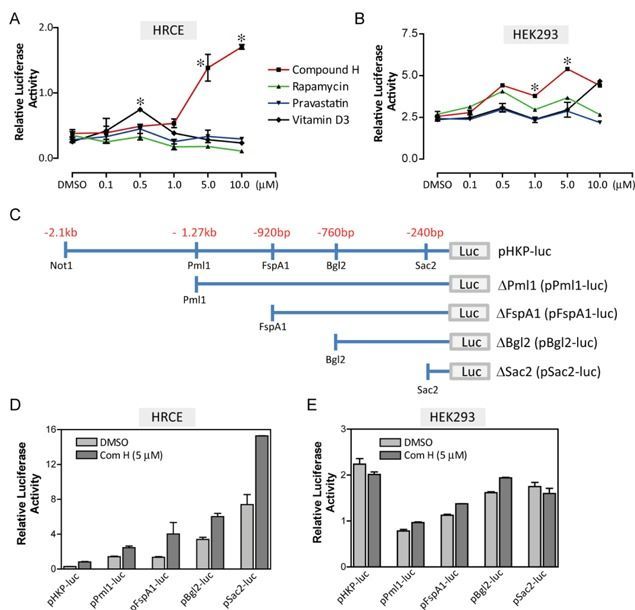
Klotho (KL) is described as an anti-aging gene because mutation of Kl gene leads to multiple pre-mature aging phenotypes and shortens lifespan in mice. Growing evidence suggests that an increase in KL expression may be beneficial for age-related diseases such as arteriosclerosis and diabetes. It remains largely unknown, however, how Kl expression could be induced. Here we discovered novel molecular mechanism for induction of Kl expression with a small molecule ‘Compound H’, N-(2-chlorophenyl)-1 H-indole-3-caboxamide. Compound H was originally identified through a high-throughput screening of small molecules for identifying Kl inducers. However, how Compound H induces Kl expression has never been investigated. We found that Compound H increased Kl expression via demethylation in CpG islands of the Kl gene. The demethylation was accomplished by activating demethylases rather than inhibiting methylases. Due to demethylation, Compound H enhanced binding of transcription factors, Pax4 and Kid3, to the promoter of the Kl gene. Pax4 and Kid3 regulated Kl promoter activity positively and negatively, respectively. Thus, our results show that demethylation is an important molecular mechanism that mediates Compound H-induced Kl expression. Further investigation is warranted to determine whether Compound H demethylates the Kl gene in vivo and whether it can serve as a therapeutic agent for repressing or delaying the onset of age-related diseases.
Keywords: klotho, methylation, Pax4, Kid3, CpG island.
Pre-mature aging phenotypes were eminent in the klotho (Kl)-deficient mice, which have ~ 10 copies of a transgene integrated in the 5’ flanking region of the Kl gene disrupting its expression [1]. The klotho mice die around ~ 2 months of age after birth due to multiple aging-related organ failures [1]. Later, the role of KL in aging was confirmed by the reproduction of the same aging phenotypes in Kl knockout homozygous (Kl −/−) mice [2]. On the other hand, overexpression of KL extends lifespan by 20–30% [2, 3]. The protein products of Kl gene can be divided into two forms: membrane-integrated form of Kl and non-integrated form of Kl which includes secreted and soluble Kl (sKl). These two type of proteins are produced from the two transcripts that arise from a single kl gene due to alternative RNA splicing [4, 5].