
Category: futurism – Page 1,373

In memory of Marvin Minsky
Nice tribute.
Marvin Minsky at One Laptop per Child office, Cambridge Mass. 2008 (credit: Bcjordan/Wikimedia Commons)
Ray Kurzweil, January 25, 2016
When I was fourteen I wrote Marvin Minsky a letter asking to meet with him. He invited me to visit him at MIT and he spent hours with me as if he had nothing else to do.
When my daughter Amy was about eleven and we went out for a meal at the Harvest Restaurant in Cambridge with my wife Sonya and his wife Gloria, Amy and Marvin built a large structure on the restaurant table using all of the silverware, experimenting with different ways that the utensils could create stable structures.
Will Humans Be Obsolete After The New Industrial Revolution?
Subscribe! http://bitly.com/1iLOHml
Are We Nearing The End Of Capitalism? http://bit.ly/1Tkwl0K
The world has undergone three industrial revolutions that have dramatically impacted the way we live. So what will happen during the fourth industrial revolution?
The Future of Jobs Employment, Skills and Workforce Strategy for the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
http://www3.weforum.org/docs/Media/WEF_Future_of_Jobs_embargoed.pdf
“Today, we are on the cusp of a Fourth Industrial Revolution.”
Fourth industrial revolution set to benefit richest, UBS report says.
http://www.theguardian.com/business/2016/jan/19/fourth-indus…eport-says
“The richest stand to gain more from the introduction of new technology than those in poorer sections of society, according to a report which warns that policymakers may be required to intervene to tackle the widening inequality.”
The Third Great Wave.
LG OLED TV : You Dream We Display
Experience the whole new future created by OLED and see how OLED will bring significant change to our life.
For more information visit▶
LG OLED TV UK URL: http://www.lg.com/uk/lgoled/

Intensive instrument playing can trigger movement disorders
Dystonia can be triggered because you’re in a rock band? That’s a new one for me.
Scientists from Germany have investigated the possible causes that may trigger movement disorders.
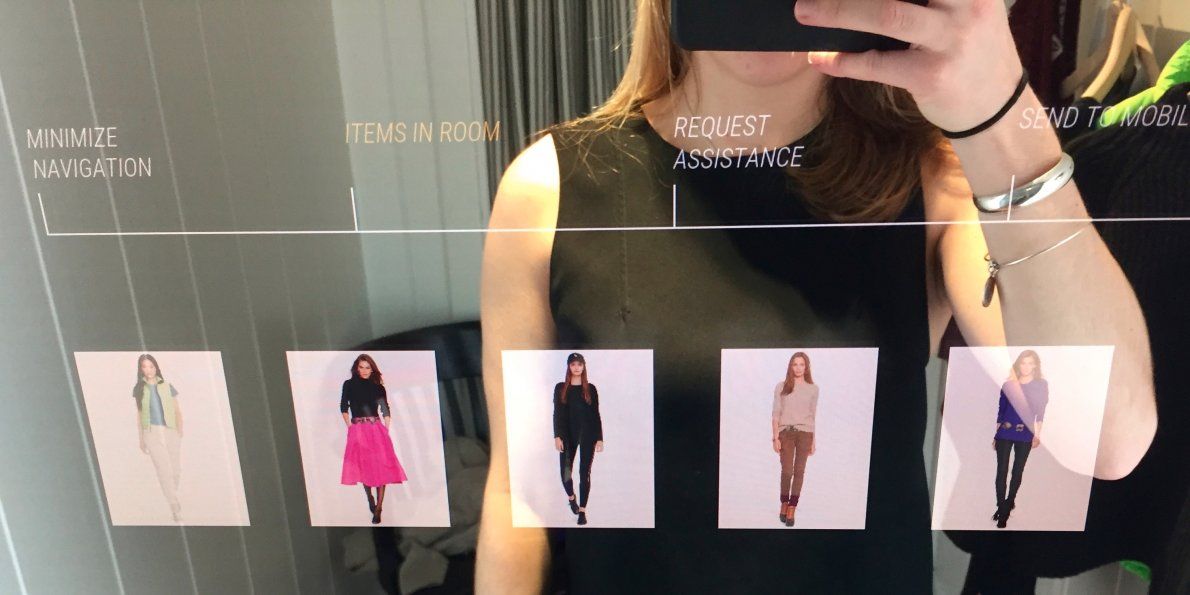

China is building malls of the future that could come to the US soon
High-end, futuristic malls in China and parts of the US are upgrading technology, hoping to attract customers with “smart” shopping centers.
“In the US, the malls look exactly the same they did 20 year ago,” Deborah Weinswig, executive director at Fung Business Intelligence Centre, said recently in a talk at a JDA Executive Luncheon. “We’ve got to make it more exciting, and more fun, and more experiential.”
Changing consumer tastes and the rise of e-commerce means shoppers are visiting malls less and less, with Weinswig reporting that the average American now visits a mall three to four times a year, as opposed to five to six. To compete with online shopping, malls need to match e-commerce in convenience and create experiential reasons to visit the mall that you cannot find online.
Physicists Propose the First Scheme to Teleport the Memory of an Organism
Quantum teleportation between two microorganisms could be happening in the near future.
Prof. Tongcang Li at Purdue University and Dr. Zhang-gi Yin at Tsinghua University just proposed the first scheme to use electro-mechanical oscillators and superconducting circuits to teleport the internal quantum state (memory) and center-of-mass motion state of a microorganism.
Sound a little complex? Then let’s break it down a bit.
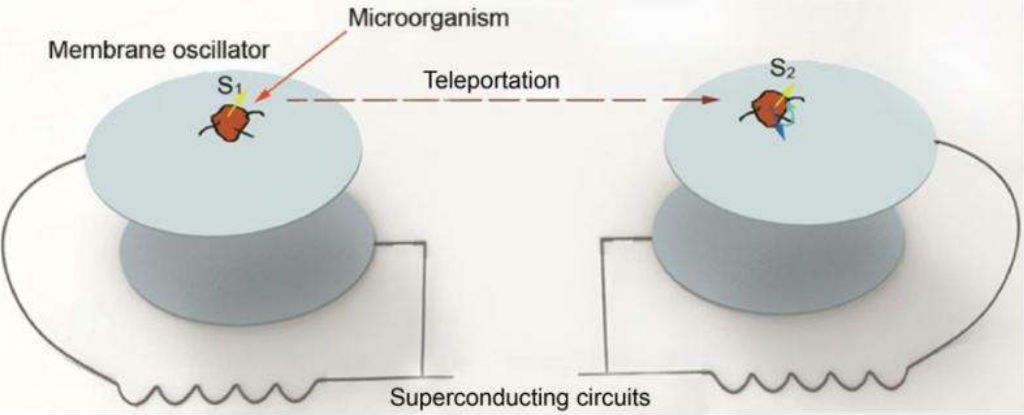
Physicists propose new method to teleport the memory of a living creature
While the possibility of teleporting entire objects from one place to another like they do in the movies is way beyond our current — and near-future — capabilities, the same can’t be said for the memory of our existence.

B.C. puts focus on tech into hyperdrive
News from BC Tech Summit.
Province’s first #BCTECH Summit a major draw for Canadian tech entrepreneurs.

WordsEye: WordsEye lets you type a picture!
Create 3D scenes simply by describing them and share your creations with friends. A new world of visual expression and a new way to communicate and express yourself online.