Now you can grill up the meat alternative at home.



On Tuesday afternoon, NASA announced 19 new partnerships with 10 US companies to help bring more cutting-edge technologies closer to production use in spaceflight. There were a lot of useful engineering ideas here, such as precision landing systems and robotic plant farms, but perhaps the most intriguing one involved the rocket company SpaceX and two of NASA’s field centers—the Glenn Research Center in Ohio and the Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama.
“SpaceX will work with Glenn and Marshall to advance technology needed to transfer propellant in orbit, an important step in the development of the company’s Starship space vehicle,” the NASA news release states. This is a significant announcement for reasons both technical and political.
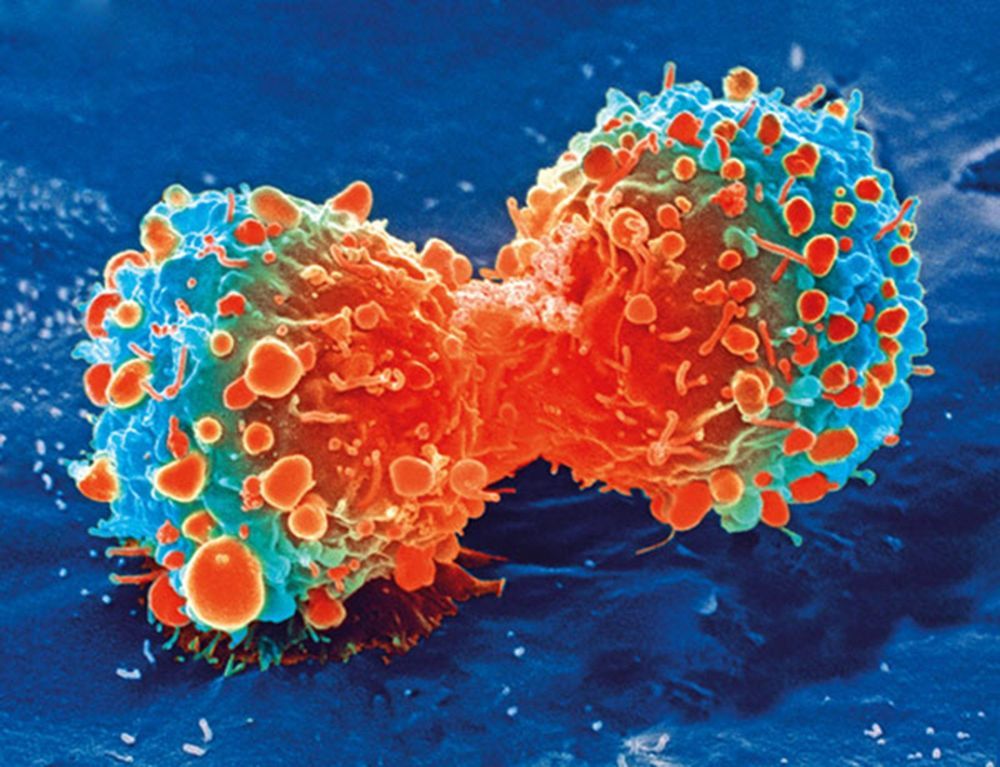
Researchers at the Stanford University School of Medicine have discovered a new signal that cancers seem to use to evade detection and destruction by the immune system.
The scientists have shown that blocking this signal in mice implanted with human cancers allows immune cells to attack the cancers. Blocking other “don’t eat me” signals has become the basis for other possible anti–cancer therapies.
Normally, immune cells called macrophages will detect cancer cells, then engulf and devour them. In recent years, researchers have discovered that proteins on the cell surface can tell macrophages not to eat and destroy them. This can be useful to help normal cells keep the immune system from attacking them, but cancer cells use these “don’t eat me” signals to hide from the immune system.

The next time you shop for cherry tomatoes at Whole Foods or another retailer, you may end up buying some grown in an indoor, controlled environment outfitted with the latest robotic technology. Ohio will get the first fully automated indoor farm in the United States. 80 Acres Farms plans to build one in Hamilton, a suburb of Cincinnati, by the end of the year. The farm will have grow centers for greens, such as herbs and kale, and will supply produce to multiple retailers and distributors.
80 Acres Farms plans to construct the fully automated indoor farm in three phases. When it finishes, the farm will be 150,000 square feet of controlled environmental agriculture (CEA). Mike Zelkind, cofounder and chief executive officer of 80 Acres Farms, explains that the company uses “renewable energy, very little water and no pesticides.” The Hamilton farm will produce leafy greens, microgreens, kale and herbs for retailers such as Whole Foods Markets, Jungle Jims, Dorothy Lane Markets, U.S. Foods and others.

