Japan’s boldest move yet to position itself as a global research powerhouse is underway, with the first of its new cohort of top-tier universities rolling out historic changes.






The majority of carbon offset schemes are significantly overestimating the levels of deforestation they are preventing, according to a study published in Science.
This means that many of the “carbon credits” bought by companies to balance out emissions are not tied to real-world forest preservation as claimed.
An international team of scientists and economists led by the University of Cambridge and VU Amsterdam found that millions of carbon credits are based on crude calculations that inflate the conservation successes of voluntary REDD+ projects.
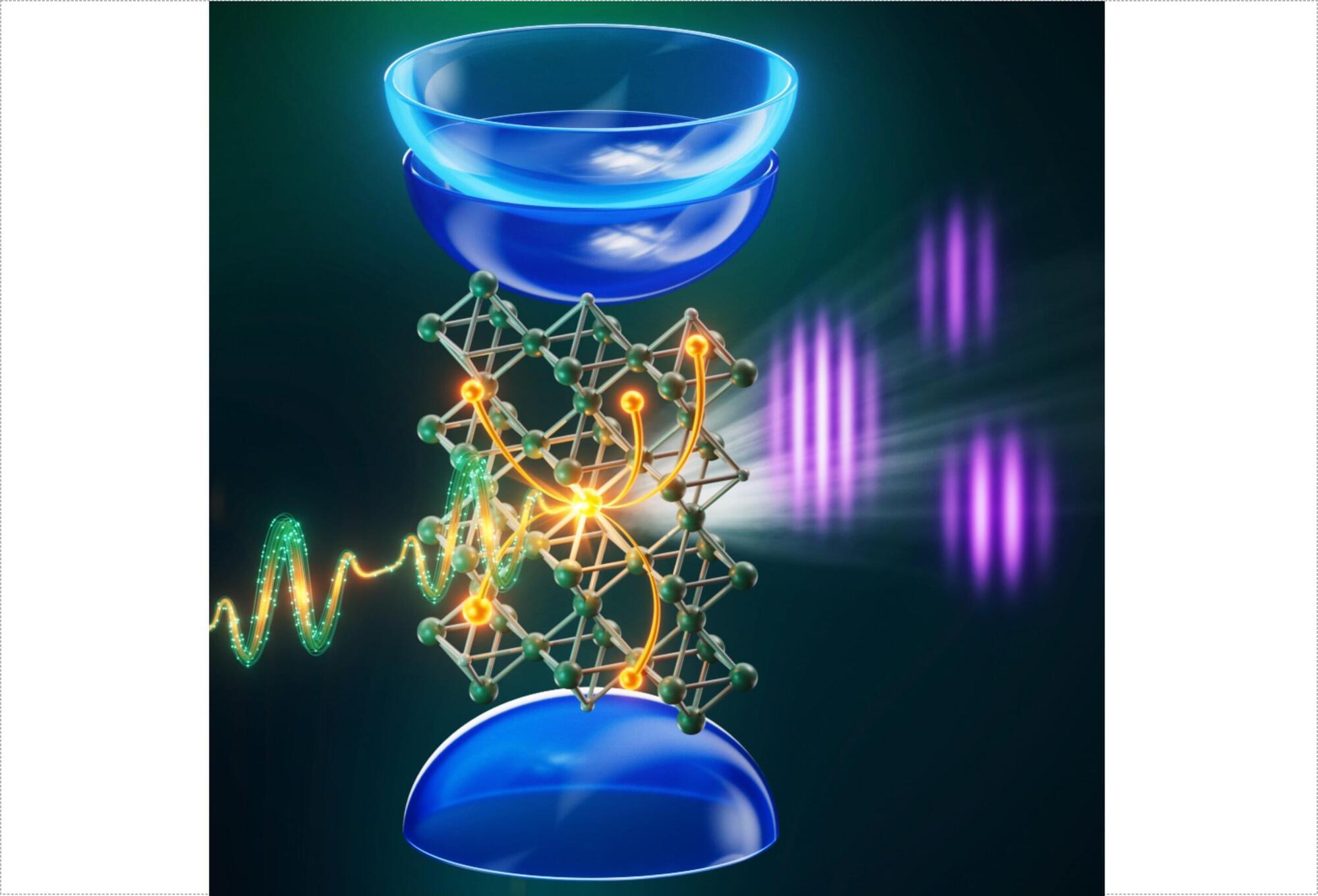
The bandgap, i.e. the energy gap between the highest lying valence and the lowest lying conduction band, is a defining property of insulating solids, governing how they absorb light and conduct electricity. Tracking how a bandgap changes under strong laser excitation has been a long-standing challenge, since the underlying processes unfold on femtosecond timescales and are difficult to track directly, especially for wide-bandgap dielectrics.
In a collaboration between the Max-Born-Institute, ARCNL Amsterdam, and Aarhus University, researchers have now shown that extreme ultraviolet (XUV) high-harmonic interferometry can provide direct access to such dynamics.
Using pairs of phase-locked near-infrared laser pulses, the team measured interference fringes and their intensity-dependent shift in the generated high-order harmonics from silica glass (SiO2) and magnesium oxide (MgO).