Philip Glass to release a short silence on the matter.
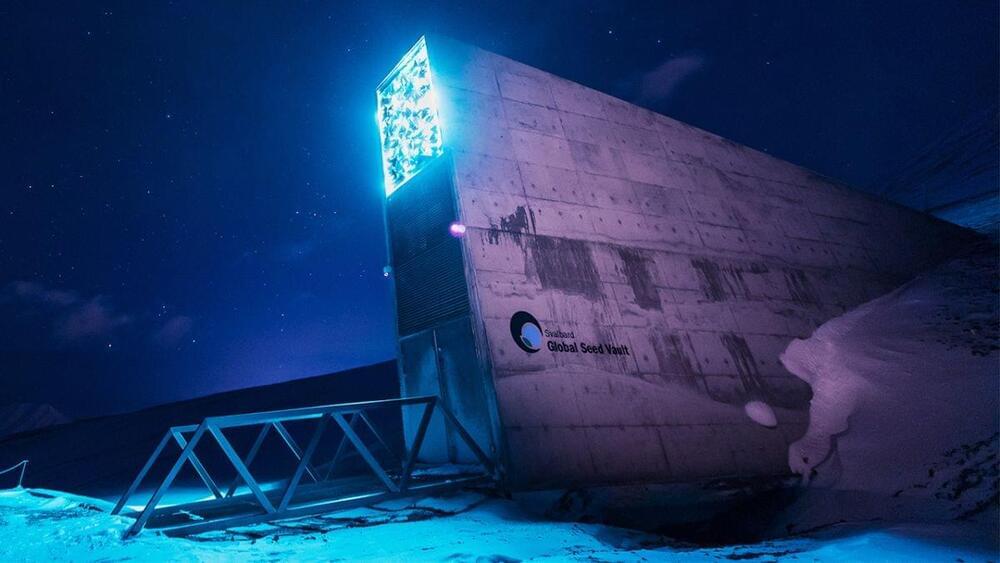
The music vault is a parallel project to the Global Seed Vault (opens in new tab), which keeps the seeds of today’s trees and plants safe for the future, just in case we need to rebuild agriculture for any reason. The vault is located on the island of Spitsbergen, Norwegian territory, within the Arctic circle. It lacks tectonic activity, is permanently frozen, is high enough above sea level to stay dry even if the polar caps melt, and even if the worst happens, it won’t thaw out fully for 200 years. Just to be on the safe side, the main vault is built 120m into a sandstone mountain, and its security systems are said to be robust. As of June 2021, the seed vault had conserved 1,081,026 different crop samples.
The music is to be stored in a dedicated vault in the same mountain used by the seed vault. The glass used is an inert material, shaped into platters 75mm (3 inches) across and 2mm (less than 1/8th of an inch) thick. A laser encodes data in the glass by creating layers of three-dimensional nanoscale gratings and deformations. Machine learning algorithms read the data back by decoding images and patterns created as polarized light shines through the glass. The silica glass platters are fully resistant to electromagnetic pulses and the most challenging of environmental conditions. It can be baked, boiled, scoured and flooded without degradation of the data written into the glass. Tests to see if it really does last many thousands of years, however, can be assumed to be ongoing.
Jurgen Willis, Vice President of Program Management at Microsoft, said, “In this proof of concept, Microsoft and Elire Group worked together to demonstrate how Project Silica can help achieve the goal of preserving and safeguarding the world’s most valuable music for posterity, on a medium that will stand the test of time, using innovative archival storage in glass.”