Many survivors of the attack by the Aum Shinrikyo doomsday cult still suffer from physical aftereffects and post-traumatic stress disorder.
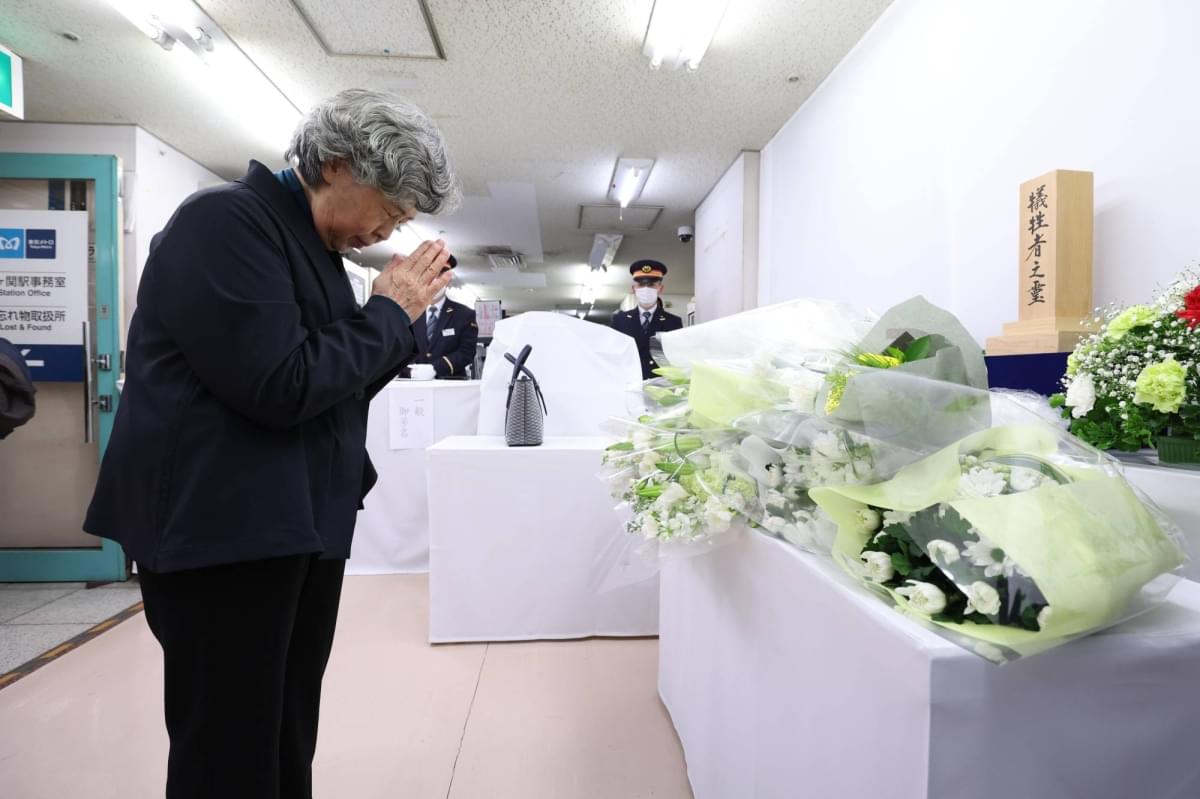


Japan on Thursday marked the 30th anniversary of the nerve gas attack on the Tokyo subway system by the AUM Shinrikyo doomsday cult, with the relatives of the victims striving to keep alive the memory of the worst terrorist attack on Japanese soil.
At Kasumigaseki Station in the Japanese capital, officials observed a moment of silence at around 8 a.m., the time when the deadly sarin nerve agent was released in train cars on March 20, 1995.
Shizue Takahashi, 78, who lost her husband, a deputy stationmaster at Kasumigaseki Station, in the attack, laid flowers at the site, and said, “It was a long 30 years. I don’t want people to forget about the incident.”
This video takes a look at how future technology could change the Fermi Paradox. Asking if humanity is looking for life in the Universe in the wrong ways, or are we looking for the wrong things. Like trying to find smoke signals, in the age of fiber optics.
While the Drake Equation estimates how many civilizations could exist in the Universe, but what is the likelihood that humanity is even capable of detecting them.
Does there need to be another calculation, say the Detection Probability Equation. Showing what’s the likelihood that humanity is able to detect alien life at a given time, and solving the Fermi Paradox.
And does this create a new paradox. Because if future technology advancements increase the number of possible cosmic civilizations, could it also decrease humanity’s ability in detecting them — leading to the detection paradox.
Other topics covered in this sci-fi documentary video include: space telescopes, dyson spheres, the movie Contact by Carl Sagan, Interstellar movie and the time dilation effects, the great silence, the great filter, and solutions and theories for the Fermi Paradox.
PATREON

The mass extinction that ended the Permian geological epoch, 252 million years ago, wiped out most animals living on Earth. Huge volcanoes erupted, releasing 100,000 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This destabilized the climate and the carbon cycle, leading to dramatic global warming, deoxygenated oceans, and mass extinction.
