The new Guinness World Record holder’s logo is nearly invisible to the naked eye.
Category: food – Page 59
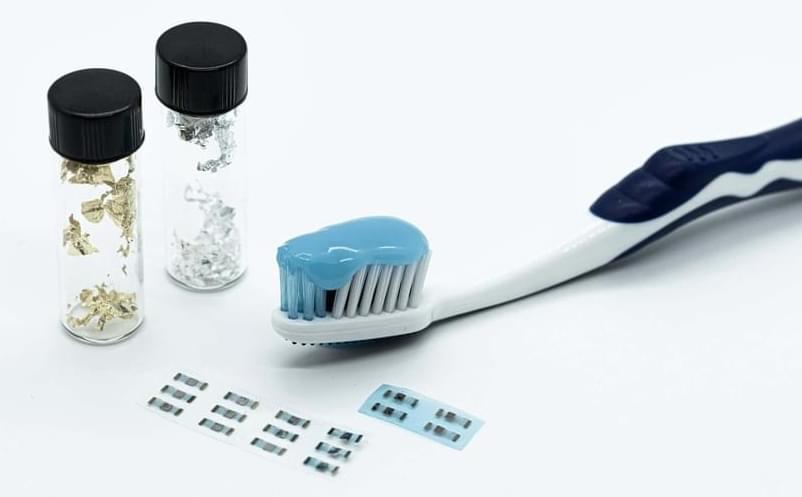
This toothpaste-based transistor could be the future of edible electronics
The edible transistor is based on an existing transistor architecture, utilizing CuPc as the active material. The key component, the electrolyte-gated OFET (EGOFET), operates at low voltages (1 V) and can function stably for more than a year. The transistor showed good reproducibility, with performance characteristics that pave the way for integrating these devices into more complex edible circuits.
The circuits are constructed on a derivative of cellulose with electrical contacts being printed using inkjet technology and a solution of gold particles (which are also commonly used in the food industry for decoration). The transistor “gate” is also food-grade. This component controls the flow of electrical current between the source and drain terminals, effectively acting as a switch or amplifier. This gate is made from a gel based on chitosan another food-grade ingredient used as a gelling agent.
The research team also explored the optical and morphological properties of CuPc thin films. They found that the thickness of the CuPc layer played a crucial role in the transistor’s performance. Thinner films displayed better charge transport properties, which are essential for creating high-performing, low-voltage devices. This detailed understanding of the material’s properties allowed the team to optimize the transistor’s design for use in real-world applications.
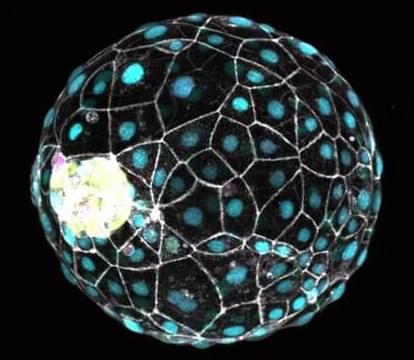
‘Pause Button’ Molecule Uncovered in Human Embryos
Mamma bears press pause on their early pregnancies, so that their cubs are born closer to a food filled spring. Researchers led by a team in Germany have now found this same pregnancy pause button exists in human cells too.
“Although we have lost the ability to naturally enter dormancy, these experiments suggest that we have nevertheless retained this inner ability and could eventually unleash it,” says molecular geneticist Nicolas Rivron from the Austrian Academy of Sciences (IMBA).
“Triggering a dormant state during an IVF procedure could provide a larger time window to assess embryo health and to synchronize it with the mother for better implantation inside the uterus.”
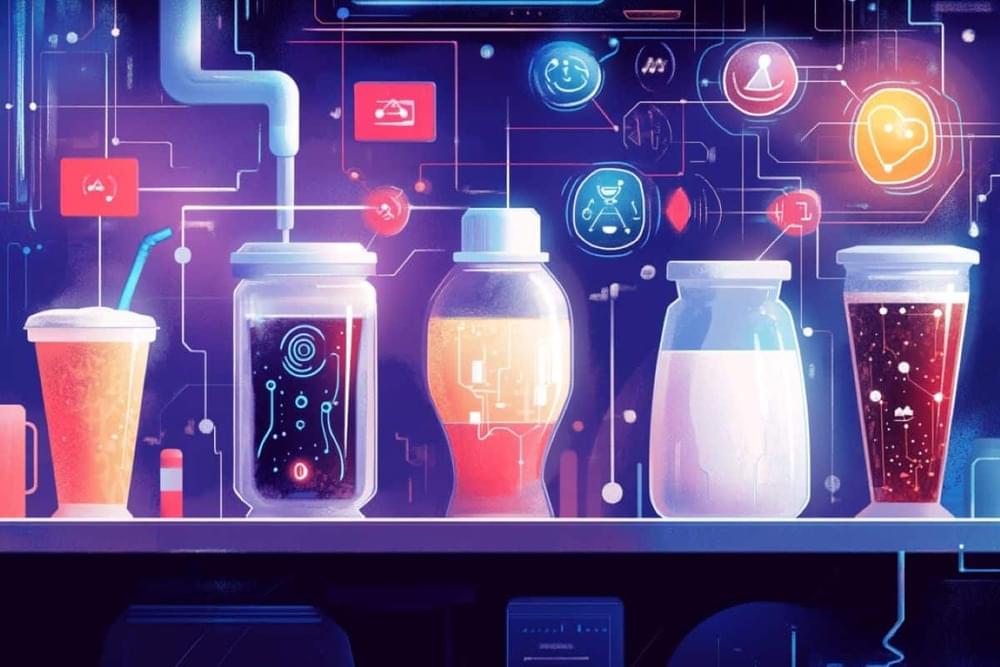

