A new story on how coming technology may change our attitudes on the death penalty. This story was a feature on Vice yesterday, as well as Motherboard:.


A new story on how coming technology may change our attitudes on the death penalty. This story was a feature on Vice yesterday, as well as Motherboard:.
One of the biggest existential challenges that transhumanists face is that most people don’t believe a word we’re saying, however entertaining they may find us. They think we’re fantasists when in fact we’re talking about a future just over the horizon. Suppose they’re wrong and we are right. What follows? Admittedly, we won’t know this until we inhabit that space ‘just over the horizon’. Nevertheless, it’s not too early to discuss how these naysayers will be regarded, perhaps as a guide to how they should be dealt with now.
So let’s be clear about who these naysayers are. They hold the following views:
1) They believe that they will live no more than 100 years and quite possibly much less.
2) They believe that this limited longevity is not only natural but also desirable, both for themselves and everyone else.
3) They believe that the bigger the change, the more likely the resulting harms will outweigh the benefits.
Now suppose they’re wrong on all three counts. How are we to think about such beings who think this way? Aren’t they the living dead? Indeed. These are people who live in the space of their largely self-imposed limitations, which function as a self-fulfilling prophecy. They are programmed for destruction – not genetically but intellectually. Someone of a more dramatic turn of mind would say that they are suicide bombers trying to manufacture a climate of terror in humanity’s existential horizons. They roam the Earth as death-waiting-to-happen. This much is clear: If you’re a transhumanist, ordinary people are zombies.
Zombies are normally seen as either externally revived corpses or bodies in a state between life and death – what Catholics call ‘purgatory’. In both cases, they remain on Earth beyond their will. So how does one deal with zombies, especially when they are the majority of the population? There are three general options:
1) You kill them, once and for all.
2) You avoid them.
3) You enable them to be fully alive.
The decision here is not as straightforward as it might seem because the prima facie easiest option (2) requires that there are no resource implications. But of course, zombies require living humans (i.e. potential transhumans) in order to exist in the manner they do, which in turn makes the zombies dangerous; hence (1) has always proved such an attractive option for dealing with zombies. After all, it is difficult to dedicate the resources needed to secure the transhumanist goal of indefinite longevity, if there are zombies trying to anchor your existential horizons in the present to make their own lives as easy as possible.
This kind of problem normally arises in the context of ecological sustainability as ‘care for future generations’: Our greedy habits of mass consumption blind us to the long-term damage it does to the environment. However, the relevant sense of ‘care’ in the transhumanist case relates to sustaining the investment base needed to reach a state of indefinite longevity. It may require diverting public resources from seemingly more pressing needs, such as having a strong national defence — as the US Transhumanist Party presidential candidate Zoltan Istvan thinks. It is certainly true that if people routinely lived indefinitely, then the existential character of ‘the horror of war’ would be considerably reduced, which may in turn decrease both the likelihood and cost of war. Well, maybe…
So what about option (3), which is probably the one that most of us would find most palatable, at least in principle?
Here there is a serious public relations problem, one not so different from development aid workers trying to persuade ‘underdeveloped’ peoples that their lives would be appreciably improved by allowing their societies to be radically re-structured so as to double their life expectancy from 40 to 80. While such societies are by no means perfect and may require significant change to deliver what they promise their members, nevertheless the doubling of life expectancy would mean a radical shift in the rhythm of their individual and collective life cycles – which could prove quite threatening to their sense of identity.
Of course, the existential costs suggested here may be overstated, especially in a world where even poor people have decent access to more global trends. Nevertheless the chequered history of development aid since the formal end of Imperialism suggests that there is little political will – at least on the part of Western nations — to invest the human and financial capital needed to persuade people in developing countries that greater longevity is in their own long-term interest, and not simply a pretext to have them work longer for someone else.
The lesson for us lies in the question: How can we persuade people that extending their lives is qualitatively different from simply extending their zombiehood?
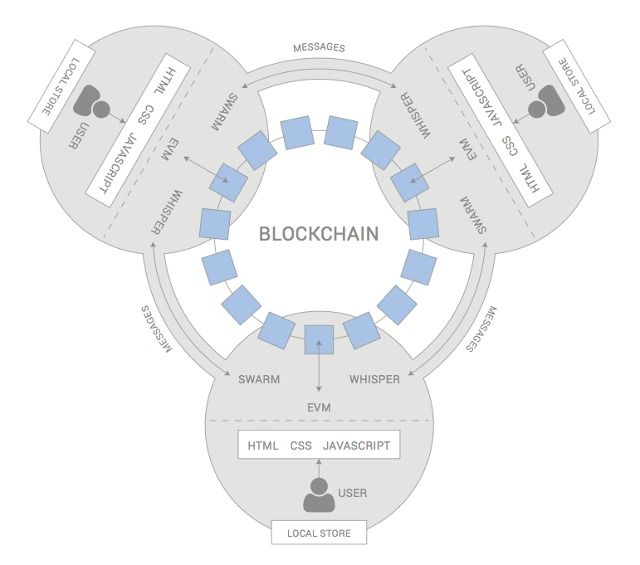
How would Ethereum’s network autonomously run transportation apps, delivery services, and other companies? And would we even want that?
It’s nothing to get too excited or alarmed about, but a robot has passed a modified version of the classic King’s Wise Men Test. It’s another classic case of simulation rather than emulation, but the experiment shows how artificial self-awareness can be programmed into our technology.
By using nanopores to read and write DNA, we’re beginning to unlock the mysteries of our own biology! — B.J. Murphy for Serious Wonder.
I was already looking forward to playing this game when it’s released, but after seeing his latest trailer I am positively IMPATIENT to get my hands on it!
No other game (or almost ANY form of media, for that matter!) has ever explored our rapidly approaching, post-human transhumanist future in such a staggeringly detailed, informed, and passionate way!

