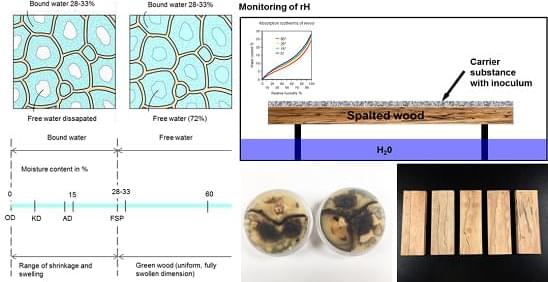
University of Colorado Boulder researchers made the first-ever airborne detection of Medium Chain Chlorinated Paraffins (MCCPs) in the Western Hemisphere. Sometimes, scientific research feels a lot like solving a mystery. Scientists head into the field with a clear goal and a solid hypothesis, bu