Electronic Tongue Uses AI to Detect Differences in Liquids
Summary: Researchers have developed an AI-powered “electronic tongue” capable of distinguishing subtle differences in liquids, such as milk freshness, soda types, and coffee blends. By analyzing sensor data through a neural network, the device achieved over 95% accuracy in identifying liquid quality, authenticity, and potential safety issues. Interestingly, when the AI was allowed to select its own analysis parameters, it outperformed human-defined settings, showing how it holistically assessed subtle data.
This technology, which uses graphene-based sensors, could revolutionize food safety assessments and potentially extend to medical diagnostics. The device’s AI insights also provide a unique view into the neural network’s decision-making process. This innovation promises practical applications across industries where quality and safety are paramount.
Scientists Are Closer Than Ever To Reverse Aging. How Does It Work? | Life Extended
Billionaires are backing top scientists racing to develop tech that could reverse aging. Cellular reprogramming promises to rejuvenate the body… but how does it work, and is it safe?
00:00 – Introduction.
00:55 – The Role Of Stem Cells.
02:33 – What Is Aging?
03:24 – What Is Cellular Reprogramming?
03:56 – How The Yamanaka Factors Can Rejuvenate Cells.
05:35 – Why Scientists Want To Partially Reprogram Cells.
06:28 – How Humans Could Become More Resilient To Age-Related Diseases.
07:00 – How Johnny Huard Uses Cellular Reprogramming.
08:10 – How Cellular Reprogramming Could Shape The Future.
08:38 – Amazon’s Jeff Bezos Is Investing Billions With Altos Labs.
09:02 – How Harvard Professor David Sinclair Used Cellular Reprogramming on Mice.
10:07 – ChatGPT’s Sam Altman Launched Retro. Biosciences.
10:57 – The Risks of Cellular Reprogramming, Including Cancer.
12:56 – How the Tech World Is Investing In Biotech.
13:50 – Credits.
MORE BUSINESS INSIDER EXPLAINS VIDEOS:
How Food Giants Are Jumping On The Ozempic Game With Frozen Meals | Business Insider Explains.
• How Food Giants Are Jumping On The Oz…
Here’s What Would Happen If We Raised Minimum Wage | Business Insider Explains | Business Insider.
• Here’s What Would Happen If We Raised…
The Rivalry Between Tech Billionaires Bill Gates And Steve Jobs | Business Insider Explains.
• The Rivalry Between Tech Billionaires…
#aging #health #businessinsider.
Business Insider tells you all you need to know about business, finance, tech, retail, and more.
Visit our homepage for the top stories of the day: https://www.businessinsider.com.

Therapy could boost lifespan by 25pc
Researchers at Duke-NUS Medical School have identified interleukin-11 (IL11) as a key factor in the ageing process. Elevated IL11 levels lead to fat accumulation and muscle loss—two major indicators of ageing. Inhibiting IL11 could enhance healthy lifespans.
Ageing populations pose significant health and economic challenges globally. Even a one-year increase in life expectancy could be valued at $38 trillion.
In a study published in Nature, the team demonstrated that anti-IL11 therapy not only counters the harmful effects of ageing but also increases lifespan by up to 25% in preclinical models. The therapy shifts metabolism from generating harmful white fat to beneficial brown fat, which helps burn calories and maintain body temperature.
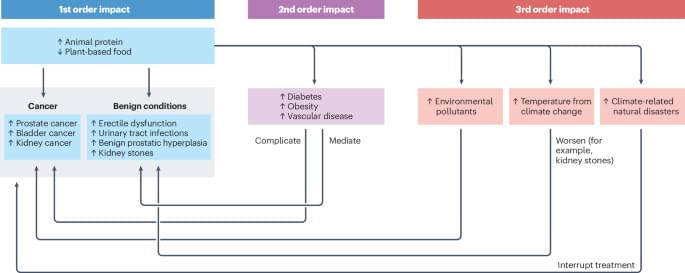
Plant-based diets and urological health
Plant-based diets have grown in popularity owing to multiple health and environmental benefits.
Here, the authors describe the evidence concerning plant-based dietary patterns and omnivorous diets with reduced consumption of animal-based food and increased consumption of plant-based foods and their associations with the most common urological cancers and benign urological conditions.

First Gut Microbiome Map for Personalized Food Responses
Summary: A recent study has mapped how molecules in food interact with gut bacteria, revealing why people respond differently to the same diets. By examining 150 dietary compounds, researchers found that these molecules can reshape gut microbiomes in some individuals, while having little effect in others.
This breakthrough could enable personalized nutrition strategies to better manage health risks. The findings offer a deeper understanding of the gut microbiome’s role in health and disease.
Student designs pangolin robot that digs, drops seed for farming
A student built a pangolin-inspired robot for planting, winning the University of Surrey’s robotics contest.
A California student created Plantolin, a pangolin-inspired robot for digging and planting, winning the University of Surrey’s contest.