NASA has announced 19 technology partnerships between the agency’s many spaceflight centers and 13 companies, including SpaceX, Blue Origin, and more. This round of Space Act Agreements (SAAs) shows a heavy focus on technologies and concepts that could benefit exploration of the Moon and deep space more generally, including lunar landers, food production, reusable rockets, and more.
Put simply, all 19 awards are great and will hopefully result in tangible products and benefits, but SpaceX has a track record of achievement on the cutting edge of aerospace that simply has not been touched over the last decade. As such, the company’s two SAAs are some of the most interesting and telling, both ultimately focused on enabling Starship launches to and landings on the Moon and any number of other destinations in the solar system. Perhaps most importantly, it signals a small but growing sect within NASA that is willing and eager to acknowledge Starship’s existence and actively work with SpaceX to both bring it to life and further spaceflight technology in general.
One agreement focuses specifically on “vertically land[ing] large rockets on the Moon”, while the other more generally seeks to “advance technology needed to transfer propellant in orbit”, a feature that Starship’s utility would be crippled without. In this particular round of SAAs, they will be “non-reimbursable” – bureaucratic-speak for a collaboration where both sides pay their own way and no money is exchanged. SpaceX’s wins ultimately show that, although NASA proper all but refuses to acknowledge Starship, the many internal centers it is nothing without are increasingly happy to extend olive branches towards the company and its ambitious next-generation rocket.


An international team of researchers has found that the gut microbiota in mice play an influential role in skeletal muscle mass maintenance and function. In their paper published in the journal Science Translational Medicine, the group describes their experiments with wild and lab-raised mice, and what they found.
Over the past several years, scientists have found that gut microbiota in humans and other animals play a far bigger role in maintaining health than previously thought. In addition to processing food, the gut microbiome plays an important role in immunity and in regulating cholesterol and triglycerides. And imbalances in the gut microbiota have been associated with conditions such as Crohn’s disease, IBS and other inflammatory diseases. Now, the researchers with this new effort have found evidence that suggests the gut microbiome also plays a role in maintaining the right amount of skeletal muscle mass and its function—at least in mice.
Skeletal muscle is one of the three main types of muscle—the other two are cardiac and smooth. Skeletal muscle is very much what it sounds like—the collection of muscles that are connected to bones in the skeleton that control movement, most specifically, the limbs.

This innovation drive, including increasing use of automation on farms like Dijkstra’s, has helped propel a country with a land mass smaller than the state of West Virginia to become the world’s second-biggest food exporter after the U.S., with agri-food exports worth more than $100 billion.
And it’s dairy, and fruit and vegetables ― where technologies like milking and harvesting robots are becoming commonplace in the Netherlands ― that account for the biggest share of that export revenue.
“Automation has been part of that success story,” said Erik Nicholson of the United Farm Workers of America. The Netherlands “is seen as a world leader because of the innovation going on there and the output it manages despite its comparatively small size.”
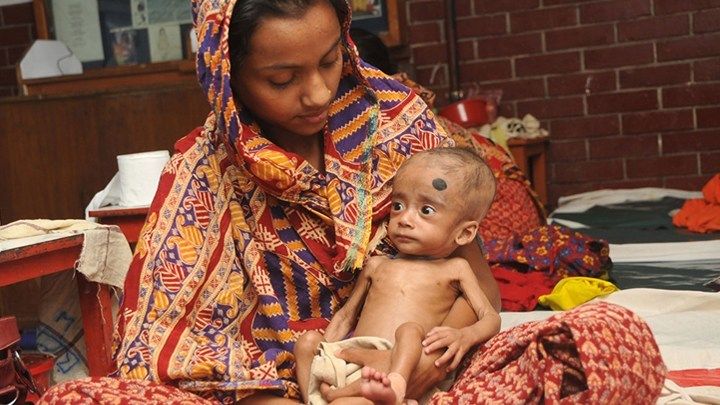

A few years ago, researchers discovered that abnormalities in microbial communities, or microbiomes, in the intestine appear to contribute to childhood malnutrition. Now comes word that this discovery is being translated into action, with a new study showing that foods formulated to repair the “gut microbiome” may help malnourished kids rebuild their health [1].
In a month-long clinical trial in Bangladesh, 63 children received either regular foods to treat malnutrition or alternative formulations for needed calories and nutrition that also encouraged growth of beneficial microbes in the intestines. The kids who ate the microbiome-friendly diets showed improvements in their microbiome, which helps to extract and metabolize nutrients in our food to help the body grow. They also had significant improvements in key blood proteins associated with bone growth, brain development, immunity, and metabolism; those who ate standard therapeutic food did not experience the same benefit.
Globally, malnutrition affects an estimated 238 million children under the age 5, stunting their normal growth, compromising their health, and limiting their mental development [2]. Malnutrition can arise not only from a shortage of food but from dietary imbalances that don’t satisfy the body’s need for essential nutrients. Far too often, especially in impoverished areas, the condition can turn extremely severe and deadly. And the long term effects on intellectual development can limit the ability of a country’s citizens to lift themselves out of poverty.
