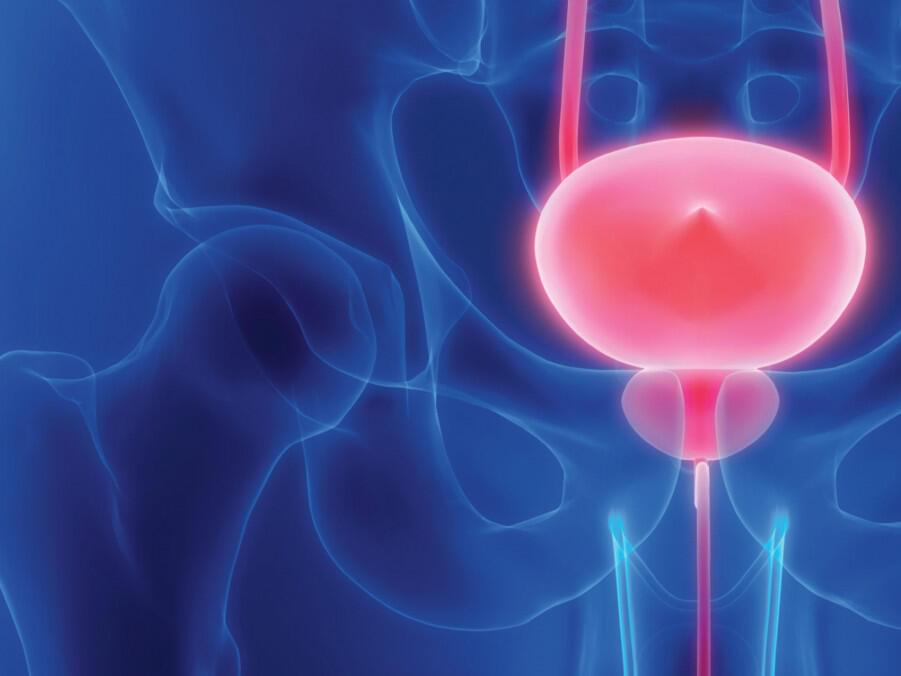
Results from a large clinical trial show that treatment with an immunotherapy drug may nearly double the length of time people with high-risk, muscle-invasive bladder cancer are cancer-free following surgical removal of the bladder. Researchers found that postsurgical treatment with pembrolizumab (Keytruda), which is approved by the Food and Drug…