With rates rising around the world, public-health leaders must prioritize prevention, treatment, funding and data.
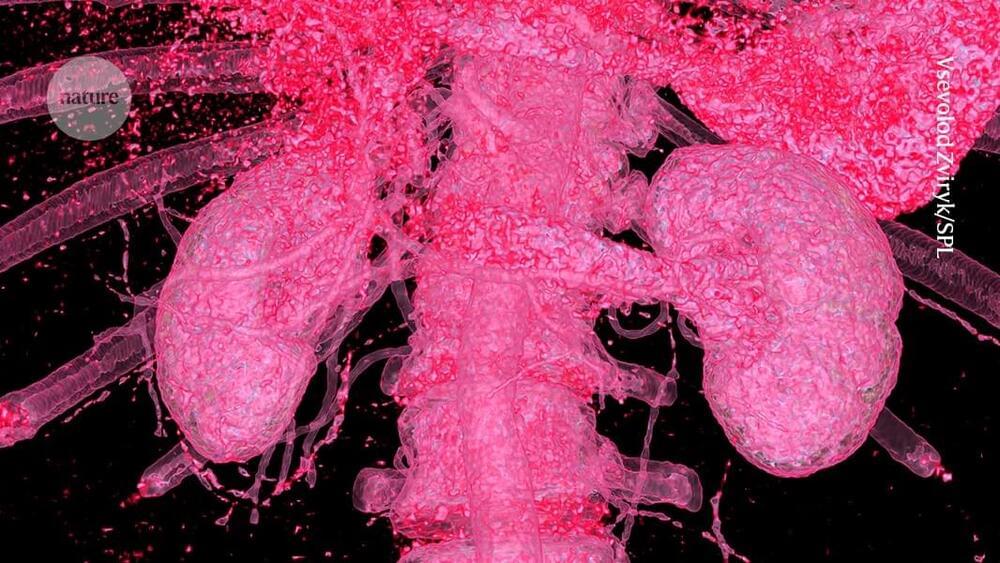

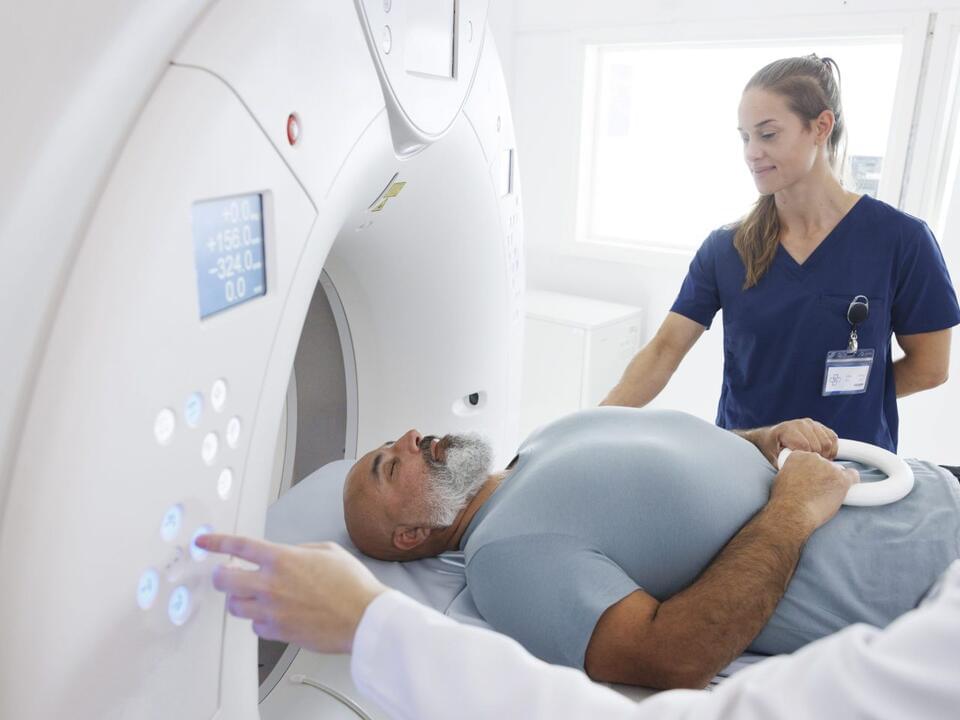
Whereas traditional colonoscopy involves snaking a camera called a colonoscope through your colon and rectum, a CT colonography, or virtual colonoscopy, consists of X-rays and a computer creating 3D images of these organs.
If you’re between the ages of 45 and 85, you should have a colorectal cancer screening routine in place, per the American Cancer Society (ACS). But a colonoscopy —in which your doctor uses a special camera to look inside your colon and rectum in search of abnormal growths called polyps —isn’t the only option to take charge of your gastrointestinal health.
You can choose from noninvasive screening methods: computed tomography (CT) colonography and/or a stool-based test. Billionaire entrepreneur and Shark Tank investor Mark Cuban tells Fortune he enjoys the relatively low cost and simplicity of the former, also called virtual colonoscopy. In short, it’s an X-ray exam that doesn’t require sedation or anesthesia.

