An innovative project to re-purpose existing drugs for their potential as antibiotics has uncovered a highly promising candidate with a potent and unique way of killing drug resistant bacteria.


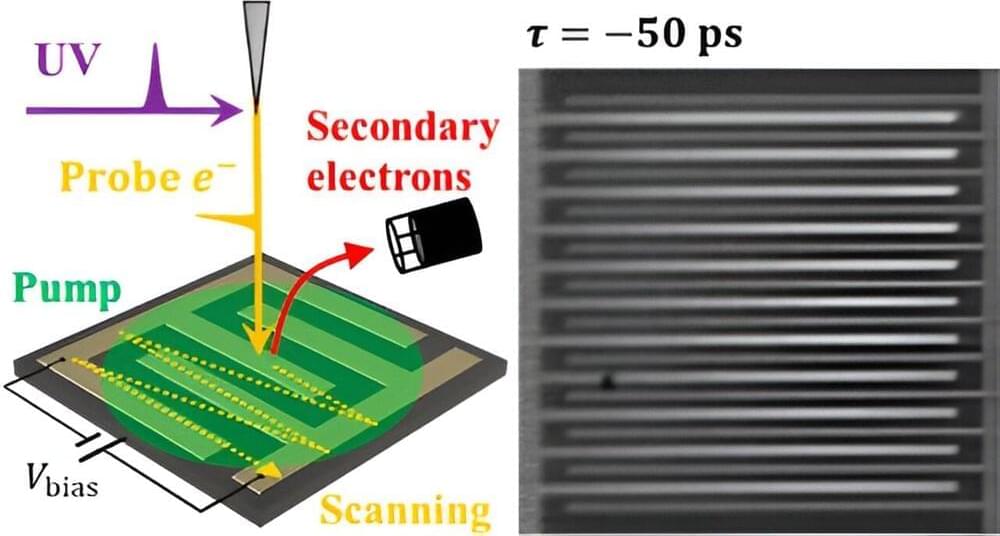
Researchers at University of Tsukuba have developed an ultrafast time-resolved scanning electron microscopy instrument by integrating a scanning electron microscope with a femtosecond laser. This innovative system facilitates the observation of the instantaneous states of various materials. Their paper is published in the journal ACS Photonics.

UCLA researchers have created a new type of imager that can capture features much smaller than the limitations of traditional optical systems. This innovation has the potential to revolutionize fields like bioimaging, lithography and material science. The research is published in the journal eLight.
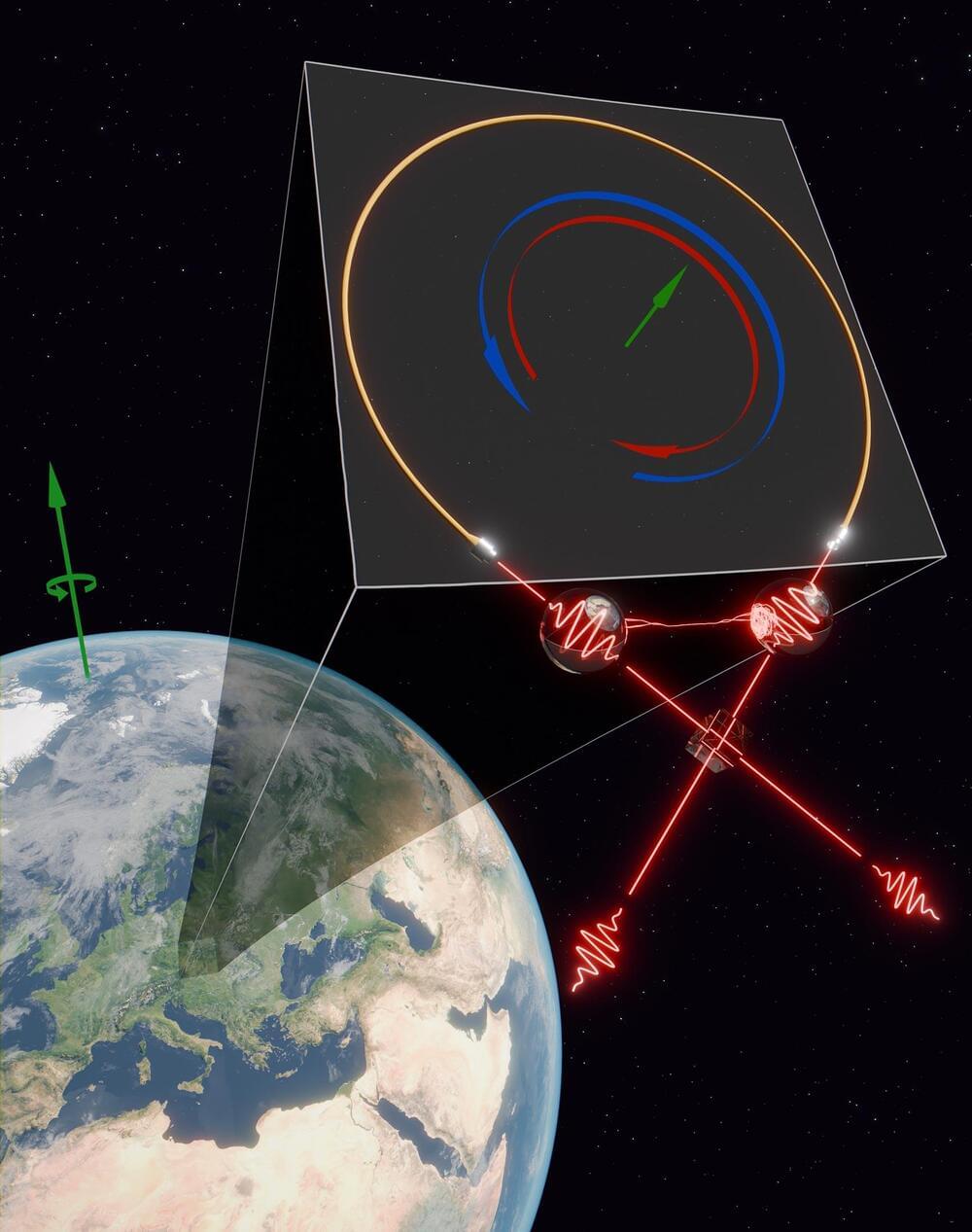
A quantum physics experiment at the University of Vienna achieved groundbreaking precision in measuring Earth’s rotation using entangled photons.
The study utilizes an enhanced optical Sagnac interferometer that leverages quantum entanglement to detect rotational effects with unprecedented precision, offering potential breakthroughs in both quantum mechanics and general relativity.
Pioneering Quantum Experiment

The SETI Institute has launched a new grants program to support the advancement of technosignature science, utilizing the Allen Telescope Array (ATA), a crucial observatory in the search for extraterrestrial technology. This program, the first of its kind, will fund research ranging from observational techniques to theoretical models in technosignature science, with grants available for non-tenured faculty and post-prelim graduate students. Credit: SETI Institute.
The SETI Institute’s new grants program supports advanced research in detecting extraterrestrial technosignatures with grants up to $100,000, leveraging the capabilities of the Allen Telescope Array.
The SETI Institute has introduced a groundbreaking grants program focused on advancing technosignature science. This unique initiative is designed to fund innovative research that tackles essential observational, theoretical, and technical challenges in the quest for technosignatures, which may reveal signs of past or present extraterrestrial technology.
