Category: futurism – Page 2


Antibody modulation of B cell responses—Incorporating positive and negative feedback
Antibodies modulate ongoing and future B cell responses. Cyster and Wilson review the various mechanisms whereby antibody feedback shapes B cell responses and present a framework for conceptualizing the ways antigen-specific antibody may influence immunity in conditions as diverse as infectious disease, autoimmunity, and cancer.
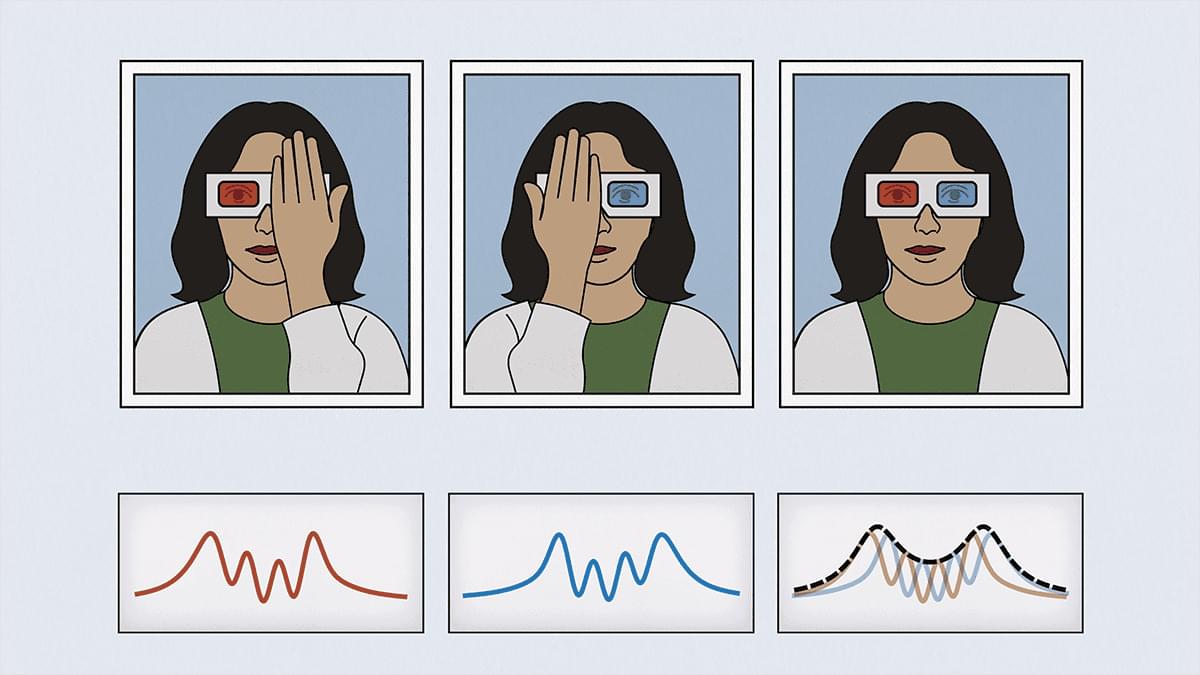

Where Do Minds Exist?
In this talk from the CSCSC 25 Conference on Complex Systems and Contemplative Studies, Dr. Michael Levin asks a question with deep resonance for both science and contemplative practice:

Rule-breaking discovery reveals new way to strengthen metal in extreme conditions
There’s a reason why blacksmiths fire metals before hammering them. Heat always softens metal, making it more malleable and easier to reshape. Or does it? In a surprising new study, Northwestern University engineers discovered that, in extreme conditions, heat doesn’t soften pure metals—it strengthens them.
Not only does this new finding challenge long-held assumptions of how metals behave, it also could provide new insights for designing metals for futuristic applications in extreme conditions, such as hypersonic flight, extraterrestrial construction and advanced manufacturing.
The study will be published Tuesday (Feb. 17) in Physical Review Letters.

