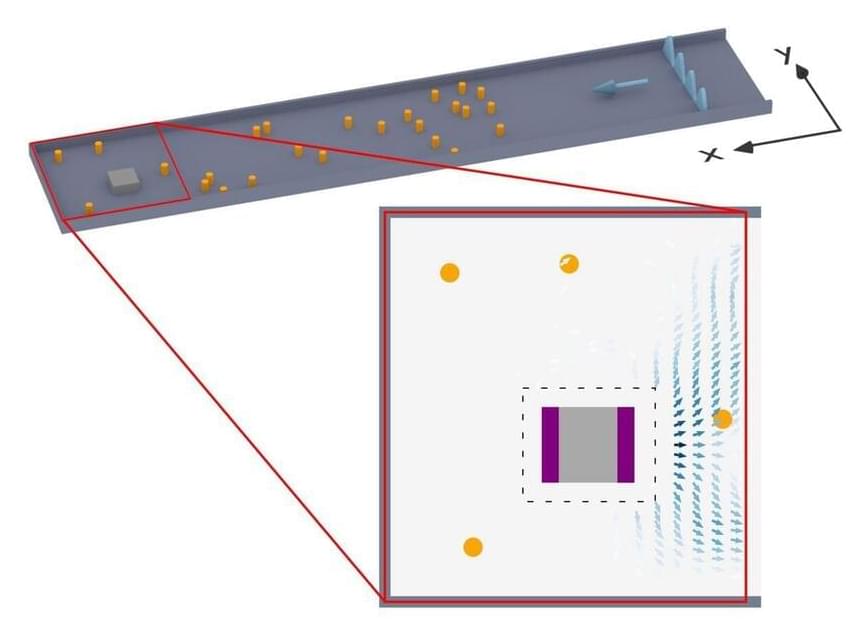
Waves pick up information from their environment through which they propagate. A theory of information carried by waves has now been developed at TU Wien—with astonishing results that can be utilized for technical applications.

Raphael Rau unveiled a new photorealistic creation and shared some insights on how it was made.

May 2024 was the hottest May on record, marking a full annual cycle of monthly records, the longest ever recorded.