MONDAY, March 25, 2024 (HealthDay News) — Intrathecal gene transfer with scAAV9/JeT-GAN may result in some benefit for children with giant axonal neuropathy, according to a study published in the March 21 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine.
Diana X. Bharucha-Goebel, M.D., from the National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, Maryland, and colleagues conducted an intrathecal dose-escalation study of scAAV9/JeT-GAN in children with giant axonal neuropathy. Fourteen participants received one of four intrathecal doses of scAAV9/JeT-GAN: 3.5 × 1013 total vector genomes (vg); 1.2 × 1014 vg; 1.8 × 1014 vg; and 3.5 × 1014 vg (in two, four, five, and three participants, respectively).
The researchers found that during a median observation period of 68.7 months, one of the 48 serious adverse events was possibly related to treatment and 129 of 682 adverse events were possibly related to treatment. In the total cohort, the mean pretreatment slope was −7.17 percentage points per year. One year posttreatment, posterior mean changes in slope were −0.54, 3.23, 5.32, and 3.43 percentage points with the 3.5 × 1013 vg, 1.2 × 1014 vg, 1.8 × 1014 vg, and 3.5 × 1014 vg doses, respectively. For slowing the slope, the corresponding posterior probabilities were 44, 92, 99 (above the efficacy threshold), and 90 percent, respectively. Sensory-nerve action potential amplitudes increased, stopped declining, or became recordable after being absent in six participants between six and 24 months after gene transfer, but remained absent in eight participants.


Cell therapy company LyGenesis today revealed that the first patient has received treatment in the Phase 2a clinical trial of its regenerative cell therapy targeting end-stage liver disease (ESLD). The therapy, known as LYG-LIV-001, treats ESLD via an allogeneic regenerative cell therapy transplanted into patients’ lymph nodes.
ESLD affects nearly 2% of the US population, with more than 50,000 Americans succumbing to chronic liver disease annually. Often stemming from cirrhosis, ESLD poses significant health risks, and many patients are ineligible for traditional liver transplants.
The Phase 2a clinical trial, an open-label, dose-escalation study, is currently recruiting 12 patients diagnosed with ESLD. Each participant will undergo close monitoring for one year to assess the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of the transplanted hepatocytes in addressing the symptoms of ESLD.


“I think of [the agreement] as marking the next chapter in our journey on AI safety, working hand in glove with the United States government,” Donelan told TIME in an interview at the British Embassy in Washington, D.C. on Monday. “I see the role of the United States and the U.K. as being the real driving force in what will become a network of institutes eventually.”
The U.K. and U.S. AI Safety Institutes were established just one day apart, around the inaugural AI Safety Summit hosted by the U.K. government at Bletchley Park in November 2023. While the two organizations’ cooperation was announced at the time of their creation, Donelan says that the new agreement “formalizes” and “puts meat on the bones” of that cooperation. She also said it “offers the opportunity for them—the United States government—to lean on us a little bit in the stage where they’re establishing and formalizing their institute, because ours is up and running and fully functioning.”
The two AI safety testing bodies will develop a common approach to AI safety testing that involves using the same methods and underlying infrastructure, according to a news release. The bodies will look to exchange employees and share information with each other “in accordance with national laws and regulations, and contracts.” The release also stated that the institutes intend to perform a joint testing exercise on an AI model available to the public.

Since ChatGPT debuted in the fall of 2022, much of the interest in generative AI has centered around large language models. Large language models, or LLMs, are the giant compute-intensive computer models that are powering the chatbots and image generators that seemingly everyone is using and talking about nowadays.
While there’s no doubt that LLMs produce impressive and human-like responses to most prompts, the reality is most general-purpose LLMs suffer when it comes to deep domain knowledge around things like, say, health, nutrition, or culinary. Not that this has stopped folks from using them, with occasionally bad or even laughable results and all when we ask for a personalized nutrition plan or to make a recipe.
LLMs’ shortcomings in creating credible and trusted results around those specific domains have led to growing interest in what the AI community is calling small language models (SLMs). What are SLMs? Essentially, they are smaller and simpler language models that require less computational power and fewer lines of code, and often, they are specialized in their focus.
In a Leicester study that looked at whether artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to predict whether a person was at risk of a lethal heart rhythm, an AI tool correctly identified the condition 80 per cent of the time.
The findings of the study, led by Dr Joseph Barker working with Professor Andre Ng, Professor of Cardiac Electrophysiology and Head of Department of Cardiovascular Sciences at the University of Leicester and Consultant Cardiologist at the University Hospitals of Leicester NHS Trust, have been published in the European Heart Journal-Digital Health.
Ventricular arrhythmia (VA) is a heart rhythm disturbance originating from the bottom chambers (ventricles) where the heart beats so fast that blood pressure drops which can rapidly lead to loss of consciousness and sudden death if not treated immediately.
