuel the growth of pre-leukemic blood cells. Scientists at Cincinnati Children’s along with an international team of researchers have discovered a surprising new connection between gut health and blood cancer risk — one that could transform how we think about aging, inflammation, and the early stages of leukemia.
As we grow older — or in some cases, when gut health is compromised by disease — changes in the intestinal lining allow certain bacteria to leak their byproducts into the bloodstream. One such molecule, produced by specific bacteria, acts as a signal that accelerates the expansion of dormant, pre-leukemic blood cells, a critical step to developing full-blown leukemia.
The team’s findings — published April 23, 2025, in the journal Nature — lay out for the first time how this process works. The study also suggests that this mechanism may reach beyond leukemia to influence risk for other diseases and among older people who share a little-known condition called clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP).
ITrust Capital: Use code IMPACTGO when you sign up and fund your account to get a $100 bonus at https://impacttheory.co/iTrustCapitalMay.
Shopify: Sign up for your one-dollar-per-month trial period at https://impacttheory.co/ShopifyApr.
On this mind-bending episode of Impact Theory, Tom Bilyeu sits down with Ben Lamm, the visionary entrepreneur behind Colossal Biosciences, to explore a world that sounds straight out of science fiction—yet is rapidly becoming our reality. Together, they pull back the curtain on the groundbreaking technology making de-extinction not only possible, but increasingly practical, from resurrecting woolly mammoths and dire wolves to saving endangered species and unraveling the secrets of longevity.
Ben explains how CRISPR gene editing has unlocked the power to make precise DNA changes—editing multiple genes simultaneously, synthesizing entirely new genetic blocks, and pushing the limits of what’s possible in biology and conservation. The conversation dives deep into the technical hurdles, ethical questions, and the unexpected magic of re-engineering life itself, whether it’s creating hairier, “woolly” mice or tackling the colossal challenge of artificial wombs and universal eggs.
But this episode goes way beyond Jurassic Park fantasies. Tom and Ben debate the future of human health, gene selection through IVF, the specter of eugenics, global competition in biotechnology, and how AI will soon supercharge the pace of biological engineering. They even touch on revolutionary solutions to our plastic crisis and what it means to inspire the next generation of scientists.
Get ready to have your mind expanded. This is not just a podcast about bringing back extinct creatures—it’s a deep dive into the next frontiers of life on Earth, the technologies changing everything, and the choices we’ll face as architects of our own biology. Let’s get legendary.
00:00 Meet Ben Lamm.
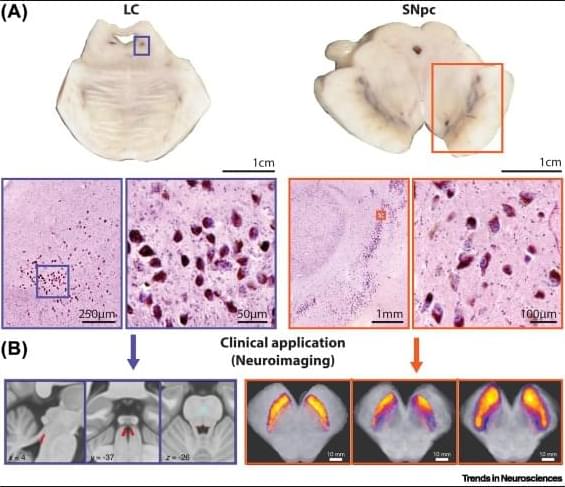
Neuromelanin is a unique pigment made by some human catecholamine neurons. These neurons survive with their neuromelanin content for a lifetime but can also be affected by age-related neurodegenerative conditions, as observed using new neuromelanin imaging techniques. The limited quantities of neuromelanin has made understanding its normal biology difficult, but recent rodent and primate models, as well as omics studies, have confirmed its importance for selective neuronal loss in Parkinson’s disease (PD). We review the development of neuromelanin in dopamine versus noradrenaline neurons and focus on previously overlooked cellular organelles in neuromelanin formation and function. We discuss the role of neuromelanin in stimulating endogenous α-synuclein misfolding in PD which renders neuromelanin granules vulnerable, and can exacerbates other pathogenic processes.
At the Artificiality Summit 2024, Michael Levin, distinguished professor of biology at Tufts University and associate at Harvard’s Wyss Institute, gave a lecture about the emerging field of diverse intelligence and his frameworks for recognizing and communicating with the unconventional intelligence of cells, tissues, and biological robots. This work has led to new approaches to regenerative medicine, cancer, and bioengineering, but also to new ways to understand evolution and embodied minds. He sketched out a space of possibilities—freedom of embodiment—which facilitates imagining a hopeful future of \.

