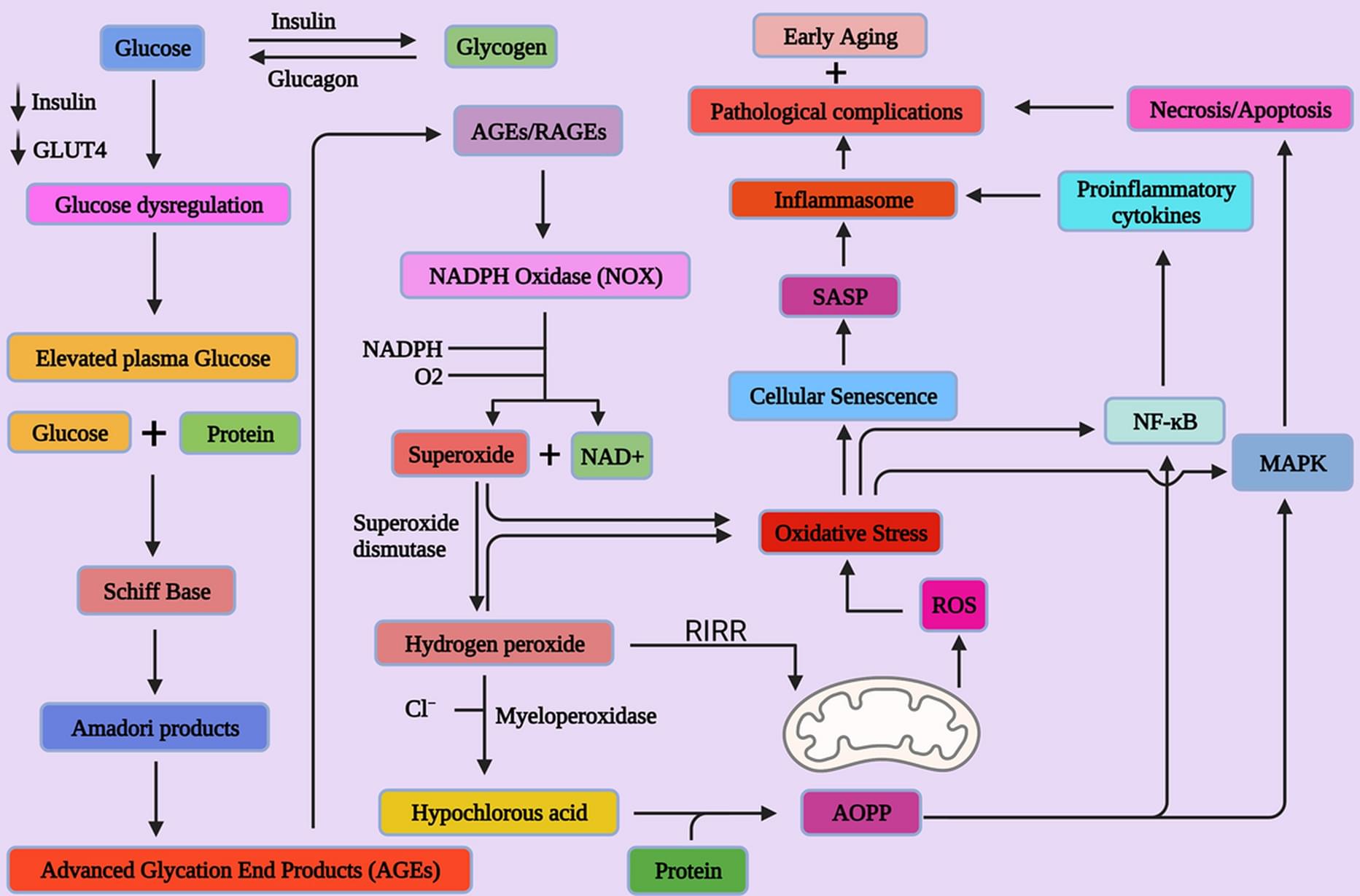
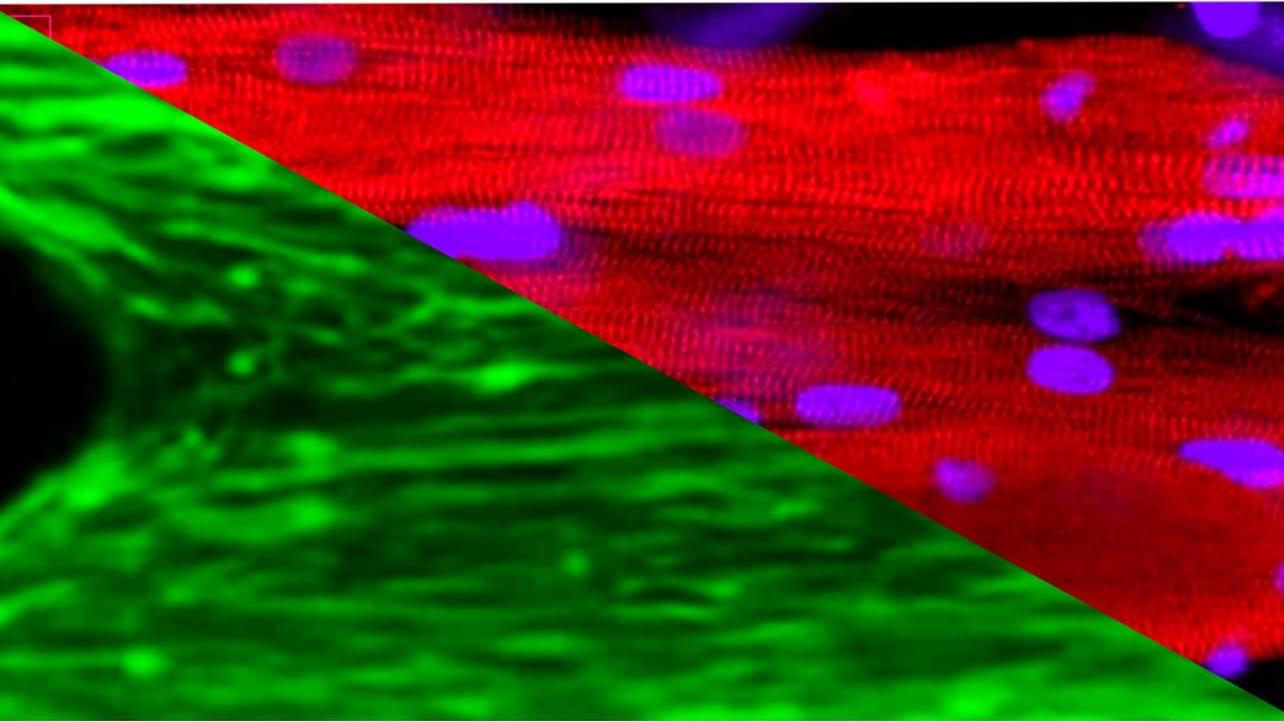
Sarcopenia, which is a progressive and extensive decline in muscle mass and strength, is common with aging and estimated to affect up to 50% of people aged 80 and older. It can lead to disability and injuries from falls and is associated with a lower quality of life and an increased mortality. Apart from lifestyle changes, there is no current clinical treatment for sarcopenia.
Space flight with the associated absence of gravity and limited strain on muscles causes muscle weakness, a prominent feature of sarcopenia, within a short period of time, providing a time lapse view on age-related atrophy-associated changes in the muscle. This relatively short window of time in space provides a microgravity model for muscular aging and opens opportunities for studying sarcopenia, which normally takes decades to develop in patients on earth.
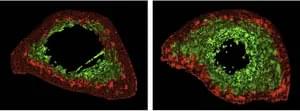
To understand the changes of muscle in microgravity, Siobhan Malany, Maddalena Parafati, and their team from the University of Florida, USA, engineered skeletal muscle microtissues from donor biopsies and launched them to the International Space Station (ISS) aboard SpaceX CRS-25. Their findings were published today in Stem Cell Reports. The microtissues were taken from both young, active donors and from aged, sedentary donors and cultured in an automated mini lab, which besides regular feeding and monitoring of cultures also enabled electrical stimulation to simulate exercise. On earth, the contraction strength of microtissues from young, active individuals was almost twice as much as the strength of tissues from older, sedentary individuals. After only two weeks in space, muscle strength trended to decline in the young tissues and was now more comparable to the strength of old tissues. A similar trend was seen for the muscle protein content, which was higher in young microtissues on earth compared to old microtissues but decreased in microgravity to levels measured in old tissues. Further, space flight changed gene expression, particularly in the younger microtissues and disturbed cellular processes related to normal muscle function. Interestingly, electrical stimulation could mitigate these changes in gene expression to some extent.