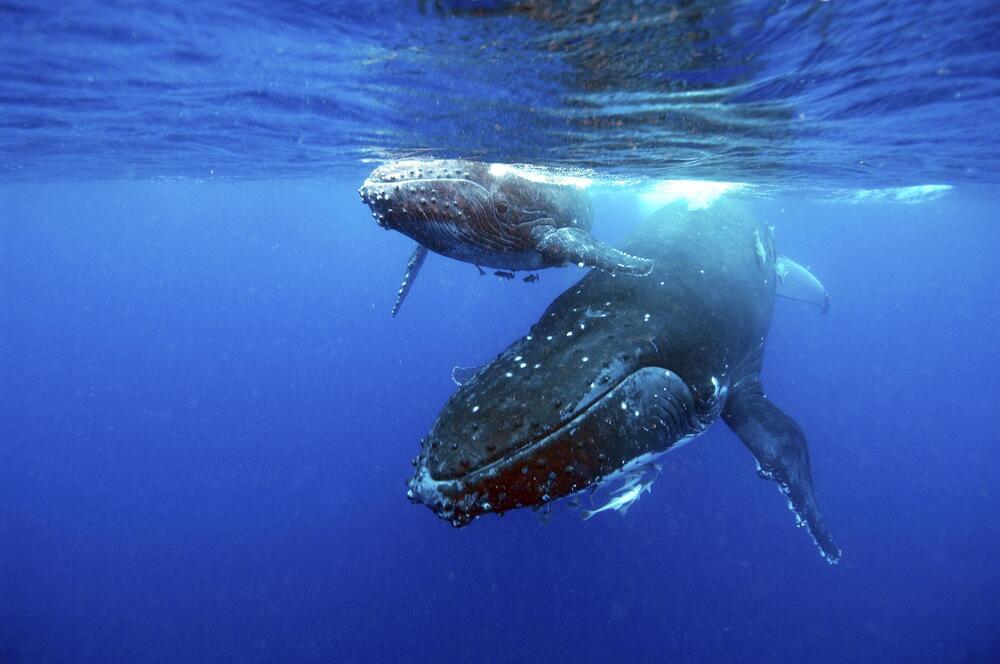
Baleen whales have evolved unique voice boxes essential for song, a new study finds—but these low-frequency vocalizations must compete with the noise of humans’ ships.



Passengers who book a special Delta flight will have the chance to witness the total solar eclipse in April from a unique vantage point: 30,000 feet in the air.
The airline announced Monday that it will operate a flight on April 8 from Dallas-Fort Worth to Detroit, timed to give people on board the chance to spend as much time as possible within the eclipse’s “path of totality.”
The eclipse is expected to be a major event because it will pass over several densely populated areas of North America, crossing Mexico, the continental U.S. and a small part of eastern Canada. In the U.S. alone, millions of skywatchers from Texas to Maine will have the chance to witness the rare astronomical event.
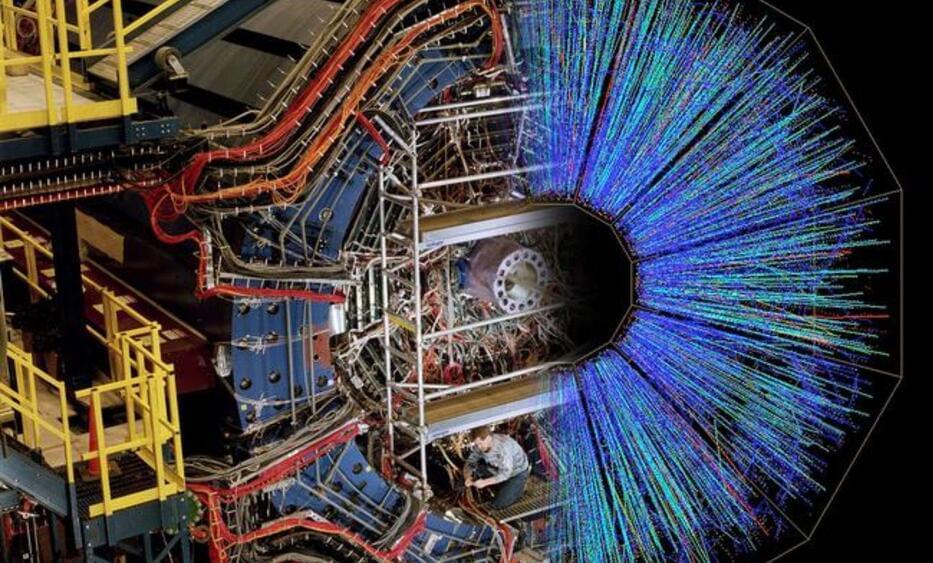