Deus Ex executive art director Jonathan Jacques-Belletete divulges on Mankind Divided’s visual look, themes and Jensen’s role as a not-quite hero.

The 2015–16 State of the Future is a compelling overview of humanity’s present situation, challenges and opportunities, potentials for the future, and actions and policies that could improve humanity’s outlook — in clear, precise, and readable text with unparalleled breadth and depth. “It is time for intolerance of irrelevant speeches and non-actions by leaders. The stakes are too high to tolerate business as usual”, warns the Executive Summary of the report.
A lucid, thought-provoking, strategically oriented exploration of the transforming world order.
Mihaly Simai, former Chairman, United Nations University
The State of the Future can make a difference in the world. Well done.
Wendell Bell, Professor Emeritus, Yale University
Global intelligence on the future of the world in the palm of your hand
KurzweilAI News
So important for many people around the world.
Eleonora Masini, former Secretary and President, World Futures Studies Federation
Absolutely worth the reader’s time… takes the reader much farther forward than most thinking.
Defense & Foreign Affairs Policy Journal
Strategic Planning for the Planet… remarkably articulate and prescient
Willian Halal, Foresight Journal
Authoritative compendium of what we know about the future of humanity and our planet.
The Futurist
Certainly, the guide to make better decisions and achieve success.
Julio Millán, President Coraza Corporación Azteca
Invaluable insights into the future for the United Nations, its Member States, and civil society.
Ban Ki-moon, Secretary-General, United Nations
The 2015–16 State of the Future brings together an extraordinarily diverse set of data, information, intelligence, and hopefully some wisdom about the future. This is the eighteenth edition of the State of the Future. We believe that each edition is better than the last. We update data, improve insights, and respond to feedback. You can add your feedback online at the Global Futures Intelligence System (themp.org). There is a comment icon in the lower right corner of the executive summary and the same for
every one of the 15 Global Challenges.
The short overviews of the 15 Global Challenges are getting longer and more detailed each year. In addition to giving you possibly the best overview in existence for each challenge, think of these as a reference to keep on your desk to return to as needed. Just as you would not speedread the encyclopedia, this section should also be taken in short doses. Take your time to reflect on what you are reading in each challenge and in the sections on the State of the Future Index and the Future Work/ Technology 2050.
This is the second year we have used the Global Futures Intelligence System to update and improve the State of the Future report. The challenges in GFIS are updated daily from news aggregations, scanning items, situation charts, and other resources, which has led to greater detail and depth than in the previous edition.
While this report presents the distilled results of recent research by The Millennium Project, GFIS contains the detailed background and data for that research, plus all of The Millennium Project’s research since its founding in 1996. It also contains the largest internationally peerreviewed set of methods to explore future possibilities ever assembled in one source. Readers of this report should subscribe to GFIS to keep up to date and participate in improving insights about future possibilities.
The purpose of futures research is to systematically explore, create, and test both possible and desirable futures in order to improve decisions. Just as the person on top of the mast on old sailing ships used to point out the rocks and safe channels to the captain below for the smooth running of the ship through uncharted waters, so too futurists with foresight systems for the world can point out problems and opportunities to leaders and the public around the world. Since decision-making is increasingly affected by globalization, global futures research is increasingly valuable for decision-making by individuals, groups, and institutions. The quality of democracies emerging around the world is enhanced by better-informed publics; understanding issues and opportunities in this report can contribute to improved democratic decision-making.
