What non-invasive methods can be developed to kill viruses on site? This is what a recent study published in ACS Nano hopes to address as a team of international researchers have developed a silicon surface containing nanospikes capable of preventing viruses from replicating or killing them entirely. This study holds the potential to help develop a passive way of mitigating the spread of viruses within a myriad of environments, including scientific laboratories and healthcare facilities.
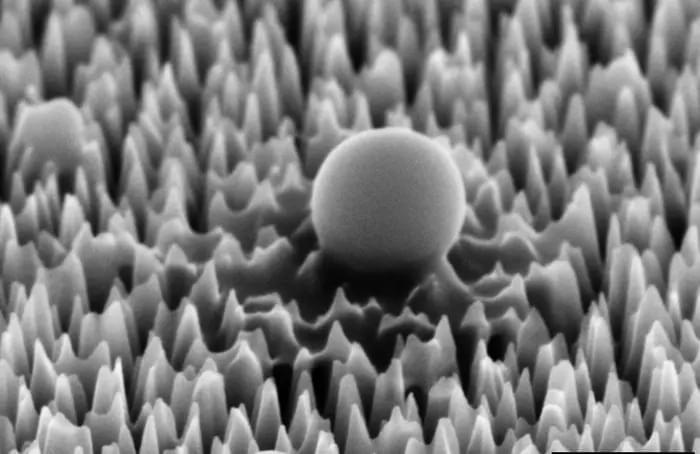
“Our virus-killing surface looks like a flat black mirror to the naked eye but actually has tiny spikes designed specifically to kill viruses,” said Dr. Natalie Borg, who is a senior lecturer in the STEM | Health and Biomedical Sciences at RIMT University and a co-author on the study. “This material can be incorporated into commonly touched devices and surfaces to prevent viral spread and reduce the use of disinfectants.”
For the study, researchers at the Melbourne Centre for Nanofabrication took inspiration from insects, some of which possess their own version of nanospikes on their wings that can damage fungi and bacteria. To produce the nanospikes, the team blasted smooth silicon wafers with ions, resulting in nanospikes measuring 290 nanometers in height and 2 nanometers thick, the latter of which is 30,000 times thinner than a human hair. They then tested their new material on the hPIV-3 virus, which is responsible for causing pneumonia and bronchitis, finding their nanospikes exhibited a 96 percent success rate in either preventing the virus from replicating or shredding them to pieces completely.



 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)