Category: life extension – Page 649

Silicon Valley is selling an ancient dream of immortality
It is tempting to dismiss scientifically inspired presentiments of immortality as arrant nonsense, but we should not underestimate the way ideas like transhumanism speak powerfully to our unconscious need for delusion. This is not only a new religion that does without God and churches — it also is a marketing strategy for new technology. A novel form of cross-promotion and co-branding, tech evangelism really aims at a deeper and more efficient penetration into the digital marketplace by offering mortality denial in the same package.
Human beings are the only animals to have evolved an insight into their own death.

New Tech Is Giving Humanity Many Potential Paths to Immortality
Both Kurzweil and the 2045 program have predicted the state of machine-human singularity being achieved by 2045, but what are the methods of achieving such an end and what are the consequences of doing so?
Herodotus’s Fountain of Youth. Rowling’s Philosopher’s Stone. Barrie’s Neverland. Ovid’s Cumaean Sibyl. The idea of immortality has been ingrained in humanity’s creative consciousness since our humble beginnings. In the present day, eternal youth may soon move out of the realms of myth and into a reality thanks to developing technologies.
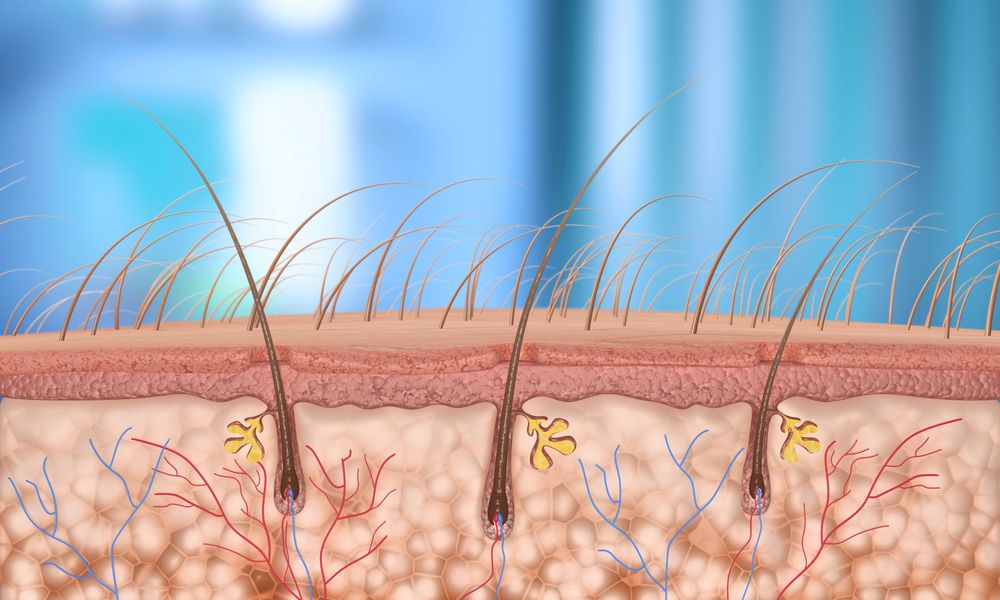
Reactivating Stem Cells Regrows Hair
Researchers at UCLA have offered new hope to people losing their hair. These scientists have discovered a way to activate stem cells in the follicles to make hair grow again.
The new study published in the journal Nature Cell Biology gives us a tantalizing hint that we can restore hair growth and treat conditions such as baldness and alopecia[1]. These conditions are associated with hormonal imbalance, stress, aging, and chemotherapy treatment.

Aging Hearts Find a New Lease of Life
According to a new study, aging hearts might find a new lease on life. Researchers have demonstrated that stem cells taken from young rats and given to aged rats rejuvenated their hearts, making them functionally younger in a number of ways.
Young at heart
The new study published in the European Heart Journal investigated the effects of cardiac stem cells on the function and structure of aged hearts[1]. There have been previous experiments using cardiosphere-derived cells (CDCs) that have delivered promising results, but they have never been tested in relation to aging.
Breakthrough device heals organs with a single touch
Researchers at The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and Ohio State’s College of Engineering have developed a new technology, Tissue Nanotransfection (TNT), that can generate any cell type of interest for treatment within the patient’s own body. This technology may be used to repair injured tissue or restore function of aging tissue, including organs, blood vessels and nerve cells.
Results of the regenerative medicine study published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
“By using our novel nanochip technology, injured or compromised organs can be replaced. We have shown that skin is a fertile land where we can grow the elements of any organ that is declining,” said Dr. Chandan Sen, director of Ohio State’s Center for Regenerative Medicine & Cell Based Therapies, who co-led the study with L. James Lee, professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering with Ohio State’s College of Engineering in collaboration with Ohio State’s Nanoscale Science and Engineering Center.
Scientists rejuvenate old hearts
In the study, 22-month-old rats — who were considered old — received stem cells from four-month-old rats.
Across the board, all of them experienced improved heart function, improved their exercise capacity by an average of 20 percent, and regrew hair faster than rats that didn’t receive the cells.
They also demonstrated longer heart cell telomeres.
Until now, scientists have tested the method to repair damage. But the Cedars-Sinai team in LA — who did the world’s first cardiac stem cell infusion in 2009 — have shown it can also reverse aging.

Congratulations to the AgeMeter campaign (https://www.lifespan.io/agemeter/) for blasting past the half way mark to 55%, and also congratulations to you all for helping fund this important biomarker system, supported by Drs. George Church, Aubrey de Grey, and David Sinclair
Let’s keep up the momentum and continue to show the world what power the crowd can have in standing up to age-related disease. # LifespanIO # CrowdfundTheCure.

Could the end of tooth decay be in sight?
One of the more important things we can do for longevity is keeping our teeth clean and keeping decay at bay. It might sound strange at first, but it is true. The harm that bacteria causes, especially in the gums, can spread to other tissues and increase inflammation throughout the body.
Some studies show a strong correlation between harmful oral bacteria and mortality rates later in life[1]. The mouth is an easy point of entry for harmful bacteria to invade the body, so it makes sense that maintaining oral hygiene should be an essential part of your health and longevity strategy.
Proteostasis: How Misfolded Proteins Cause Age-related Diseases
Coming from a fusion of the words ‘protein’ (a molecule that a cell uses as a machine or scaffolding) and ‘stasis’ (meaning to keep the same), the term ‘proteostasis’ can essentially be simplified into “Each function reliant on proteins is running as it should. There are enough proteins to serve a function, and the concentrations of proteins are being maintained at healthy levels.”
Proteostasis is the process that cells perform in order to have all their proteins functioning properly; this, in turn, allows cells to work properly. Since cells are the building blocks of our bodies, when they work properly, we are healthy.
When proteostasis is not maintained, cells become dysfunctional and can die; this failure can lead to aging, cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, inflammation, developmental defects, and other problems. The loss of proteostasis is thought to be a primary reason we age, and we discuss how this happens in more detail here.