This report is for thought leaders, decision-makers, and all those who care about the world and its future. Readers will learn how their interests fit into the global situation and how the global situation may affect them and their interests. The State of the Future and GFIS provide an additional eye on global change. These are information utilities that
people can draw from as relevant to their unique needs. They provide an overview of the global strategic landscape. Business executives use the research as input to their strategic planning. University professors, futurists, and other consultants find this information useful in teaching and research.
The Millennium Project is a global participatory think tank of futurists, scholars, scientists, business planners, and policy makers who work for international organizations, governments, corporations, NGOs, and universities and who volunteer their time to improve each edition of the State of the Future. It was selected to be among the top
10 think tanks in the world for new ideas and paradigms by the 2013 and 2014 University of Pennsylvania’s GoTo Think Tank Index and as a 2012 Computerworld Honors Laureate for its innovations in collective intelligence systems.
The purposes of The Millennium Project are to assist in organizing futures research, improve thinking about the future, and make that thinking available through a variety of media for consideration in policymaking, advanced training, public education, and feedback, ideally in order to accumulate wisdom about potential futures.
The Project’s diversity of opinions and global views is ensured by its 56 Nodes around the world. These are groups of individuals and organizations that interconnect global and local perspectives. They identify participants, conduct interviews, translate and distribute questionnaires, and conduct research and conferences. It is through their contributions that the world picture of this report and indeed all of The Millennium Project’s work emerge.
Through its research, publications, addresses at conferences, and Nodes, The Millennium Project helps to nurture an international collaborative spirit of free inquiry and feedback for increasing collective intelligence to improve social, technical, and environmental viability for human development. Feedback on any sections of the book is most
welcome and may help shape the next State of the Future, GFIS, and the general work of The Millennium Project.

IBM Watson CTO: Quantum computing could advance artificial intelligence by orders of magnitude.
Quantum computers have already been used to test artificial intelligence by researchers in China, albeit in a very limited capacity. Earlier in 2015, a team from the country’s University of Science and Technology developed a quantum system capable of recognising handwritten characters in a demonstration they dubbed quantum artificial intelligence.
This demonstration was on a quantum computer using only four qubits, leading to speculation of what a system using hundreds – or even thousands – of qubits would be capable of. Such machines do not yet exist, at least not commercially, but Canada-based quantum computing firm D-Wave systems recently claimed it has built a 1,000 qubit quantum computer.
According to Seth Lloyd, a professor of mechanical engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), a machine of just 300 qubits could be used to “map the whole universe”, processing all the information that has existed since the Big Bang.

#Handy New Wireless Charger Can Simultaneously Power 30 Mobile Phones at Distance.
Scientists at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have developed an omnidirectional wireless charging technology that can charge multiple devices at once, at a distance and, crucially, at peak efficiency regardless of which way the devices are facing.
An effective wireless transmitting power of 30 watts means the device can, according to the researchers, power either 30 smartphones or five laptops simultaneously.
The results were published in last month’s issue of the journal IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, and a spinoff company is now conducting pilot studies to apply this technology in cafes and offices.