A debate over the most efficient way to watch a cult classic TV series’ episodes, in every possible order, lies at the heart of this mathematical breakthrough.




“The problems the Bay Area is facing are the problems of success,” says Grant. The northern California metropolis is among the top 50 science cities in the Nature Index, measured by its contribution to the authorship of 82 high-quality research journals. When assessed solely on the output of its corporate institutions, it ranks number one. The question is whether the Bay Area can, in the face of mounting social problems, retain these companies and the brilliant researchers whose work they depend on.
Scientific innovation has long powered the San Francisco Bay Area’s economy, but community and political challenges could undermine progress.

I did a live 15 minute interview on Armenia’s Public TV and the country’s most popular morning show, sharing information about transhumanism and the FAST Global Innovation Forum I spoke at. Give it a watch here:
This video was made possible by Skillshare. Be one of the first 500 people to sign up with this link and get your first 2 months of premium subscription for FREE! http://skl.sh/Singularity
In the last video in this series we discussed the ancient origins of artificial intelligence progressing forward to the beginnings of the development of modern computing based artificial intelligence, encompassing the philosophies, theories and inventions of many talented individuals and groups.
The focus of this video will continue right were the last one left off, so sit back, relax and join me on an exploration on the official birth of modern artificial intelligence leading to present day!
Thank you to the patron(s) who supported this video ➤
Wyldn pearson collin R terrell kiyoshi matsutsuyu
Subscribe ➤ http://subscribe.singularityprosperity.com/youtube


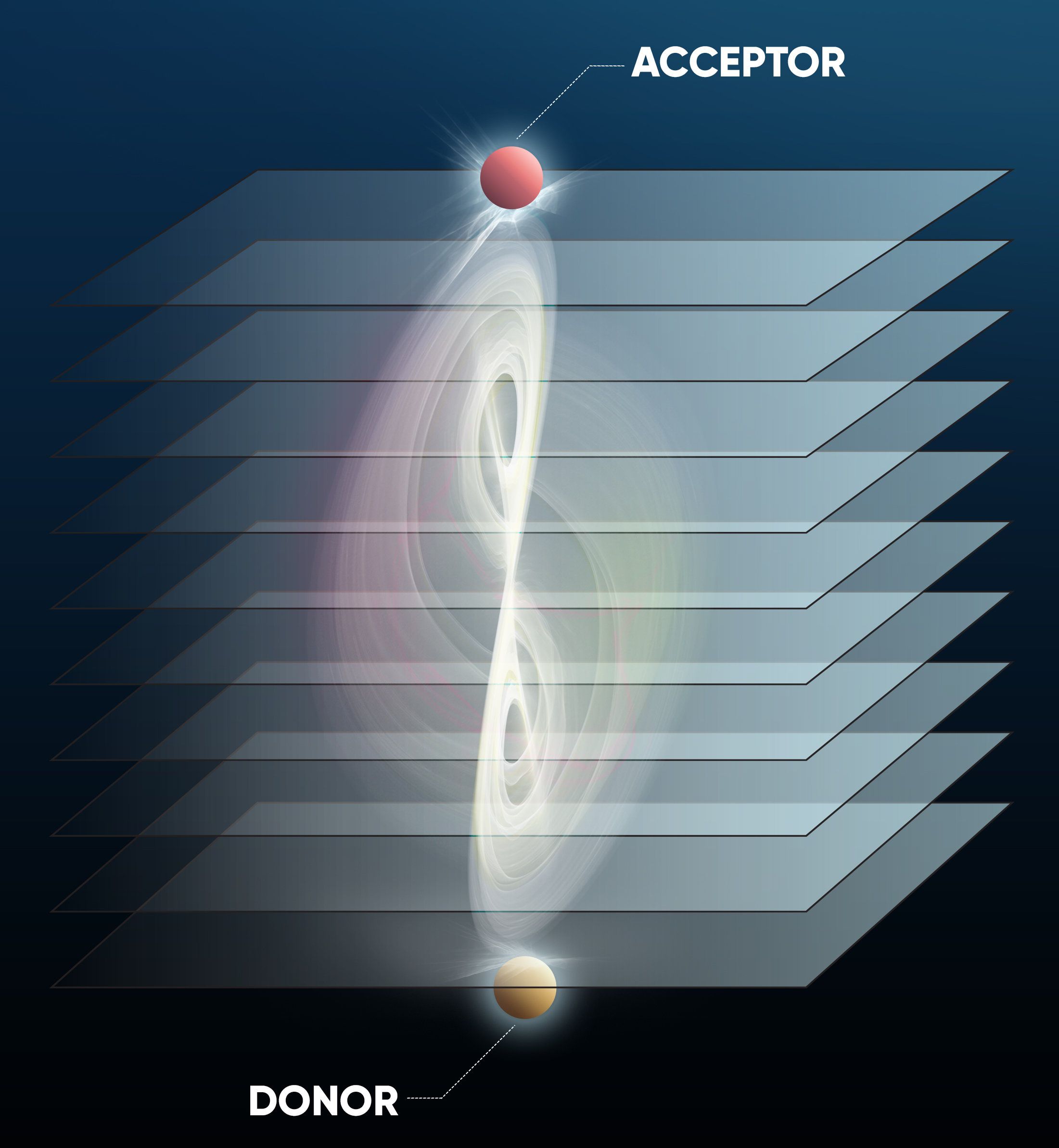
Using engineered nanocomposite structures called metamaterials, a City College of New York-led research team reports the ability to measure a significant increase in the energy transfer between molecules. Reported in the journal ACS Photonics, this breakthrough breaks the F\xF6rster resonance energy transfer (FRET) distance limit of ~10–20 nanometers, and leads to the possibility of measuring larger molecular assemblies.
And since FRET is a staple technique in many biological and biophysical fields, this new development could benefit pharmaceuticals, for instance.
“Energy transfer between molecules plays a central role in phenomena such as photosynthesis and is also used as a spectroscopic ruler for identifying structural changes of molecules,” said Vinod Menon, professor of physics in City College’s Division of Science. “However, the process of energy transfer is usually limited in the distance over which it occurs, typically reaching 10 to 20 nm.”

Salty water just below the surface of Mars could hold enough oxygen to support the kind of microbial life that emerged and flourished on Earth billions of years ago, researchers reported Monday. Current latest trending Philippine headlines on science, technology breakthroughs, hardware devices, geeks, gaming, web/desktop applications, mobile apps, social media buzz and gadget reviews.