Scientists say they will need to conduct studies to find out the severity of the new variant.
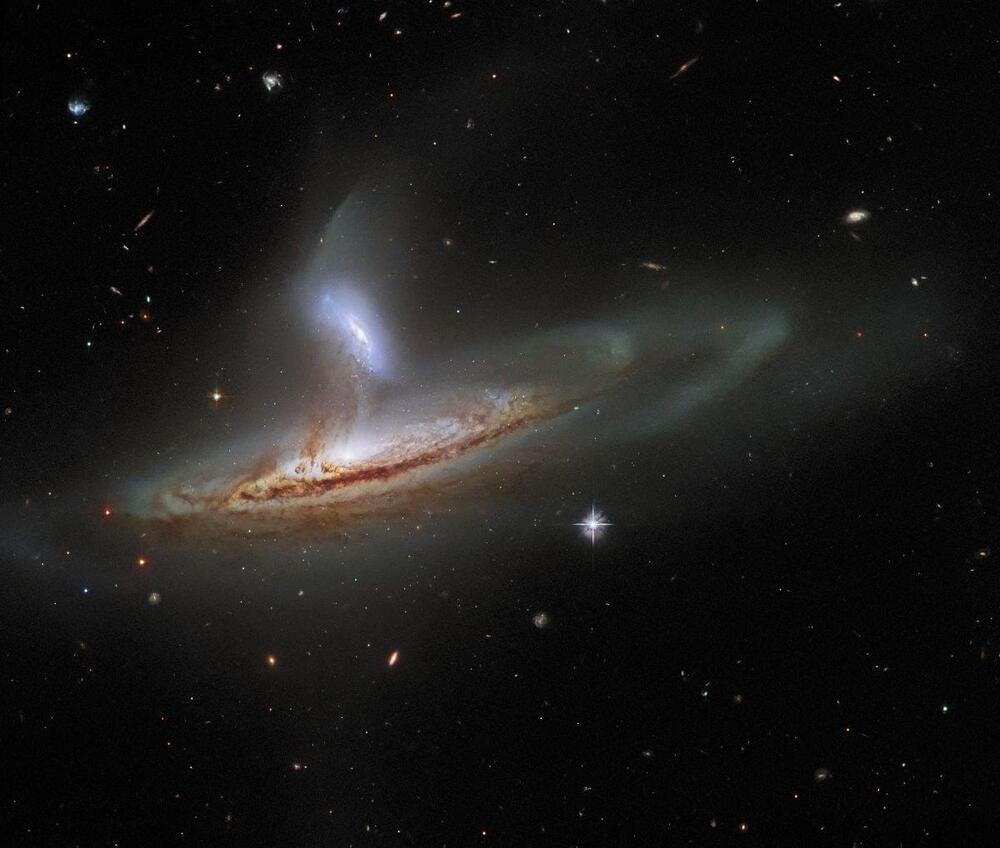


You can see the galaxies warping in three dimensions.
— The best Hubble Space Telescope images of all time! — Hubble eyes two stunning galaxies before future James Webb Space Telescope observations — Distant galaxies appear to overlap in new Hubble telescope image
It’s also fortunate that the instrument took this image in visible light. Both IC 1,559 and NGC 169 have active galactic nuclei (AGN), meaning their cores are “monumentally energetic,” per NASA. In other words, they have supermassive black holes expelling vast quantities of energy in the full range of the electromagnetic spectrum.

Photonic computing processes information using light, whilst neuromorphic computing attempts to emulate the human brain. Bring the two together, and we may have the perfect platform for next generation AI, as this video explores.
If you like this video, you may also enjoy my previous episodes on:
Organic Computing:
Brain-Computer Interfaces:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xMxJYhUg0pc.
More videos on computing and related topics can be found at:
https://www.youtube.com/explainingcomputers.
You may also like my ExplainingTheFuture channel at: https://www.youtube.com/explainingthefuture.



