Jeff Falk Rice University 713−348−6775 [email protected]
Jade Boyd Rice University 713−348−6778 [email protected]
Erin Hare University of Pittsburgh 412−864−7194 [email protected]
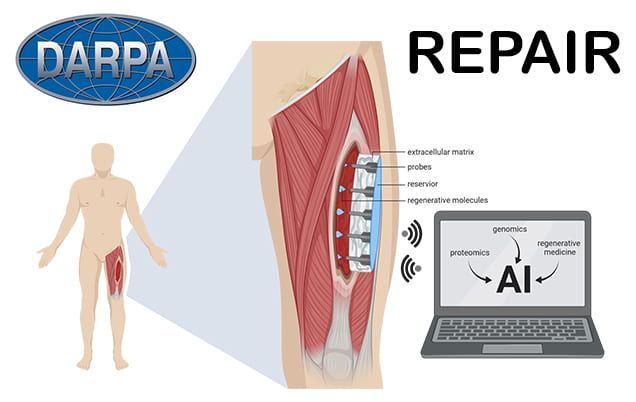
Jeff Falk Rice University 713−348−6775 [email protected]
Jade Boyd Rice University 713−348−6778 [email protected]
Erin Hare University of Pittsburgh 412−864−7194 [email protected]

The House is preparing to vote on Thursday on a coronavirus-relief bill that would provide Americans with paid sick leave, food assistance, free coronavirus testing, and more substantial unemployment benefits.
But Ocasio-Cortez pushed for a more sweeping response, including expanding Medicare or Medicaid to cover all Americans, a freeze on evictions, a universal basic income, ending work requirements for food-assistance programs, criminal-justice reform, and freezing student-debt collection.
“This is not the time for half measures,” she tweeted on Thursday. “We need to take dramatic action now to stave off the worst public health & economic affects. That includes making moves on paid leave, debt relief, waiving work req’s, guaranteeing healthcare, UBI, detention relief (pretrial, elderly, imm).”
“In the case of the Industrial Revolution, people’s lives didn’t improve for seven decades,” Frey says. “That’s two generations. I think we need to be very concerned about some of these short-term effects on people.”
Frey says for seven decades wages were stagnant, food consumption decreased and “people’s living standards deteriorated.” The economy was doing quite well, but most of the workers weren’t seeing the benefits of that economy.
“Because people’s living standards deteriorated, people rioted against mechanized factories. The Luddites are often portrayed as these irrational enemies of progress, and to some extent, that’s right if you take a very long term view,””
The case against the flawed argument that automation won’t be so bad.
40% of the world’s insect species are in decline, and scientists believe that a third are threatened with extinction. From pesticides to invasive species, there are various reasons, but any losses could have a major impact on our food systems.

In a new publication in Nature Plants, assistant professor of Plant Science at the University of Maryland Yiping Qi has established a new CRISPR genome engineering system as viable in plants for the first time: CRISPR-Cas12b. CRISPR is often thought of as molecular scissors used for precision breeding to cut DNA so that a certain trait can be removed, replaced, or edited. Most people who know CRISPR are likely thinking of CRISPR-Cas9, the system that started it all. But Qi and his lab are constantly exploring new CRISPR tools that are more effective, efficient, and sophisticated for a variety of applications in crops that can help curb diseases, pests, and the effects of a changing climate. With CRISPR-Cas12b, Qi is presenting a system in plants that is versatile, customizable, and ultimately provides effective gene editing, activation, and repression all in one system.
“This is the first demonstration of this new CRISPR-Cas12b system for plant genome engineering, and we are excited to be able to fill in gaps and improve systems like this through new technology,” says Qi. “We wanted to develop a full package of tools for this system to show how useful it can be, so we focused not only on editing, but on developing gene repression and activation methods.”
It is this complete suite of methods that has ultimately been missing in other CRISPR systems in plants. The two major systems available before this paper in plants were CRISPR-Cas9 and CRISPR-Cas12a. CRISPR-Cas9 is popular for its simplicity and for recognizing very short DNA sequences to make its cuts in the genome, whereas CRISPR-Cas12a recognizes a different DNA targeting sequence and allows for larger staggered cuts in the DNA with additional complexity to customize the system. CRISPR-Cas12b is more similar to CRISPR-Cas12a as the names suggest, but there was never a strong ability to provide gene activation in plants with this system. CRISPR-Cas12b provides greater efficiency for gene activation and the potential for broader targeting sites for gene repression, making it useful in cases where genetic expression of a trait needs to be turned on/up (activation) or off/down (repression).