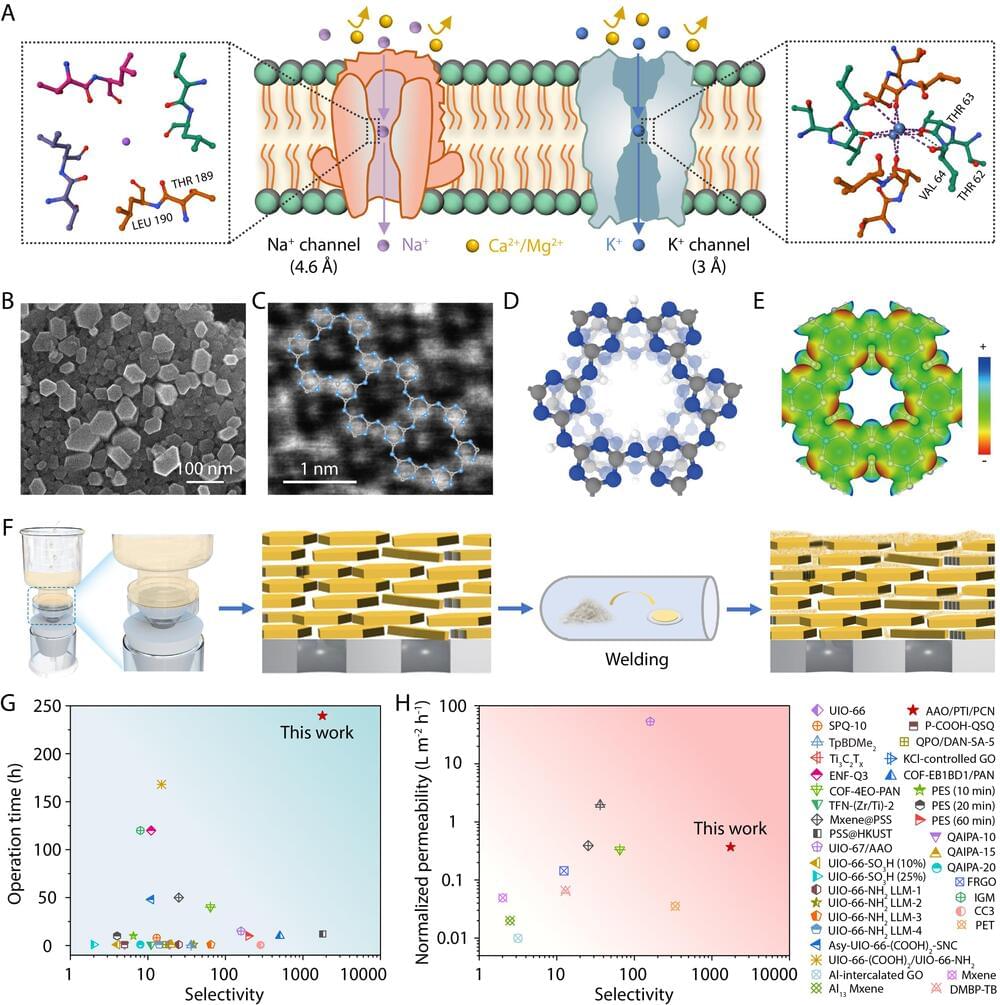
In a breakthrough for lithium recovery technologies, researchers from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with collaborators, have developed a crystalline carbon nitride membrane that could transform the lithium extraction industry.
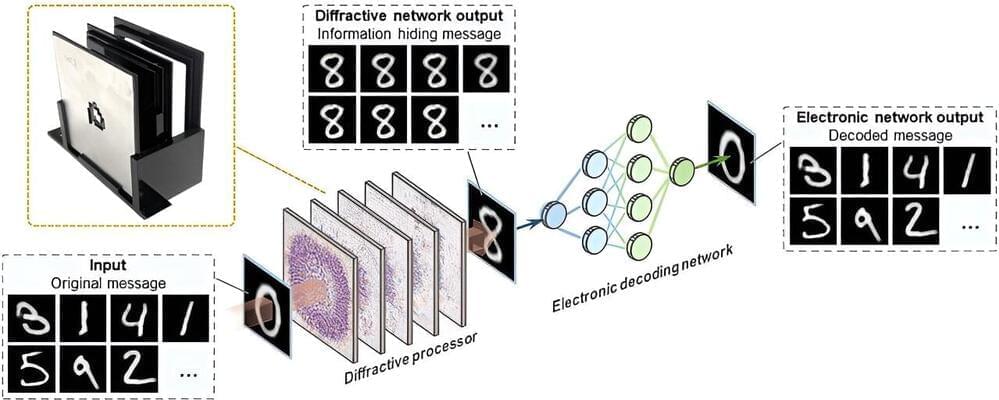
Researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) have developed an innovative information-hiding camera to optically transform and conceal input images into ordinary-looking patterns, providing a powerful solution for visual information security. The work is published in the journal Science Advances.
