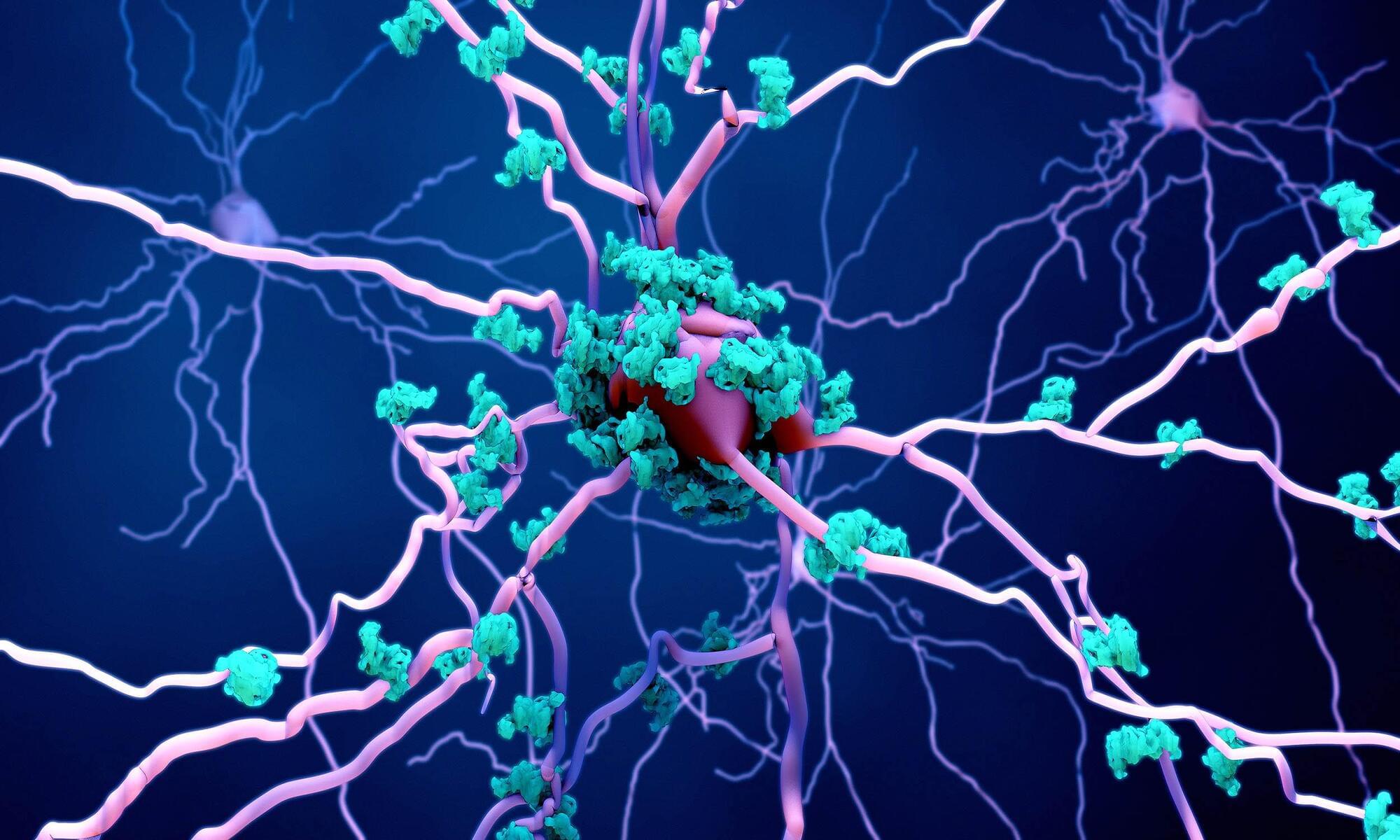
Researchers have discovered a safe, non-invasive way to enhance the brain’s waste clearance system by mechanically stimulating lymphatic vessels just beneath the facial skin.
Category: life extension – Page 69
How our bones are repaired by skeletal stem cells: Scientist discover four major subtypes
Whether you are a competitive athlete or an older adult, strong bones are essential—not only for movement, but also for overall health. Now, a new study has shed new light on how our bones are maintained and repaired by stem cells—and how that process is disrupted with age and in situations of poor healing. The findings could open doors to therapies that speed recovery from injuries, improve bone health, and boost performance longevity.
“Stem cells are the source of all new bone formation, and so work like this is really the foundation of developing new treatments for conditions of poor skeletal health and delayed or impaired fracture regeneration,” said Thomas Ambrosi, who led this study while he was a postdoctoral fellow in Charles Chan’s laboratory at Stanford University and later in his current position as an assistant professor of Orthopedic Surgery at UC Davis. The study was published in Cell Stem Cell.
“This work exemplifies the mission of the Wu Tsai Human Performance Alliance to advance science that helps people stay healthy, recover faster, and achieve peak performance,” said Michael Longaker, MD, a senior author on the study, a professor in the School of Medicine at Stanford University, and a member of the Wu Tsai Human Performance Alliance at Stanford.

