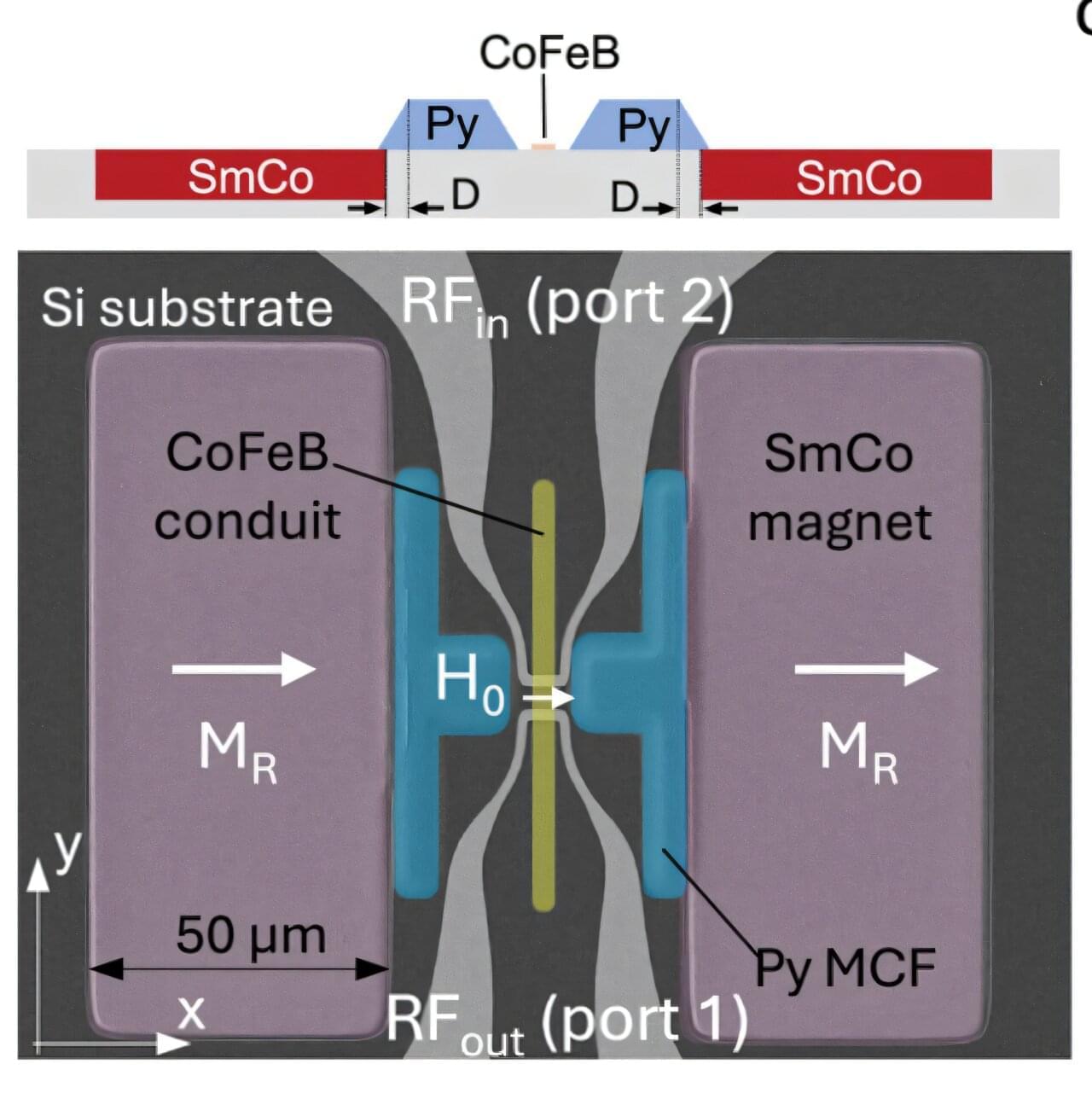
The Politecnico di Milano has created the first integrated and fully tunable device based on spin waves, opening up new possibilities for the telecommunications of the future, far beyond current 5G and 6G standards. The study, published in the journal Advanced Materials, was conducted by a research group led by Riccardo Bertacco of the Department of Physics of the Politecnico di Milano, in collaboration with Philipp Pirro of Rheinland-Pfälzische Technische Universität and Silvia Tacchi of Istituto Officina dei Materiali—CNR-IOM.
Magnonics is an emerging technology that uses spin waves —collective excitations of electronic spins in magnetic materials—as an alternative to electrical signals. The spread of this technology has been restricted until now by the need for an external magnetic field, which has prevented it being incorporated into chips.
The new device developed at the Politecnico overcomes this hurdle: it is miniaturized (100 × 150 square micrometers, so much smaller than current radiofrequency signal processing devices based on acoustic waves); it is fully integrated on silicon—and therefore compatible with existing electronic platforms, and it functions without external magnets, thanks to an innovative combination of permanent SmCo micromagnets and magnetic flux concentrators.