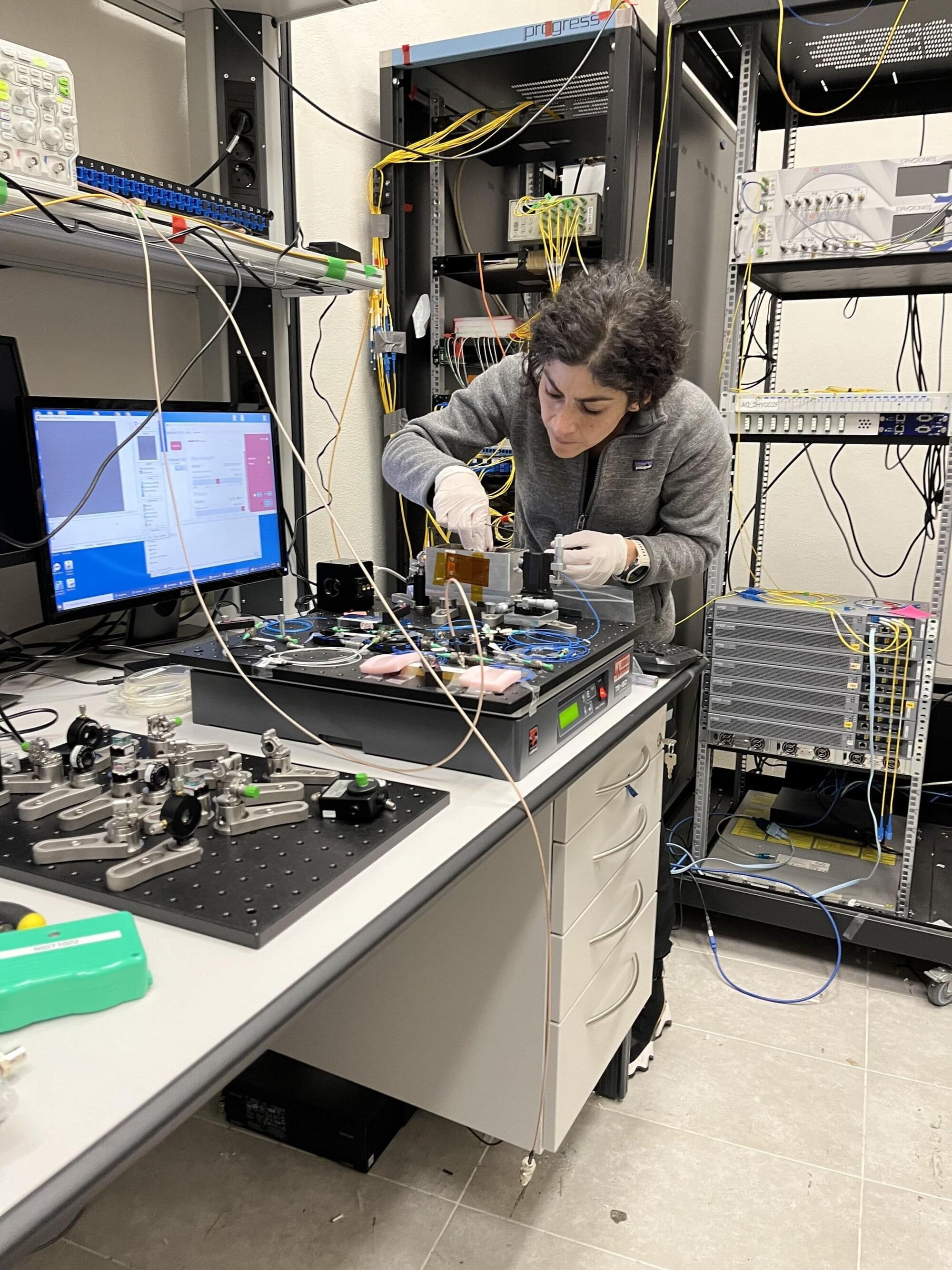
Researchers have shown, for the first time, that transmission of ultrastable optical signals from optical clocks across tens of kilometers of deployed multicore fiber is compatible with simultaneous transmission of telecommunications data.
The achievement demonstrates that these emerging high-capacity fiber optic networks could be used to connect optical clocks at various locations, enabling new scientific applications.
As global data demands continue to surge, multicore fiber is being installed to help overcome the limits of existing networks. These fibers pack multiple light-guiding cores into a single strand, greatly increasing capacity for applications like streaming, finance and artificial intelligence.