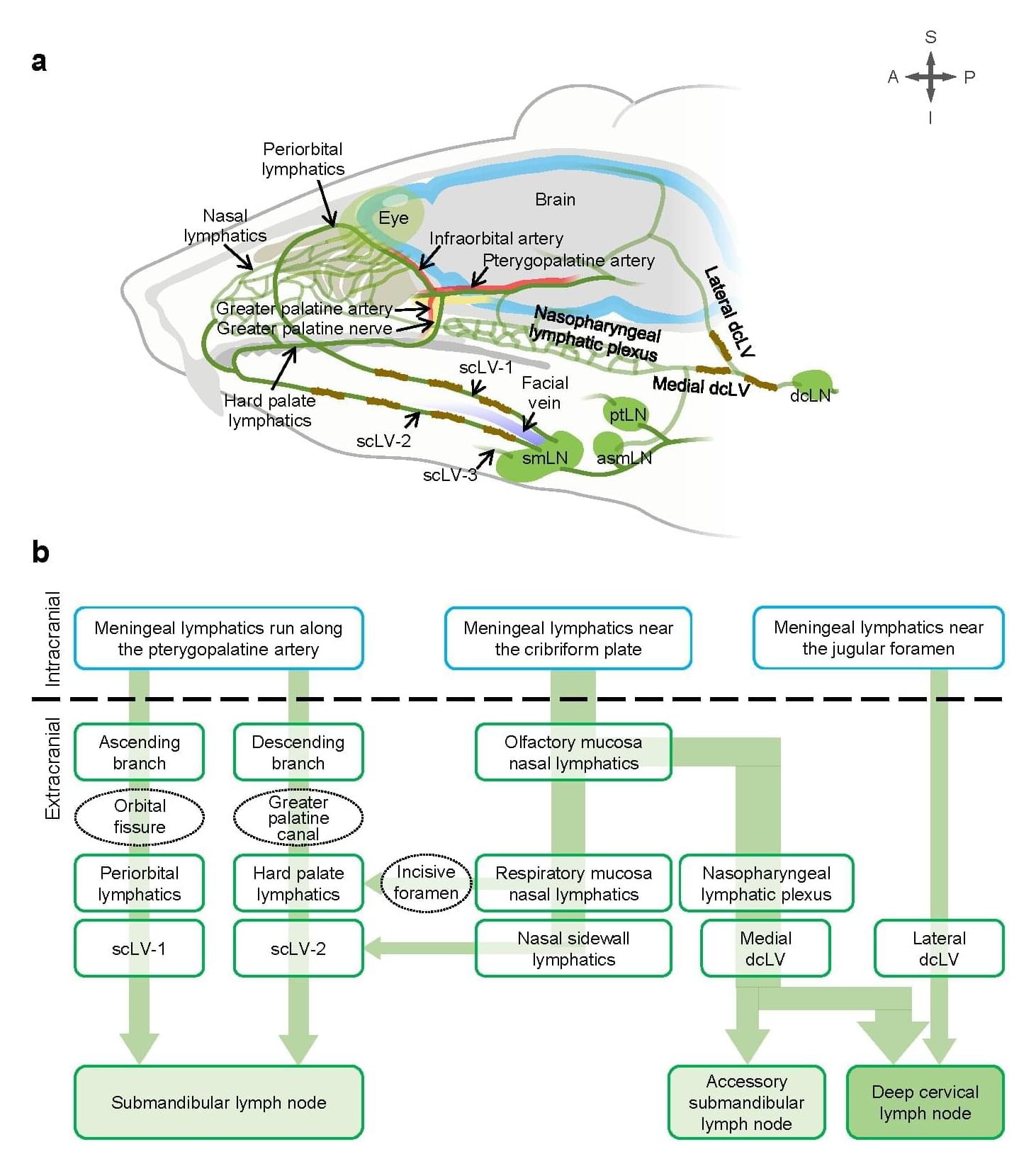
Non-invasive mechanical stimulation can enhance brain waste clearance
Scientists at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) have uncovered a non-invasive method to boost the brain’s natural waste drainage system—a discovery that could open new avenues for tackling age-related neurological disorders.
In a study published in Nature, researchers from the IBS Center for Vascular Research, led by Director Koh Gou Young, along with senior researchers Jin Hokyung, Yoon Jin-Hui, and principal researcher Hong Seon Pyo, demonstrate that precisely stimulating the lymphatics under skin on the neck and face can significantly enhance the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)—the liquid that cushions the brain and helps remove toxic waste —through lymphatic vessels.
This offers a new approach to clearing brain waste using safe, non-invasive mechanical stimulation, rather than relying on drugs or surgical interventions.
Max More: transhumanism, cryonics and the future societies
We dived deep into the difference between cryonics and biostasis, the philosophy of extropy, the future of cryonics, ethical and political dilemmas connected with biostasis, the proactionary principle, reframing the “death” idea, the future of human identity and much more!
Telomere Shortening: The ABSOLUTE Limit to Human Lifespan??
Ever wonder why we can’t live forever? The answer might be ticking inside every one of your cells. In this video, Dr. Bill Andrews dive into the fascinating…
CRISPR gene editing in blood stem cells linked to premature aging effects: Study offers solutions
Scientists at the San Raffaele Telethon Institute for Gene Therapy (SR-Tiget), Milan, have found that gene editing using CRISPR-Cas9 in combination with AAV6 vectors can trigger inflammatory and senescence-like responses in blood stem cells, compromising their long-term ability to regenerate the blood system.
The study, published in Cell Reports Medicine, outlines new strategies to overcome this hurdle, improving both the safety and efficacy of gene-editing-based therapies for inherited blood disorders.
The research was led by Dr. Raffaella Di Micco, group leader at SR-Tiget, New York Stem Cell Foundation Robertson Investigator and Associate Professor at the School for Advanced Studies (IUSS) of Pavia, in collaboration with Professor Luigi Naldini, Director of SR-Tiget, and several European research partners.

The Revolution Against Aging And Death Festival (RAADFest): James Strole
New YT video, featuring RAADFest creator, James Strole!
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY