Have you seen the clickbait campaign that focuses on the research of Dr. Steven Gundry. It employs a slimy, photo-tile lure that asks you to turn up your speakers and then hawks a product or service disguised as a breakthrough discovery. These scams force the viewer to stay on the page. Typically, there is no indication of how long the video is, or any way to skip forward,
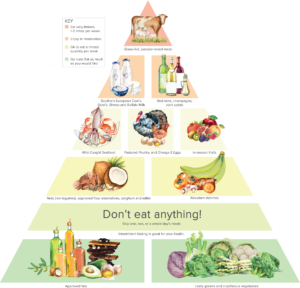
But often, it is hard to tell if a photo tile is news or clickbait. Big companies like Yahoo and Outbrain intermingle genuine news with marketing scams, teasers and outright fake news into an array of little photos at the end of every feature. This particular clickbait may be a story of a dogged counter-cultural researcher with a genuinely relevant finding. It could be newsworthy…I’m just not sure. Dr. Gundry clearly believes that our health is adversely affected by many of the plant based foods that we thought was healthy, because of a defense mechanism linked to lectin.
Steven Gundry Food Pyramid
Passing judgement on Dr. Gundry’s evolutionary claims and diet recommendations begs for independent clinical studies, or at least the analysis and commentary of scholars in nutrition, gastroenterology and evolution. But, like Robert Atkins and Dean Ornish, Dr. Gundry seems earnest in his research and motives. I don’t think that he is selling anything other than his opinion.
I found web sites and white papers that summarize his research and conclusions without a scammy video. If true, this would be an eye-opener—completely unexpected! While his points fascinate, I don’t have the tools to determine if this may be legit. This certainly merits vetting.
For example, Gundry claims that farmers have selectively reinforced a genetic mutation in cows, which appeared only two thousand years ago—and that this has resulted in a lectin-like protein in milk called Casein A1. (Normal cows make Casein A2, a safe protein). Apparently, the only herds of “normal” cows are on farms in southern Europe. Could this result in food poisoning for the rest of us? Dr. Gundry is pretty convincing that the answer could be “Yes”.
This article is a stub without a conclusion. Rather than passing judgement, I encourage further inquiry. Reader feedback is invited. What do you think about Dr. Gundry’s analysis and claims. Might there be adverse problems associated with many “healthy” vegetables and out of season fruits? Tell me, doctor: Must I give up sun-dried tomato and eggplant?!
This is Philip Raymond’s first post on food and nutrition. More often, he covers Bitcoin, online privacy and quantum physics.
Raymond chairs CRYPSA, produces The Bitcoin Event, edits Wild Duck and moderates LinkedIN Bitcoin P2P, the largest Bitcoin discussion group. He delivered the keynote address at Cryptocurrency Expo in Dubai last month and sits on the New Money Systems board at Lifeboat Foundation.