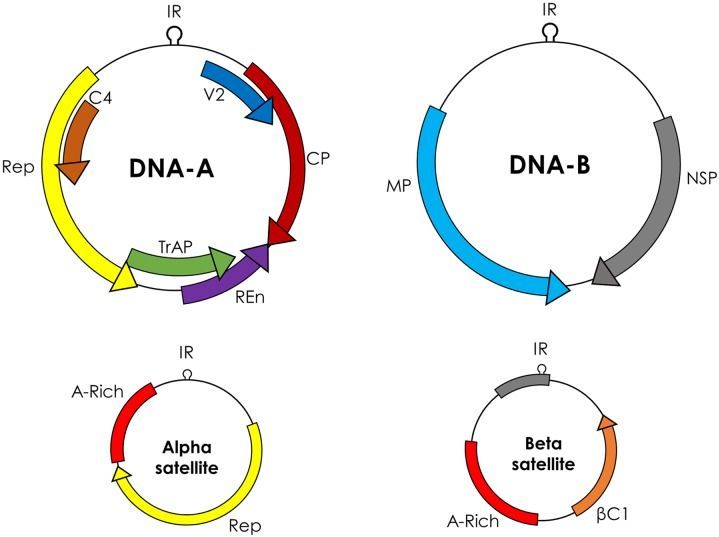
Plant viruses infect many economically important crops, including wheat, cotton, maize, cassava, and other vegetables. These viruses pose a serious threat to agriculture worldwide, as decreases in cropland area per capita may cause production to fall short of that required to feed the increasing world population. Under these circumstances, conventional strategies can fail to control rapidly evolving and emerging plant viruses. Genome-engineering strategies have recently emerged as promising tools to introduce desirable traits in many eukaryotic species, including plants. Among these genome engineering technologies, the CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced palindromic repeats)/CRISPR-associated 9 (CRISPR/Cas9) system has received special interest because of its simplicity, efficiency, and reproducibility. Recent studies have used CRISPR/Cas9 to engineer virus resistance in plants, either by directly targeting and cleaving the viral genome, or by modifying the host plant genome to introduce viral immunity. Here, we briefly describe the biology of the CRISPR/Cas9 system and plant viruses, and how different genome engineering technologies have been used to target these viruses. We further describe the main findings from recent studies of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated viral interference and discuss how these findings can be applied to improve global agriculture. We conclude by pinpointing the gaps in our knowledge and the outstanding questions regarding CRISPR/Cas9-mediated viral immunity.
Keywords: plant virus, CRISPR/Cas9, genome engineering, geminivirus, virus resistance.
In the context of the rapidly growing global population, food security has emerged as one of the major challenges facing our generation (Cheeseman, 2016). The global population has increased by 60%, but per capita production of grains has fallen worldwide in the last 20 years (Suweis et al., 2015). If the population growth rate, which is 1.13 percent per year for 20161 persists, the world population will double again within a mere 50 years, and it is estimated that food production will need to at least double till 2050 to meet demand (Suweis et al., 2015). Increases in food production per unit of land have not kept pace with increases in population and cropland area per capita has fallen by more than half since 1960 (Cheeseman, 2016).