The bold new idea could offer an alternate explanation for cosmic expansion.
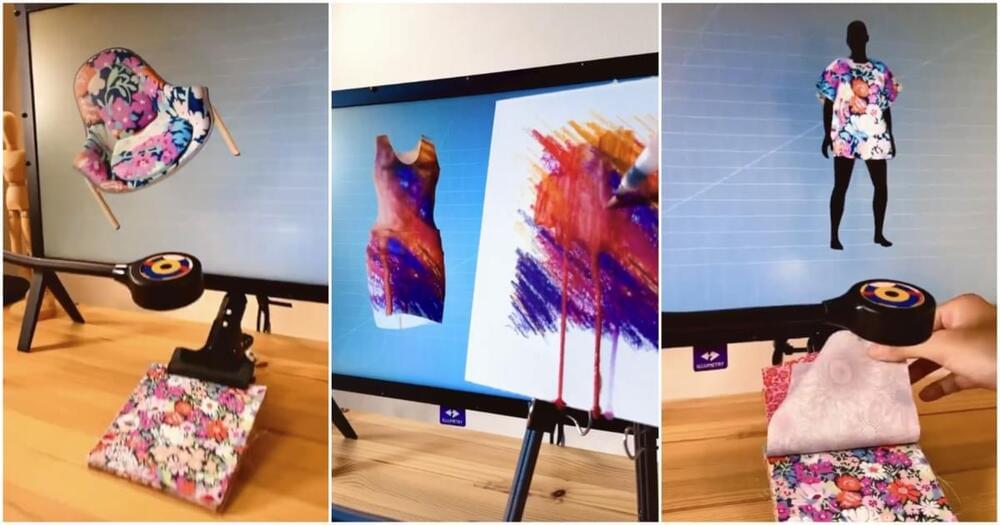



Users of Photoshop, Substance 3D, and other Adobe products are now required to provide the company with unlimited access to their creations.
This tutorial aims to provide a survey of the Bayesian perspective of causal inference under the potential outcomes framework. We review the causal estimands, assignment mechanism, the general structure of Bayesian inference of causal effects, and sensitivity analysis. We highlight issues that are unique to Bayesian causal inference, including the role of the propensity score, the definition of identifiability, the choice of priors in both low and high dimensional regimes. We point out the central role of covariate overlap and more generally the design stage in Bayesian causal inference. We extend the discussion to two complex assignment mechanisms: instrumental variable and time-varying treatments. We identify the strengths and weaknesses of the Bayesian approach to causal inference. Throughout, we illustrate the key concepts via examples.
Instructor:
Fan Li, Professor, Department of Statistical Science, Department of Biostatistics \& Bioinformatics, Duke University.
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/seanmcarrollBlog post with audio player, show notes, and transcript: https://www.preposterousuniverse.com/podcast/2024/06/03…