However, many plants survived, leaving behind fossils which scientists have used to model a dramatic 10° rise in global temperatures.
“While fossilized spores and pollen of plants from the Early Triassic do not provide strong evidence for a sudden and catastrophic biodiversity loss, both marine and terrestrial animals experienced the most severe mass extinction in Earth’s history,” explained Dr. Maura Brunetti of the University of Geneva, lead author of the article in Frontiers in Earth Science.
Please join my mailing list here 👉 https://briankeating.com/list to win a meteorite 💥
Sabine (@SabineHossenfelder) argues that superdeterminism eliminates free will, challenging the idea of causal choice and possibly undermining science if the laws of physics govern all phenomena. However, inspired by daily life experiences in Southern California, I present a defense of indeterminism, countering the claim that everything is predetermined, while also exploring the ideas of cosmologists Raphael Bousso and Alan Guth.
Sabine Hossenfelder, a theoretical physicist, has argued in favor of superdeterminism, a theory that suggests the universe is deterministic and that our choices are predetermined.
Does Superdeterminism save Quantum Mechanics? Or does it kill free will and destroy science? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytyjgIyegDI
According to her, the apparent randomness in quantum mechanics is an illusion, and the universe is actually a predetermined, clockwork-like system. She claims that if we knew enough about the initial conditions of the universe, we could predict every event, including human decisions.
Hossenfelder’s argument relies on the idea that the randomness in quantum mechanics is not fundamental, but rather a result of our lack of knowledge about the underlying variables. She suggests that if we could access these “hidden variables,” we would find that the universe is deterministic. However, this argument is flawed.
For example, consider the double-slit experiment, where particles passing through two slits create an interference pattern on a screen. Hossenfelder would argue that the particles’ behavior is predetermined, and that the apparent randomness is due to our lack of knowledge about the initial conditions. However, this ignores the fact that the act of observation itself can change the outcome of the experiment, a phenomenon known as wave function collapse.
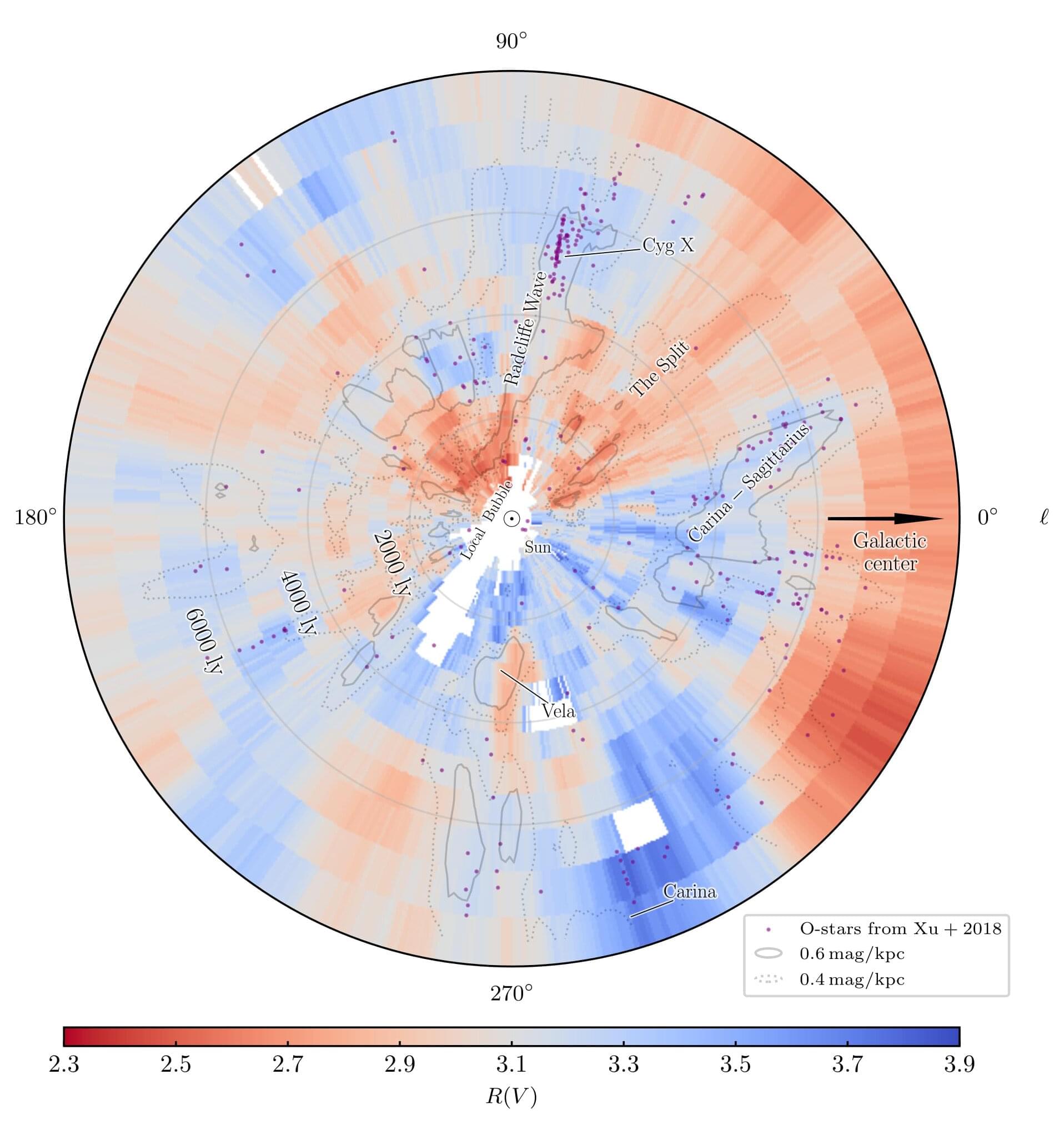
When we observe distant celestial objects, there is a possible catch: Is that star I am observing really as reddish as it appears? Or does the star merely look reddish, since its light has had to travel through a cloud of cosmic dust to reach our telescope?
