Chatbots can wear a lot of proverbial hats: dictionary, therapist, poet, all-knowing friend. The artificial intelligence models that power these systems appear exceptionally skilled and efficient at providing answers, clarifying concepts, and distilling information. But to establish trustworthiness of content generated by such models, how can we really know if a particular statement is factual, a hallucination, or just a plain misunderstanding?
In many cases, AI systems gather external information to use as context when answering a particular query. For example, to answer a question about a medical condition, the system might reference recent research papers on the topic. Even with this relevant context, models can make mistakes with what feels like high doses of confidence. When a model errs, how can we track that specific piece of information from the context it relied on — or lack thereof?
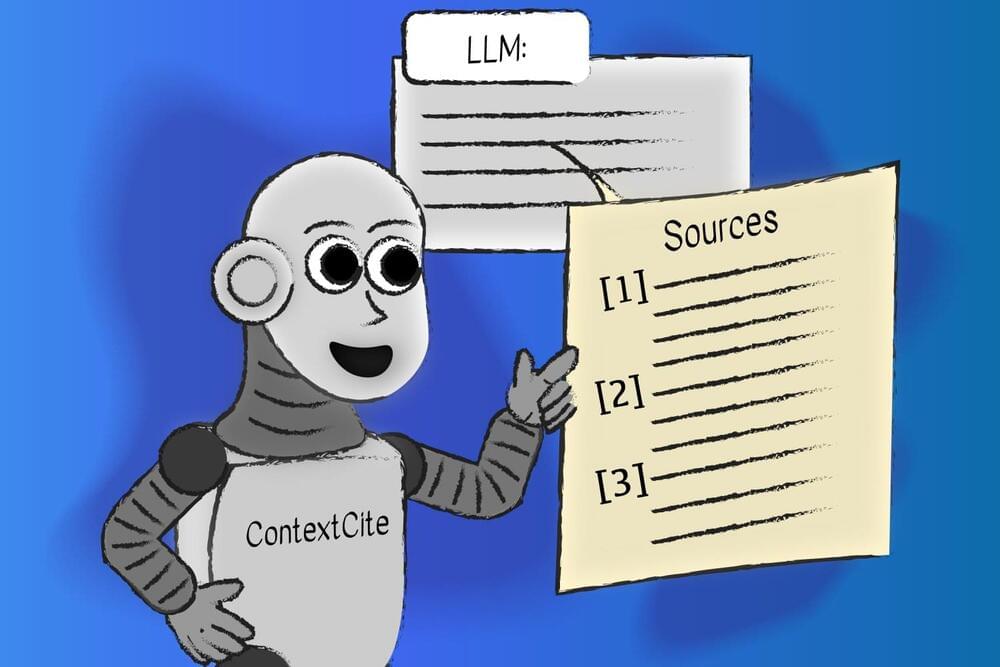
To help tackle this obstacle, MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) researchers created ContextCite, a tool that can identify the parts of external context used to generate any particular statement, improving trust by helping users easily verify the statement.
The ContextCite tool from MIT CSAIL can find the parts of external context that a language model used to generate a statement. Users can easily verify the model’s response, making the tool useful in fields like health care, law, and education.