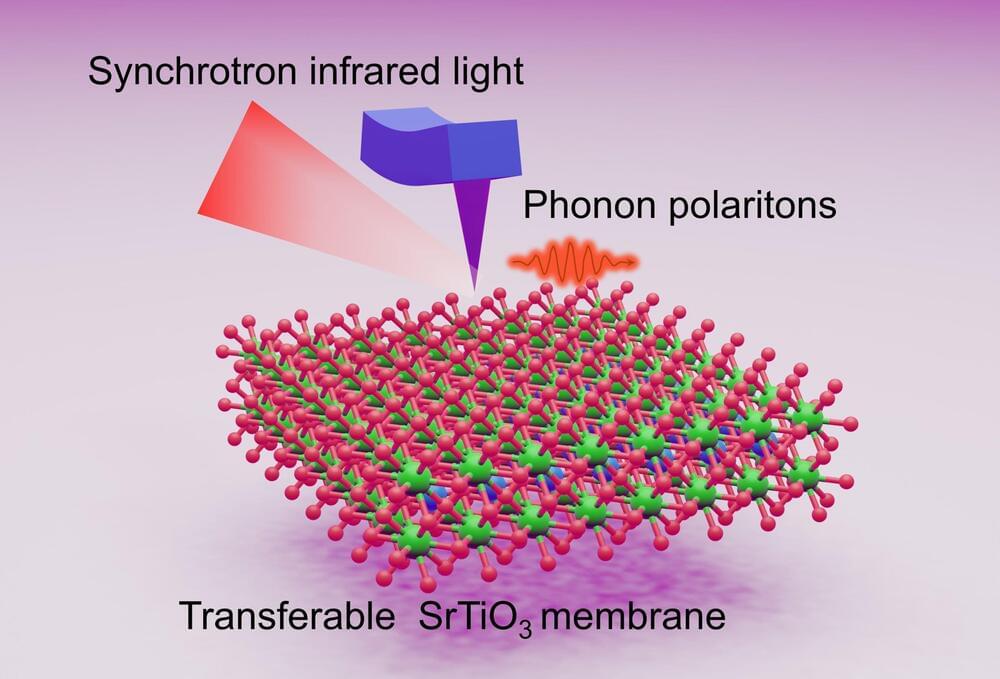
A new study reveals that oxide membranes can confine infrared light to a greater extent than traditional methods, promising advancements in imaging resolution and applications in photonics and thermal management.
Researchers have successfully shown that a particular type of oxide membranes can effectively confine, or “squeeze,” infrared light. This breakthrough could enhance future infrared imaging technologies. These thin-film membranes outperform traditional bulk crystals in confining infrared light.
“The thin-film membranes maintain the desired infrared frequency, but compress the wavelengths, allowing imaging devices to capture images with greater resolution,” says Yin Liu, co-corresponding author of a paper on the work and an assistant professor of materials science and engineering at North Carolina State University.

From Stanford & Chan Zuckerberg Biohub TextGrad Automatic “Differentiation” via Text.
From stanford & chan zuckerberg biohub.
TextGrad.
Automatic “Differentiation” via Text.
Mert Yuksekgonul, Federico Bianchi, Joseph Boen, Sheng Liu, Zhi Huang, Carlos Guestrin, James Zou June 2024 https://huggingface.co/papers/2406.
AI is undergoing a paradigm shift, with breakthroughs achieved…