HONG KONG — Pet cats and dogs cannot pass the new coronavirus on to humans, but they can test positive for low levels of the pathogen if they catch it from their owners.
That’s the conclusion of Hong Kong’s Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation Department after a dog in quarantine tested weakly positive for the virus Feb. 27, Feb. 28 and March 2, using the canine’s nasal and oral cavity samples.
A unidentified spokesman for the department was quoted in a news release as saying. “There is currently no evidence that pet animals can be a source of infection of COVID-19 or that they become sick.”
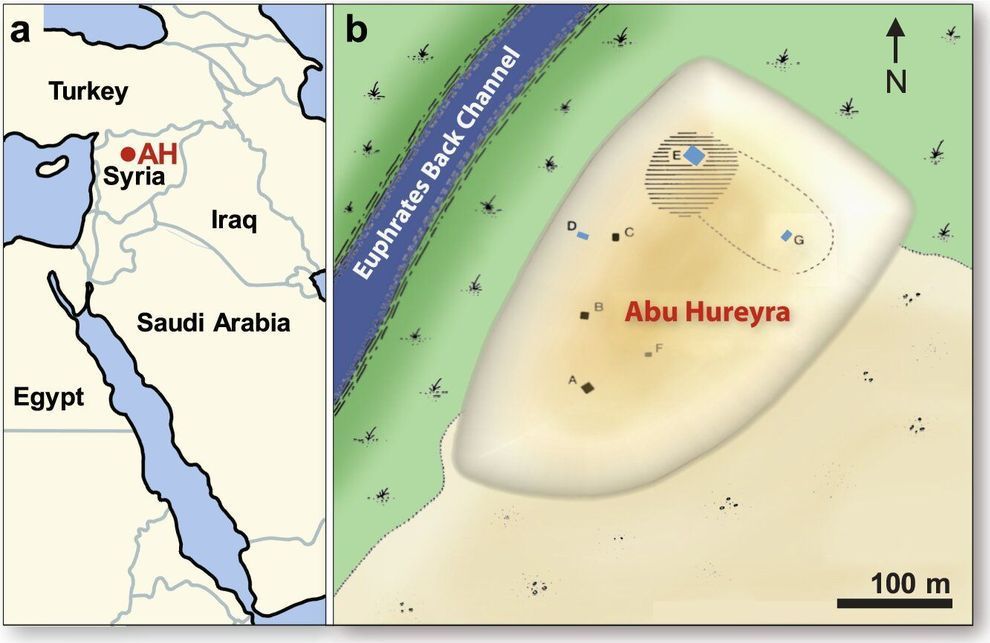
Before the Taqba Dam impounded the Euphrates River in northern Syria in the 1970s, an archaeological site named Abu Hureyra bore witness to the moment ancient nomadic people first settled down and started cultivating crops. A large mound marks the settlement, which now lies under Lake Assad.
But before the lake formed, archaeologists were able to carefully extract and describe much material, including parts of houses, food and tools—an abundance of evidence that allowed them to identify the transition to agriculture nearly 12,800 years ago. It was one of the most significant events in our Earth’s cultural and environmental history.
Abu Hureyra, it turns out, has another story to tell. Found among the cereals and grains and splashed on early building material and animal bones was meltglass, some features of which suggest it was formed at extremely high temperatures—far higher than what humans could achieve at the time—or that could be attributed to fire, lighting or volcanism.
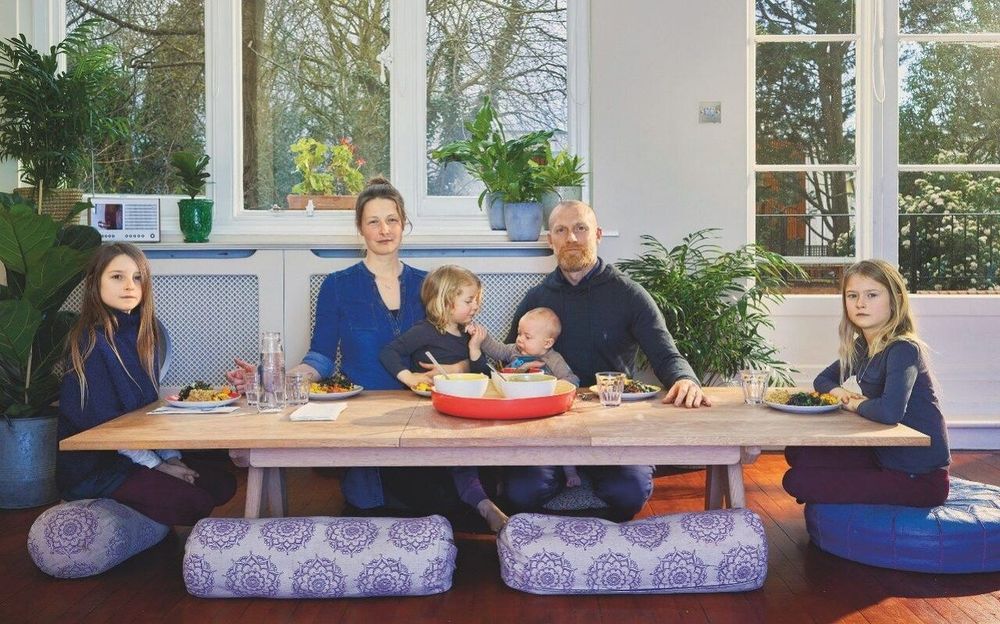


It’s 5pm in the Farrant household and Jack, six, and Thomas, four, are currently manifesting their desires in the form of Lego. To an outsider this looks like two small children playing with toys, but their mother Catherine proudly points out that Jack has built a yacht – something he is helping his family to acquire via visualisation exercises.
‘Dinner’s ready,’ calls out the nanny. In line with the family’s Paleo diet – of anti-inflammatory, natural foods – they have octopus cooked with lemongrass, and fish-bone broth. ‘Yes, my favourite,’ cries Jack happily, while his mum explains exactly what the broth is: ‘It’s an age-old elixir that’s made from boiling wild bones. It’s very high in iodine, which most of us are deficient in.’
After dinner, the children can continue to express their creativity, or watch some television – though if they’re going to do the latter after 6pm they need to put on their ‘blue-light blockers’, glasses with amber lenses to block the blue light of technology from affecting their sleep. ‘We also do red-light therapy,’ explains Catherine, pointing to a red dinosaur lamp in the boys’ bedroom. ‘It’s to help the body’s natural rhythms of sunset with exposure to red colours at night, and blue and white light in the morning.’