Scientists have discovered living microbes producing methane in the fractured rocks deep inside Sweden’s Siljan impact crater, offering insights into Earth’s earliest life and the search for life beyond our planet.
This breakthrough not only sheds light on one of Earth’s most ancient metabolic processes —methanogenesis—but also strengthens the link between meteorite impact structures and microbial survival in extreme environments. The findings are published in the journal mBio.
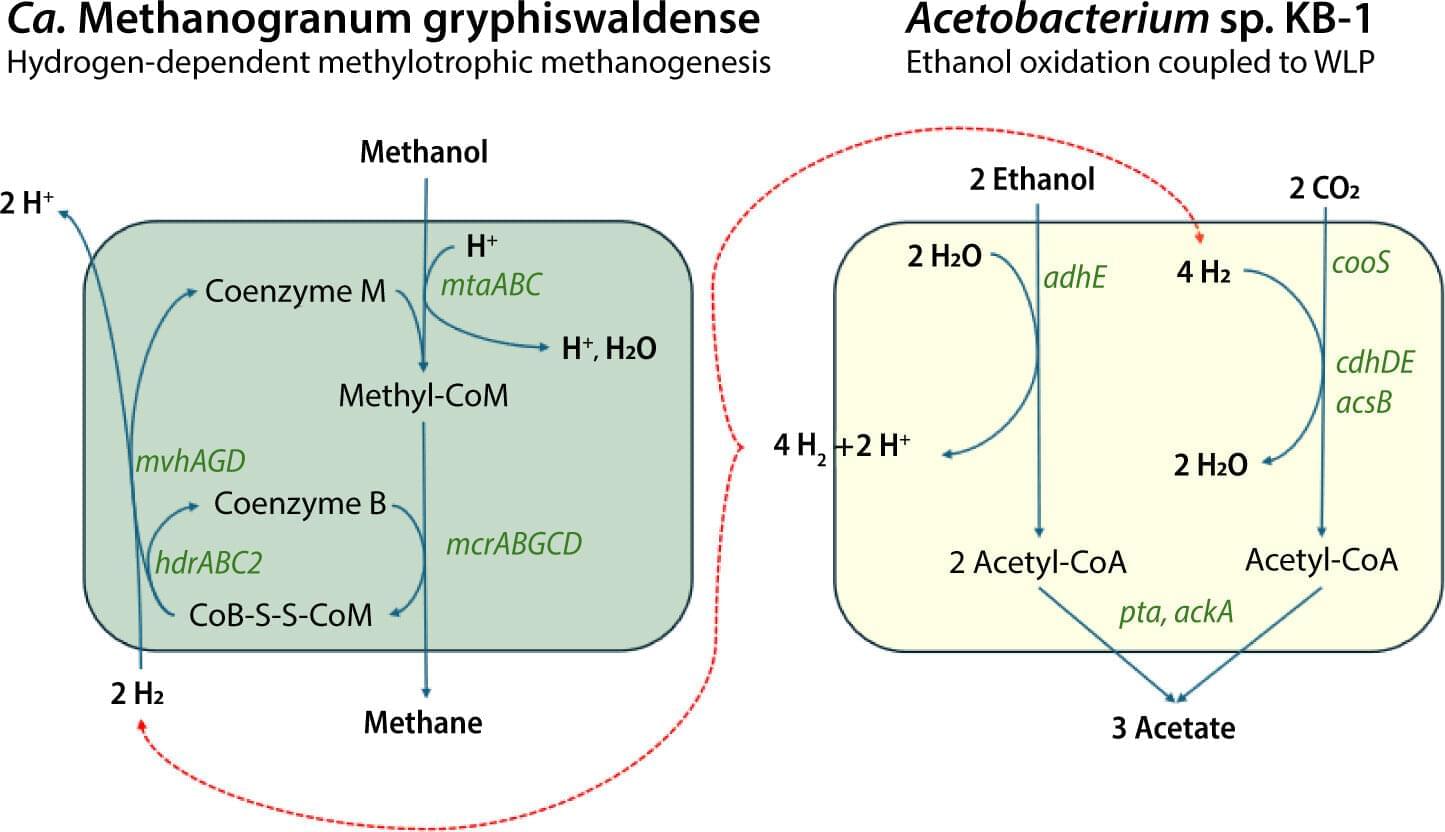
Methanogenesis is considered one of the earliest metabolisms on Earth, and its presence in deep subsurface environments has long intrigued scientists. Now, for the first time, active microbial methane production has been confirmed in a terrestrial impact crater. Using cultures enriched from fluids 400 meters below the surface, the team demonstrated methane generation from several carbon sources, including indigenous oil.