Dr. Abba Zubair, MD: “Our hope is to study these space-grown cells to improve treatment for age-related conditions such as stroke, dementia, neurodegenerative diseases and cancer.”
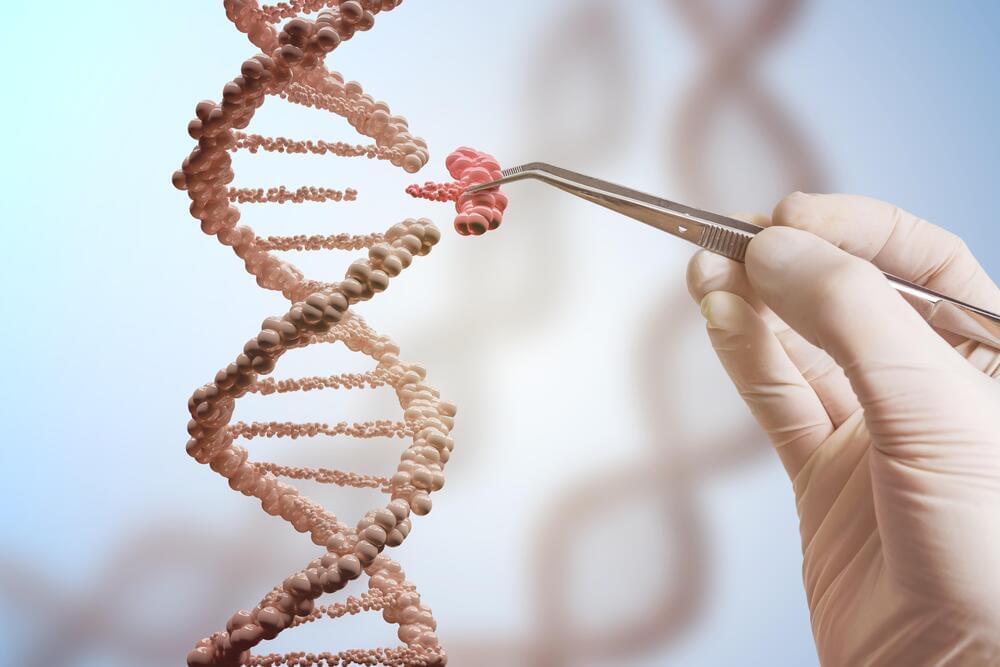
What can microgravity teach us about stem cell growth? This is what a recent study published in NPJ Microgravity hopes to address as a pair of researchers from the Mayo Clinic investigated past research regarding the growth properties of stem cells, specifically regeneration, differentiation, and cell proliferation in microgravity and whether the stem cells can maintain these properties after returning to Earth. This study holds the potential to help researchers better understand how stem cell growth in microgravity can be transitioned into medical applications, including tissue growth for disease modeling.
“The goal of almost all space flight in which stem cells are studied is to enhance growth of large amounts of safe and high-quality clinical-grade stem cells with minimal cell differentiation,” said Dr. Abba Zubair, MD, who is a faculty at the Mayo Clinic and the sole co-author on the study. “Our hope is to study these space-grown cells to improve treatment for age-related conditions such as stroke, dementia, neurodegenerative diseases and cancer.”
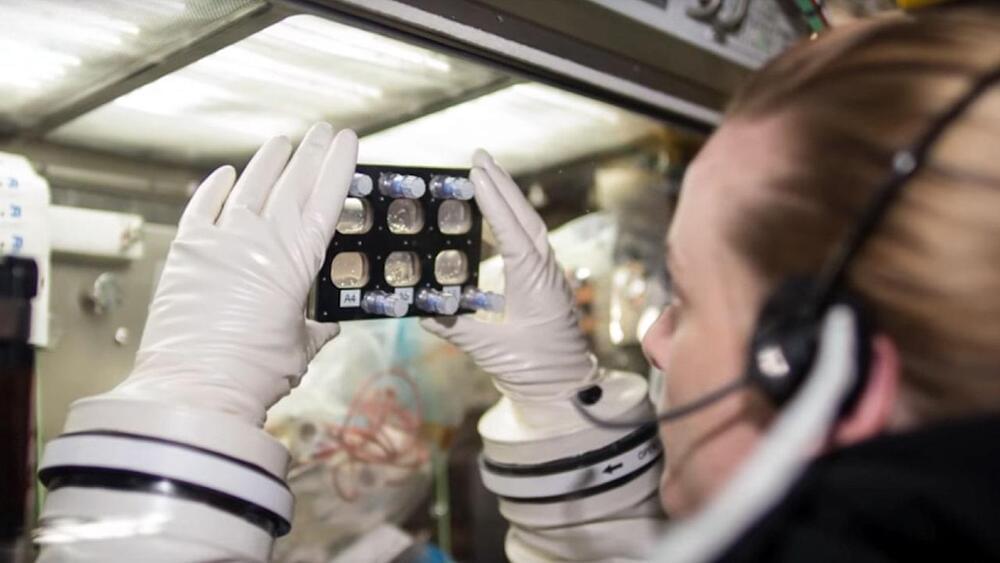
For the study, the researchers examined past research that launched stem cell cultures to the International Space Station (ISS) to have astronauts onboard evaluate the stem cells’ growth patterns and behavior under microgravity conditions. Dr. Zunair has launched stem cells to the ISS on three occasions and the various types of stem cells examined on the ISS in previous research include mesenchymal stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells, cardiovascular progenitor stem cells, and neural stem cells.