Interesting find on hippocampus and ingestive control.
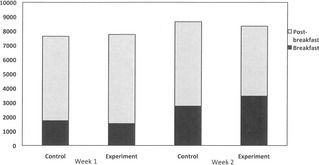
In animals, a Western style diet–high in saturated fat and added sugar–causes impairments in hippocampal-dependent learning and memory (HDLM) and perception of internal bodily state (interoception). In humans, while there is correlational support for a link between Western-style diet, HDLM, and interoception, there is as yet no causal data. Here, healthy individuals were randomly assigned to consume either a breakfast high in saturated fat and added sugar (Experimental condition) or a healthier breakfast (Control condition), over four consecutive days. Tests of HDLM, interoception and biological measures were administered before and after breakfast on the days one and four, and participants completed food diaries before and during the study. At the end of the study, the Experimental condition showed significant reductions in HDLM and reduced interoceptive sensitivity to hunger and fullness, relative to the Control condition. The Experimental condition also showed a markedly different blood glucose and triglyceride responses to their breakfast, relative to Controls, with larger changes in blood glucose across breakfast being associated with greater reductions in HDLM. The Experimental condition compensated for their energy-dense breakfast by reducing carbohydrate intake, while saturated fat intake remained consistently higher than Controls. This is the first experimental study in humans to demonstrate that a Western-style diet impacts HDLM following a relatively short exposure–just as in animals. The link between diet-induced HDLM changes and blood glucose suggests one pathway by which diet impacts HDLM in humans.
Citation: Attuquayefio T, Stevenson RJ, Oaten MJ, Francis HM (2017) PLoS ONE 12: e0172645. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0172645
Editor: Lin Lu, Peking University, CHINA