For accurate observations, astronomers need to know the amount of dust between them and their distant targets. Not only does dust make objects appear reddish (“reddening”), it also makes them appear fainter than they really are (“extinction”). It’s like we are looking out into space through a dirty window. Now, two astronomers have published a 3D map that documents the properties of dust all around us in unprecedented detail, helping us make sense of what we observe.
The research is published in the journal Science.

At least two mass extinction events in Earth’s history were likely caused by the “devastating” effects of nearby supernova explosions, a new study suggests.
Researchers at Keele University say these super-powerful blasts—caused by the death of a massive star—may have previously stripped our planet’s atmosphere of its ozone, sparked acid rain and exposed life to harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
They believe a supernova explosion close to Earth could be to blame for both the late Devonian and Ordovician extinction events, which occurred 372 and 445 million years ago respectively.
Blog post with audio player, show notes, and transcript: https://www.preposterousuniverse.com/podcast/2019/06/17/epis…formation/
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/seanmcarroll.
Cosmologists have a standard set of puzzles they think about: the nature of dark matter and dark energy, whether there was a period of inflation, the evolution of structure, and so on. But there are also even deeper questions, having to do with why there is a universe at all, and why the early universe had low entropy, that most working cosmologists don’t address. Today’s guest, Anthony Aguirre, is an exception. We talk about these deep issues, and how tackling them might lead to a very different way of thinking about our universe. At the end there’s an entertaining detour into AI and existential risk.
Anthony Aguirre received his Ph.D. in Astronomy from Harvard University. He is currently associate professor of physics at the University of California, Santa Cruz, where his research involves cosmology, inflation, and fundamental questions in physics. His new book, Cosmological Koans, is an exploration of the principles of contemporary cosmology illustrated with short stories in the style of Zen Buddhism. He is the co-founder of the Foundational Questions Institute, the Future of Life Institute, and the prediction platform Metaculus.
In 1989, political scientist Francis Fukuyama predicted we were approaching the end of history. He meant that similar liberal democratic values were taking hold in societies around the world. How wrong could he have been? Democracy today is clearly on the decline. Despots and autocrats are on the rise.
You might, however, be thinking Fukuyama was right all along. But in a different way. Perhaps we really are approaching the end of history. As in, game over humanity.
Now there are many ways it could all end. A global pandemic. A giant meteor (something perhaps the dinosaurs would appreciate). Climate catastrophe. But one end that is increasingly talked about is artificial intelligence (AI). This is one of those potential disasters that, like climate change, appears to have slowly crept up on us but, many people now fear, might soon take us down.
John Smart has taught and written for over 20 years on topics like foresight and futurism as well as the drivers, opportunities, and problems of exponential processes throughout human history. John is President of the Acceleration Studies Foundation, co-Founder of the Evo-Devo research community, and CEO of Foresight University. Most recently, Smart is the author of Introduction to Foresight, which in my view is a “one-of-a-kind all-in-one instruction manual, methodological encyclopedia, and daily work bible for both amateur and professional futurists or foresighters.”
During our 2-hour conversation with John Smart, we cover a variety of interesting topics such as the biggest tech changes since our 1st interview; machine vs human sentience; China’s totalitarianism and our new geostrategic global realignment; Citizen’s Diplomacy, propaganda, and the Russo-Ukrainian War; foresight, futurism and grappling with uncertainty; John’s Introduction to Foresight; Alvin Toffler’s 3P model aka the Evo-Devo Classic Foresight Pyramid; why the future is both predicted and created despite our anti-prediction and freedom bias; Moore’s Law and Accelerating Change; densification and dematerialization; definition and timeline to general AI; evolutionary vs developmental dynamics; autopoiesis and practopoiesis; existential threats and whether we live in a child-proof universe; the Transcension Hypothesis.
My favorite quote that I will take away from this interview with John Smart is: