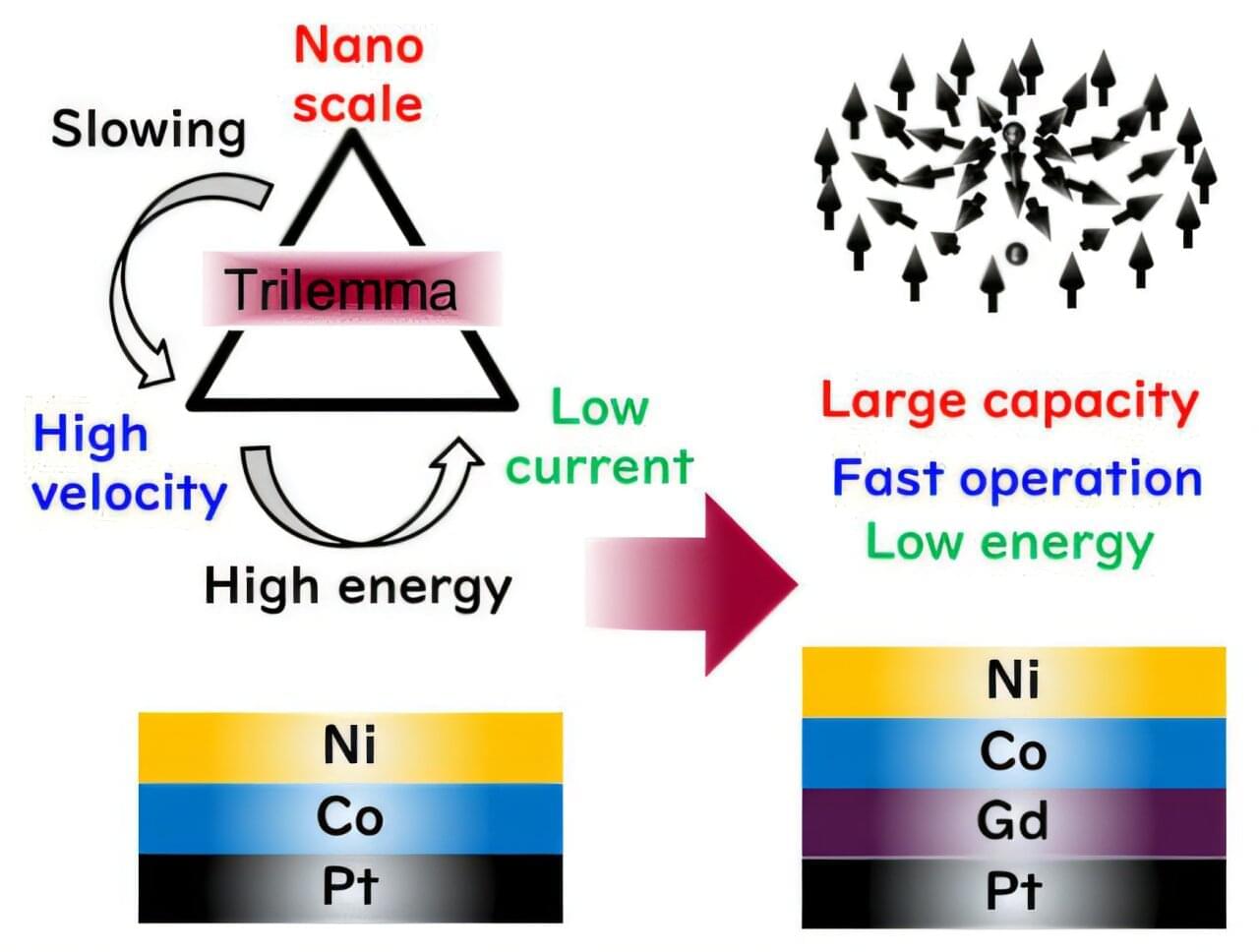
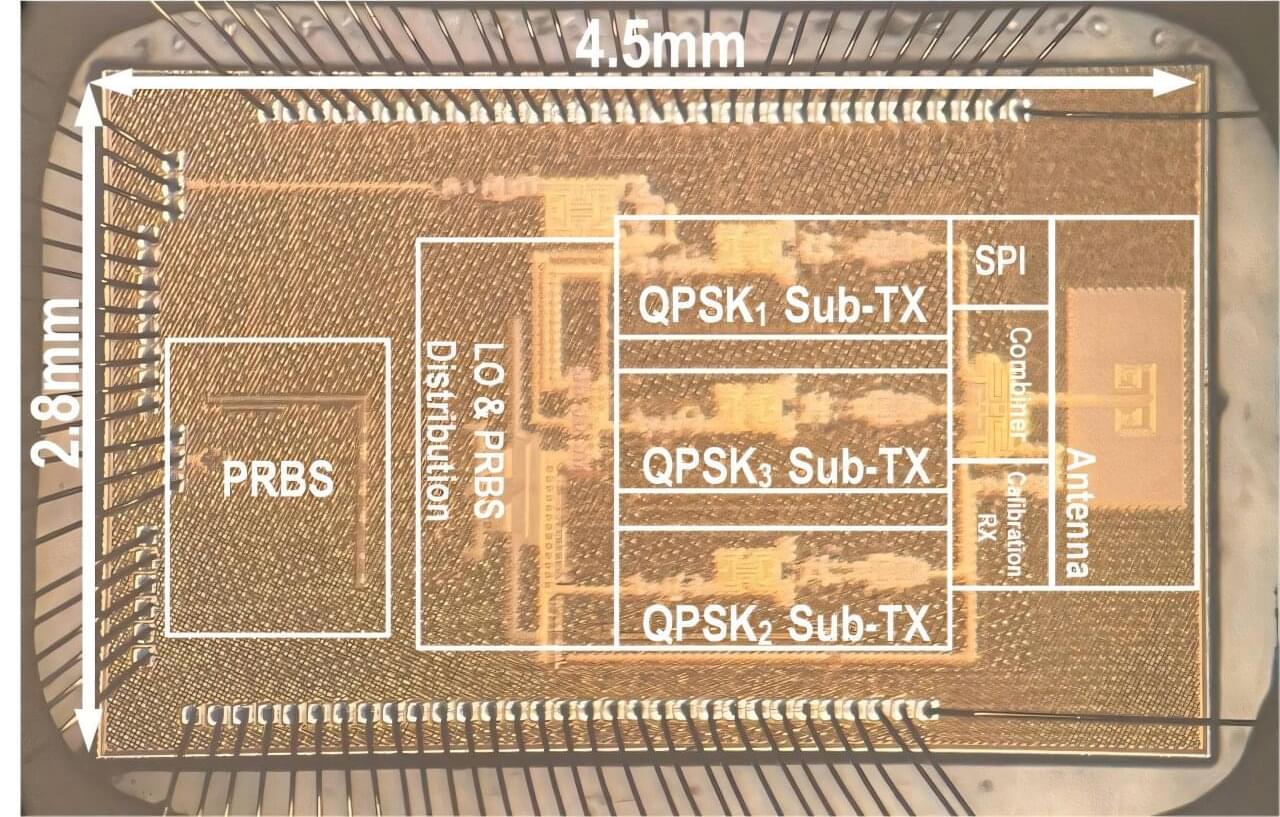
The future won’t be built on one breakthrough. It will be shaped by how well we mesh AI, quantum, 5G, IoT, and human intelligence into secure, resilient systems. Technology advantage now comes from orchestration, not adoption.
My latest Forbes article explores why this convergence will define the next decade.
#AI #QuantumComputing #EmergingTechnology #Cybersecurity #Leadership #FutureOfTech.
Link to article.
The next decade of innovation will not be defined by a single breakthrough technology. Instead, it will be shaped by the convergence of multiple emerging technologies.