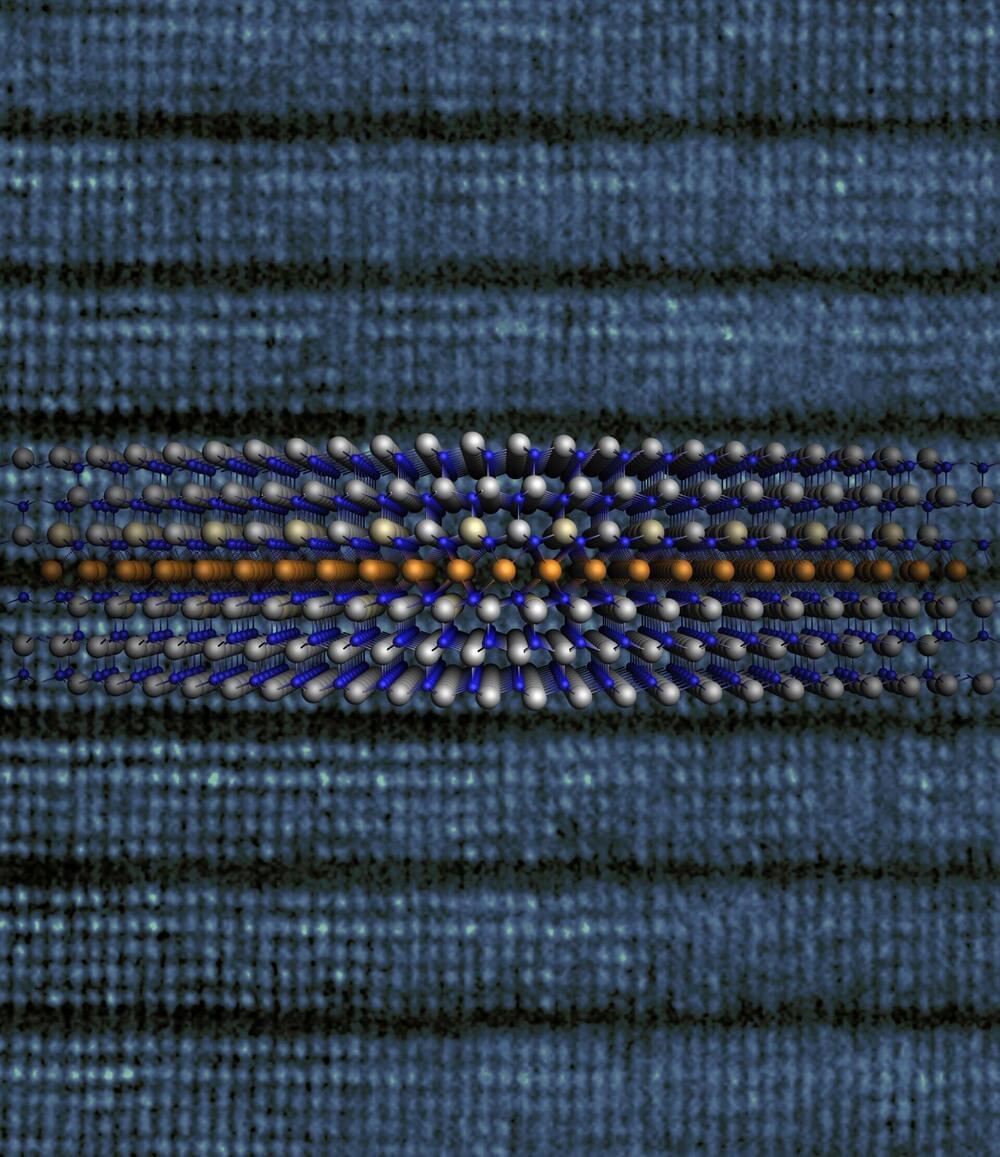
A study led by Nagoya University in Japan revealed that a simple thermal reaction of gallium nitride (GaN) with metallic magnesium (Mg) results in the formation of a distinctive superlattice structure. This represents the first time researchers have identified the insertion of 2D metal layers into a bulk semiconductor.
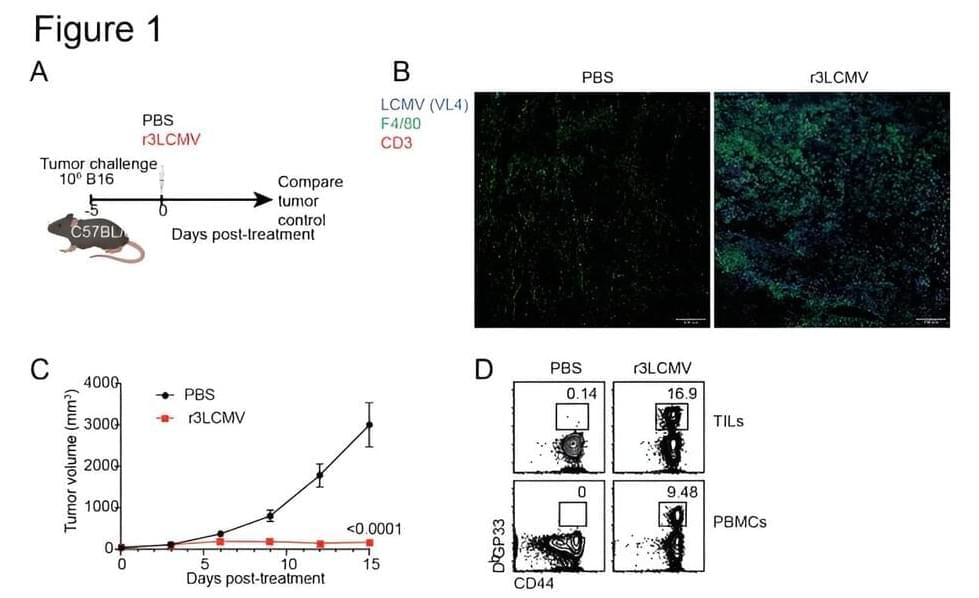
Currently, so-called “oncolytic viruses” such as herpes are used to treat some types of cancer because of their ability to kill cancer cells. But these therapies are not effective with some tumors and their use poses safety concerns, especially in immunosuppressed patients, underscoring the need for safer alternatives, Penaloza-MacMaster said.
In addition to helping clear the tumors, the therapy also helped prevent future cancer in these mice. Healthy mice that were first treated with the LCMV therapy were more resistant to developing tumors later in life.
This phenomenon might be explained by a poorly understood biological process known as “trained immunity.” Trained immunity occurs when a previous infection enhances the immune system’s ability to respond to different diseases in the future. For example, studies have shown that children who received the tuberculosis (TB) vaccine exhibit improved protection against other microorganisms, not just TB. This differs from the typical vaccine response, such as with the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, which primarily protects against this specific virus.
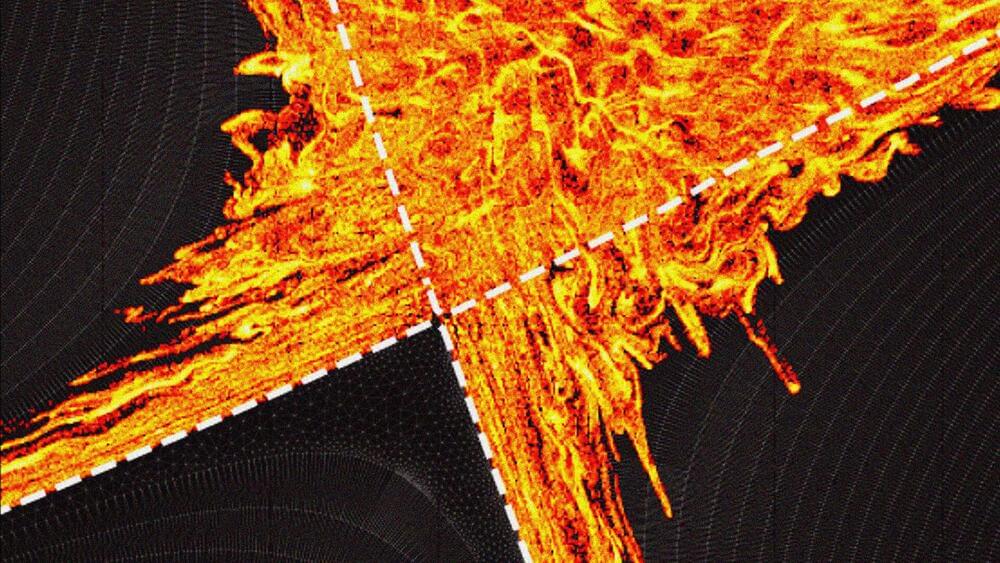

By Rachel Kremen, Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory
The furious exhaust heat generated by a fusing plasma in a commercial-scale reactor may not be as damaging to the vessel’s innards as once thought, according to researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL), Oak Ridge National Laboratory and the ITER Organization (ITER).