The top 10 emerging technologies include self-fertilizing crops, on-demand drug manufacturing, breath-sensing diagnostics and 3D-printed houses. Check the full list of emerging tech.
Category: food – Page 175
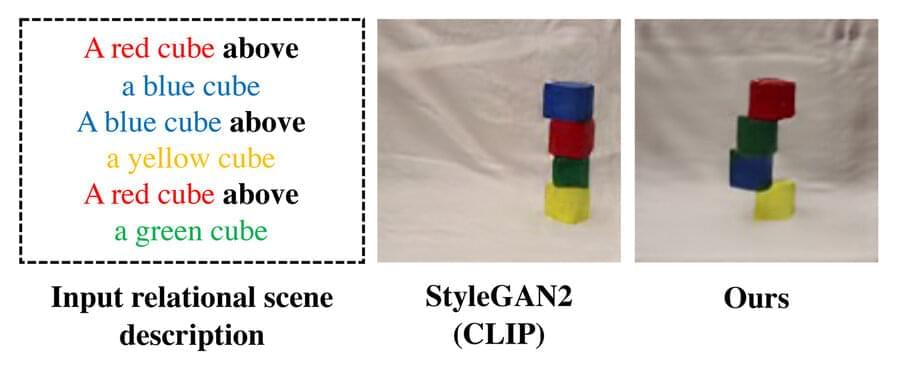
Artificial intelligence that understands object relationships
When humans look at a scene, they see objects and the relationships between them. On top of your desk, there might be a laptop that is sitting to the left of a phone, which is in front of a computer monitor.
Many deep learning models struggle to see the world this way because they don’t understand the entangled relationships between individual objects. Without knowledge of these relationships, a robot designed to help someone in a kitchen would have difficulty following a command like “pick up the spatula that is to the left of the stove and place it on top of the cutting board.”
In an effort to solve this problem, MIT researchers have developed a model that understands the underlying relationships between objects in a scene. Their model represents individual relationships one at a time, then combines these representations to describe the overall scene. This enables the model to generate more accurate images from text descriptions, even when the scene includes several objects that are arranged in different relationships with one another.

Bed Bath & Beyond
Just to show that AI is not about to take over in the near future, due to the high inflation in the US, I decided to shop around and buy a ton of mouthwash from https://bedbathandbeyond.com. (I got BreathRX which I recommend.) They sold me a bunch at half the average price I found on the internet, and I looked forward to getting a big box of it. (Or maybe two or three boxes.)
To my great surprise they decided to send me lots of little packages of 1 to 3 bottles from all over the country. In many cases, they would send me a box big enough to hold 12 bottles, put 1 bottle in it, wrap the bottle for safety, and then add air bubble packaging plus air bag packages. They must have lost a fortune on this order!
Shop online or in-store at Bed Bath & Beyond for the best bedding, bathroom, kitchen, and home décor! Plus, create a wish list with a wedding or gift registry.
CERN’s ALICE Detector Takes the Next Step in Understanding the Interaction Between Hadrons
The ALICE collaboration has for the first time observed the residual strong interaction between protons and phi mesons. In an article recently published in Physical Review Letters, the ALICE collaboration has used a method known as femtoscopy to study the residual interaction between two-quark an.
Sustainable agriculture continues to spread at an accelerated pace and farmers need all the help they can get in order to cope with the increasing workload. California-based company Iron Ox specializes in the use of robotics and artificial intelligence in agriculture, and Grover is the latest robot to join its team.
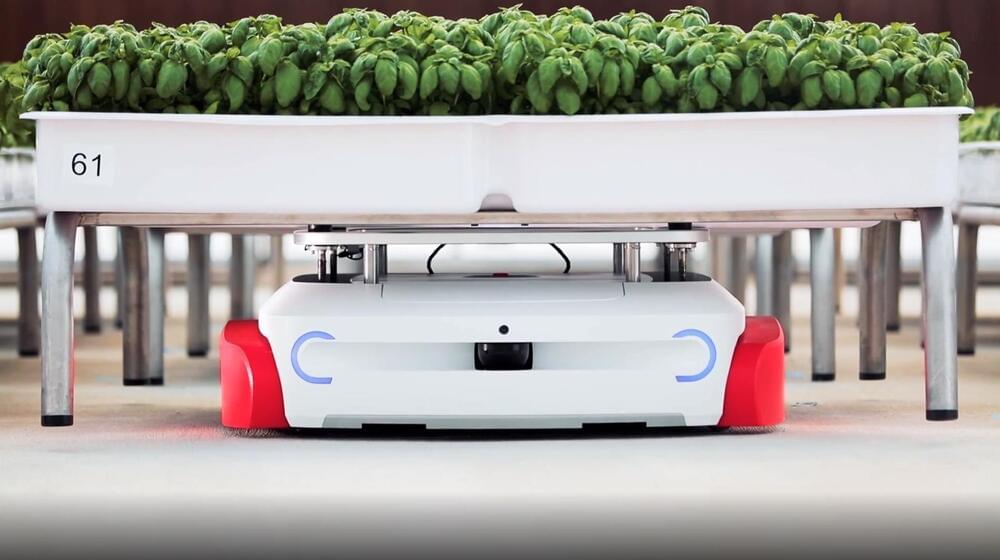

