Microsoft confirms a 3-phase strategy to deprecate NTLM, improve auditing, prioritize Kerberos, and disable NTLM by default in future Windows releases



Over the past few months, a large-scale cloud storage subscription scam campaign has been targeting users worldwide with repeated emails falsely warning recipients that their photos, files, and accounts are about to be blocked or deleted due to an alleged payment failure.
Based on numerous emails seen by BleepingComputer, the campaign has escalated over the past few months, with people receiving multiple versions of the scam each day, all appearing to be sent by the same scammers.
While the email text, the messages all attempt to create a sense of urgency by claiming a payment problem or storage issue must be resolved immediately, or people’s files will be deleted or blocked.
In response to user feedback on AI integration, Mozilla announced today that the next Firefox release will let users disable AI features entirely or manage them individually.
The new “Block AI enhancements” toggle will be available in Firefox 148 on February 24 and will help block current and future generative AI features in the desktop browser from a single location. Users will also have the option to enable specific AI tools while keeping others disabled.
“We’ve heard from many who want nothing to do with AI. We’ve also heard from others who want AI tools that are genuinely useful. Listening to our community, alongside our ongoing commitment to offer choice, led us to build AI controls,” said Firefox head Ajit Varma.
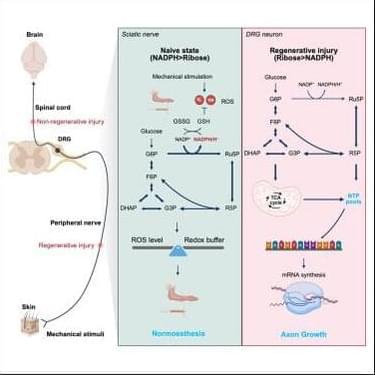
Pentose phosphate pathway in axonal regeneration.
Various signaling pathways play an important role in neuronal homeostasis and regeneration.
The researchers in this study determine that the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) plays a dual role in enabling homeostatic and regenerative adaptations to environmental stimuli and injuries.
They show that sciatic nerve axoplasms are enriched PPP and maintains redox balance via NADPH production but following sciatic nerve injury, the PPP is required for regeneration by fueling ribonucleotide synthesis through ribose-5-phosphate.
However, after spinal cord injury (SCI), PPP remain inactive and neuronal transketolase overexpression or oral ribose supplementation, promotes metabolic reprogramming, restores sensory and motor axonal growth. sciencenewshighlights ScienceMission https://sciencemission.com/pentose-phosphate-pathway-is-a-metabolic-checkpoint
The pentose phosphate pathway plays a dual role in enabling homeostatic and regenerative adaptations to environmental stimuli and injuries and can be leveraged to promote regeneration and recovery after spinal cord injury.


A hidden immune cascade linking the gut and bone marrow may explain how IBD turns inflammation into colon cancer.
Scientists at Weill Cornell Medicine have identified a complex immune process in the gut that may help explain why people with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) face a much higher risk of colorectal cancer. The preclinical study shows how a specific immune signal can trigger a wave of white blood cells from the bone marrow into the gut, creating conditions that support tumor growth. The findings also suggest new approaches for detecting disease activity, tracking risk, and developing future treatments.
The role of TL1A in gut inflammation.