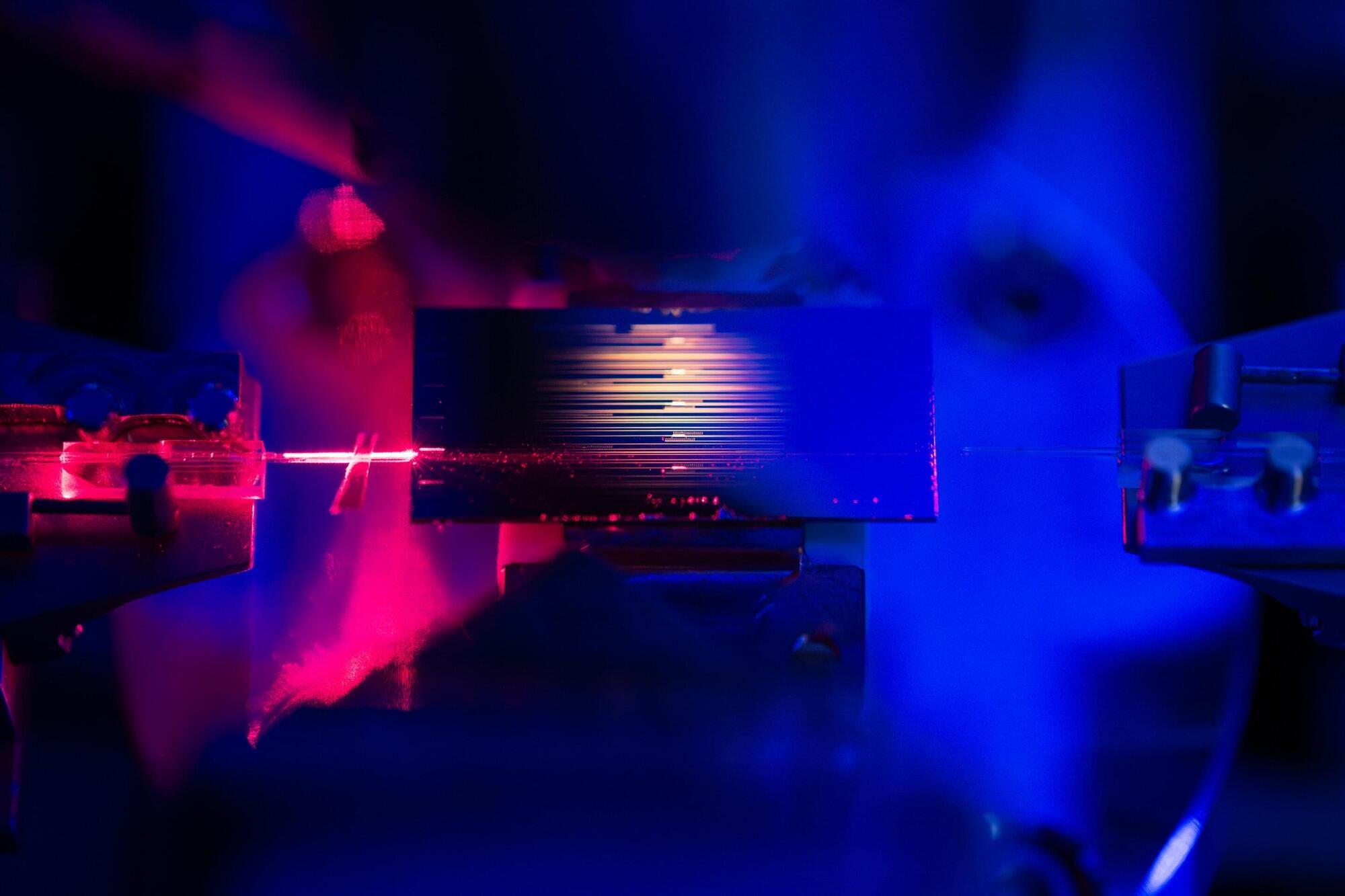
Light does a lot of work in the modern world, enabling all types of information technology, from TVs to satellites to fiber-optic cables that carry the internet across oceans. Stanford physicists recently found a way to make that light work even harder with an optical amplifier that requires low amounts of energy without any loss of bandwidth, all on a device the size of a fingertip.
Similar to sound amplifiers, optical amplifiers take a light signal and intensify it. Current small-sized optical amplifiers need a lot of power to function. The new optical amplifier, detailed in the journal Nature, solves this problem by using a method that essentially recycles the energy used to power it.
“We’ve demonstrated, for the first time, a truly versatile, low-power optical amplifier, one that can operate across the optical spectrum and is efficient enough that it can be integrated on a chip,” said Amir Safavi-Naeini, the study’s senior author and associate professor of physics in Stanford’s School of Humanities and Sciences. “That means we can now build much more complex optical systems than were possible before.”