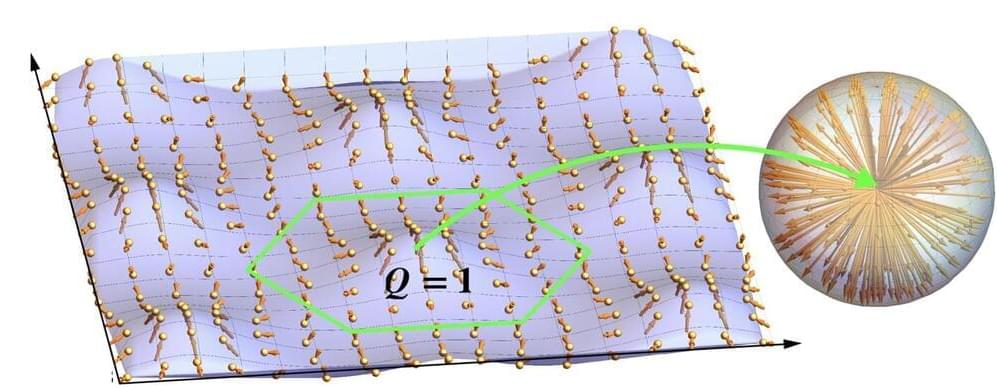
Topological wave structures are wave patterns that exhibit specific topological properties, or in other words, properties that remain unvaried under smooth deformations of a physical system. These structures, such as vortices and skyrmions, have attracted significant attention within the physics research community.
While physicists have carried out extensive studies focusing on topological wave structures in various wave systems, surprisingly their most classical example remains unexplored. These are water waves, oscillations or disturbances that propagate on the surface of water or other fluid.
Researchers at RIKEN recently set out to fill this gap in the literature, by offering a description of various water-wave topological structures. Their paper, published in Physical Review Letters, offers a theoretical framework that could inform future experiments aimed at emulating topological wave phenomena.

A team of scientists on board an exploration vessel off the coast of South America have made a startling discovery: four previously unknown massive underwater mountains, ranging from 5,200 to 8,800 feet tall. The discovery highlights just how little we know about the oceans covering much of our planet. According to recent estimates, more than 80 percent of the ocean has never been mapped, let alone explored.
“The tallest is over one-and-a-half miles in height, and we didn’t really know it was there,” Schmidt Ocean Institute’s Jyotika Virmani — whose team has been studying “seamounts” from on board the vessel Falkor — told New Scientist.
Using sonar equipment, Virmani and team investigated gravity anomalies while sailing down from Costa Rica to Chile. These anomalies are usually the result of a hard-to-discern mass — in this case, entire mountains sticking out of the ocean floor.
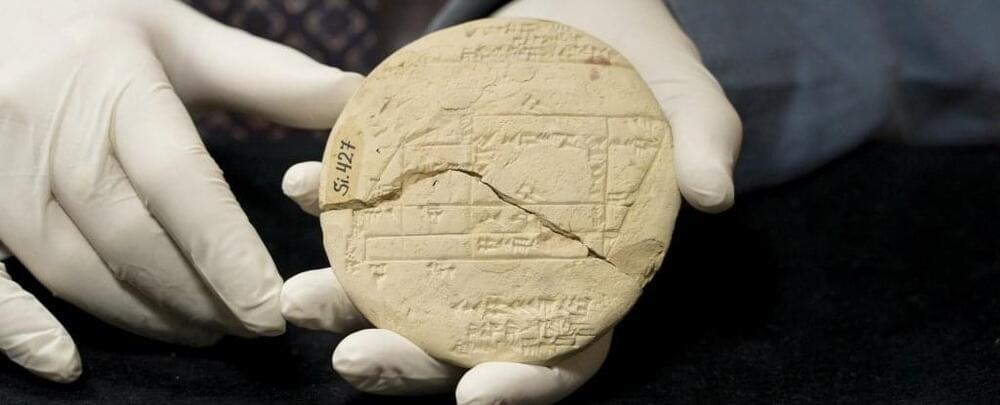

Cira 2021: An ancient fragment of clay tablet dating back to 3,700 years ago, during the Old Babylonian period, contains what is now the oldest known example of applied geometry, a mathematician has discovered. That’s more than a millennium prior to the birth of Pythagoras.
And this history-altering artifact, known as Si.427, had just been sitting in a museum in Istanbul for more than 100 years.
“Si.427 dates from the Old Babylonian (OB) period — 1900 to 1,600 BCE,” said mathematician Daniel Mansfield of the University of New South Wales (UNSW) in Australia.