Extract from “Evolution, Basal Cognition and Regenerative Medicine”, kindly contributed by Michael Levin in SEMF’s 2023 Interdisciplinary Summer School (http…

What if the secret to longevity wasn’t in the mind or the gut — but in the heart?
Speaking at the inaugural New York Times Well Festival on Wednesday, psychiatrist and researcher Dr. Robert Waldinger announced he and his team were “shocked” by “the biggest predictor of who was going to live long and stay healthy.”
Waldinger, the director of the Harvard Study of Adult Development — the longest-running scientific study of adult life — revealed the predictor was “how connected you were to other people and particularly the warmth of your connection to other people.”
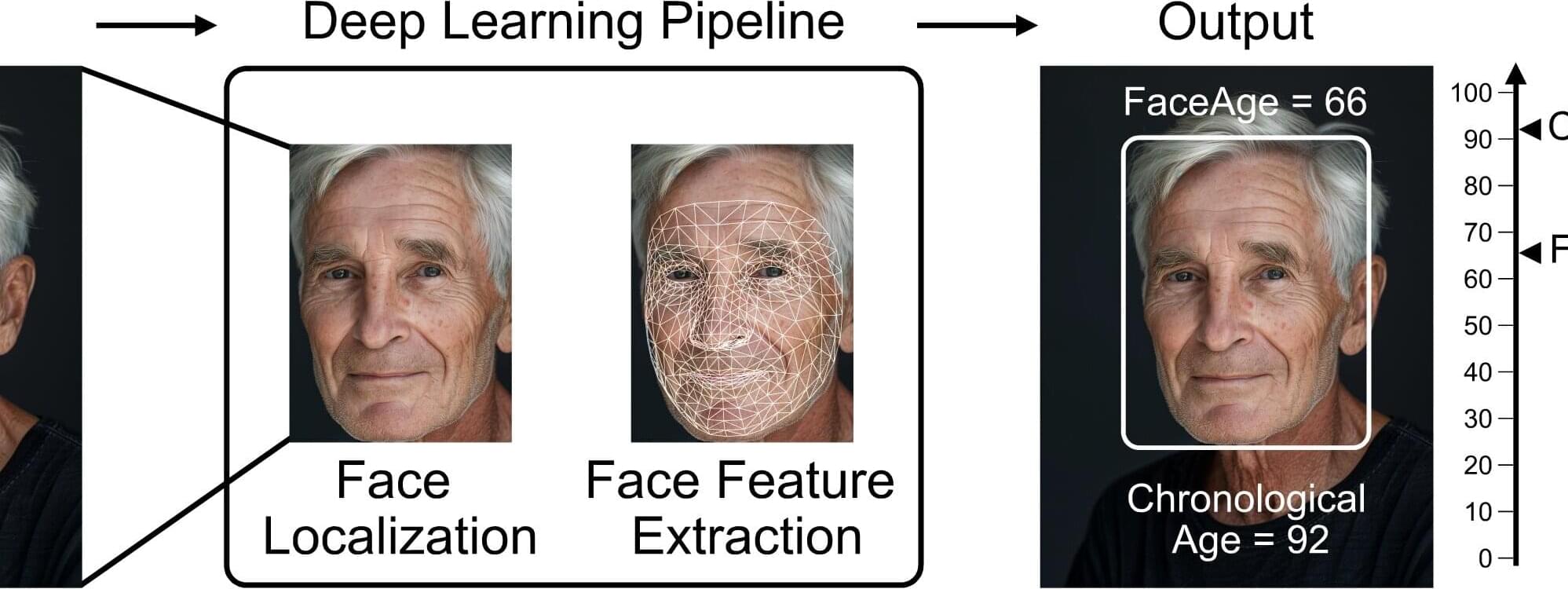
Eyes may be the window to the soul, but a person’s biological age could be reflected in their facial characteristics. Investigators from Mass General Brigham developed a deep learning algorithm called “FaceAge” that uses a photo of a person’s face to predict biological age and survival outcomes for patients with cancer.
They found that patients with cancer, on average, had a higher FaceAge than those without and appeared about five years older than their chronological age.
Older FaceAge predictions were associated with worse overall survival outcomes across multiple cancer types. They also found that FaceAge outperformed clinicians in predicting short-term life expectancies of patients receiving palliative radiotherapy.