Autonomous Farming Robot Wants to Revolutionize Sustainable Agriculture, Can Lift 1,000 Lb
Sustainable agriculture continues to spread at an accelerated pace and farmers need all the help they can get in order to cope with the increasing workload. California-based company Iron Ox specializes in the use of robotics and artificial intelligence in agriculture, and Grover is the latest robot to join its team.
The Mystery Behind China’s Secret Cockroach Farms
Cockroach farming is practiced in China on a massive scale. At present, there are hundreds of cockroach farms in China, with the total number of cockroaches produced annually exceeding the global human population. The insects produced in these unique farms are mostly used in the production of cosmetics and medicines, or for animal feed.
In 2018, Chinese pharmaceutical company Gooddoctor claims that it has earned US$684 million in revenue through selling a “healing potion” made from cockroaches that is used annually by thousands of hospitals and millions of Chinese patients to treat respiratory, gastric, and other diseases.
However, the use of cockroaches in China is not just limited to the pharmaceutical and beauty industries. The protein-rich insects are also processed and fed as an organic meal to poultry farm animals, used to deal with food waste, and are often served in special recipes in some Chinese restaurants.
Spermidine Impacts Health and Longevity
Join us on Patreon!
https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Papers referenced in the video:
Polyamine-rich food decreases age-associated pathology and mortality in aged mice.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19735716/
Long-term treatment with spermidine increases health span of middle-aged Sprague-Dawley male rats.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32285289/
Cardioprotection and lifespan extension by the natural polyamine spermidine.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27841876/
Spermidine Prolongs Lifespan and Prevents Liver Fibrosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Activating MAP1S-Mediated Autophagy.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28386016/
Higher spermidine intake is linked to lower mortality: a prospective population-based study.
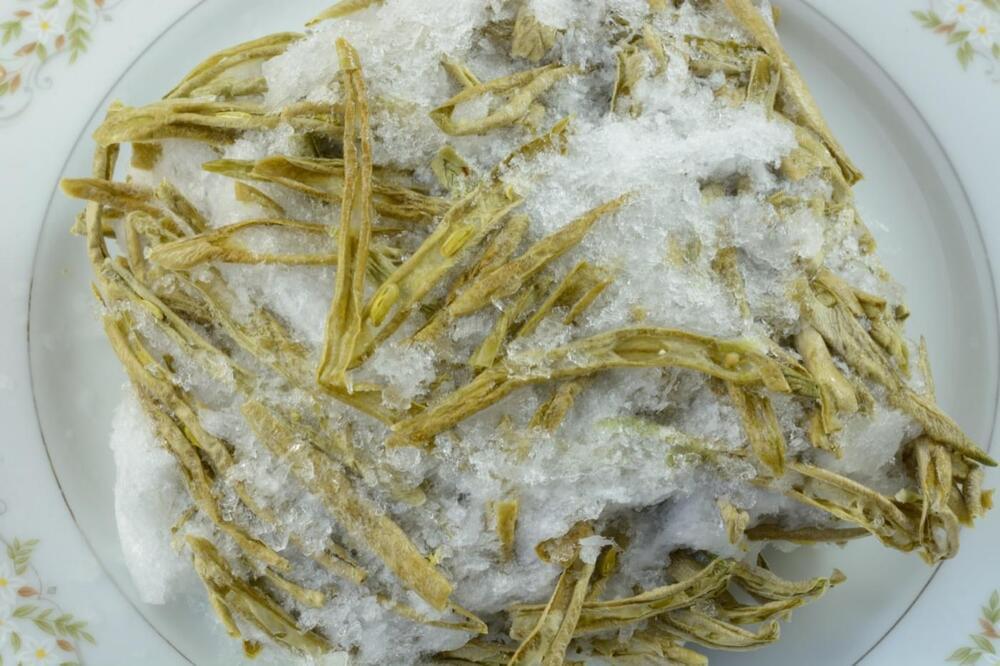

New Cold Storage Method Solves Freezer Burn —And Saves Energy
12:10 minutes.
But United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) food scientists, working with a team at the University of California-Berkeley, have a method that could help solve this problem. Normal food freezing, called isobaric, keeps food at whatever pressure the surrounding air is. But what if you change that? Isochoric freezing, the new method, adds pressure to the food while lowering temperature, so the food becomes cold enough to preserve without its moisture turning into ice. No ice means no freezer burn. And, potentially, a much lower energy footprint for the commercial food industry: up to billions fewer kilowatt-hours, according to recent research.
Researchers develop eco-friendly, reusable ice cubes that do not melt
The new jelly ice cube is not plastic and won’t melt.
SmartFarm harvests air moisture for autonomous, self-sustaining urban farming
Advanced hydrogel used in SmartFarm was also tested for space-based agriculture.