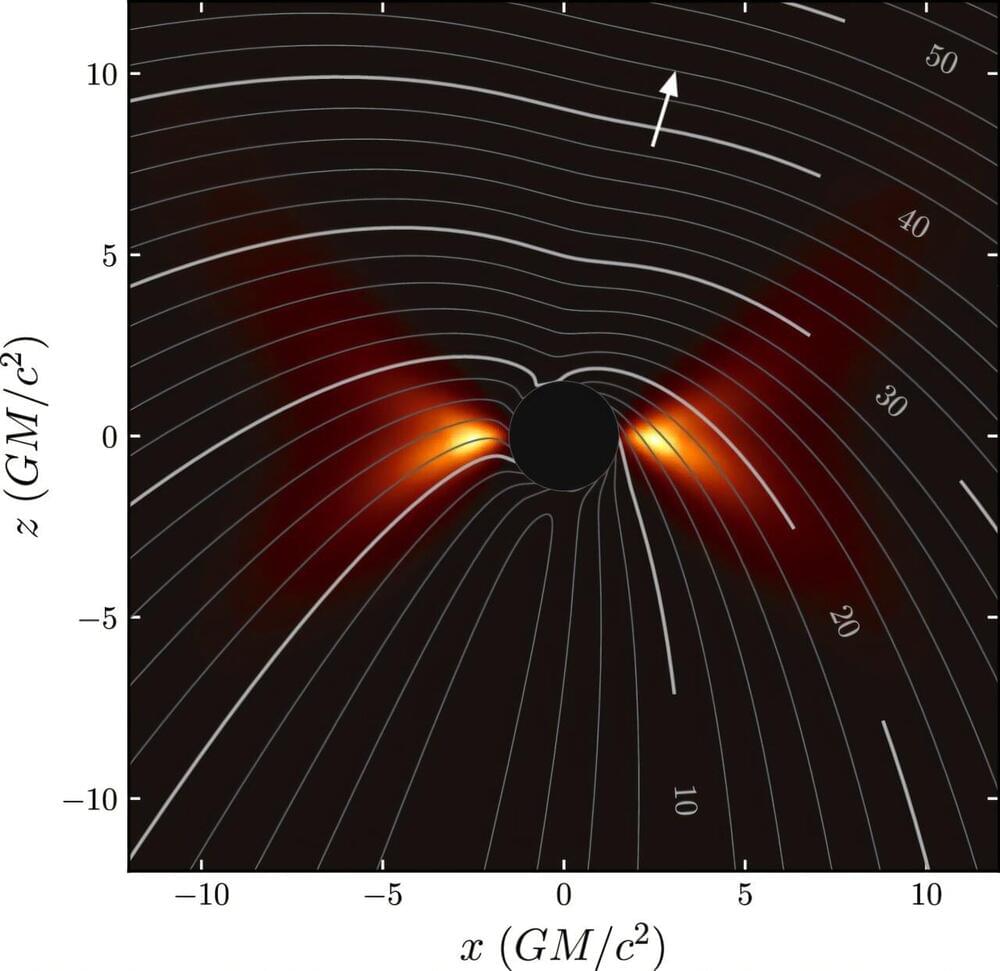
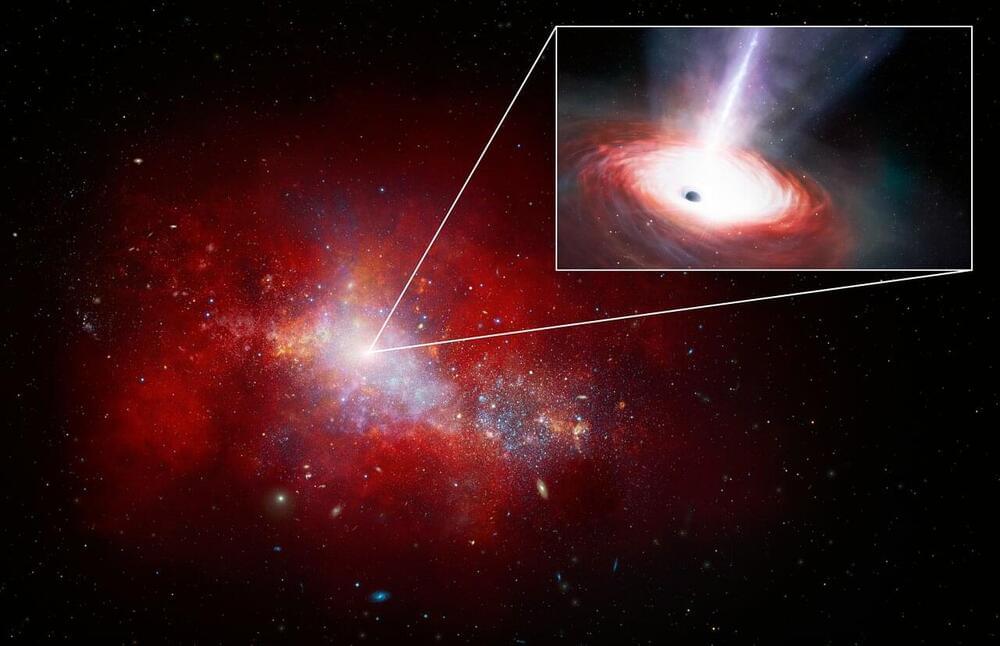
What is the origin of fast radio bursts (FRBs) and what can this teach us about the galaxies where they reside? This is what a recent study published in Nature hopes to address as a team of researchers investigated how FRB signals that originate from magnetars could reside in galaxies outside the Milky Way with the goal of better understanding the processes responsible for producing FRBs, and specifically the galaxies they inhabit. Since FRBs and magnetars remain some of the most mysterious objects in the universe, this study holds the potential to help researchers gain greater insight into not only their formation and evolution, but also how this bodes for finding life beyond Earth.
“The immense power output of magnetars makes them some of the most fascinating and extreme objects in the universe,” said Kritti Sharma, who is a PhD Candidate at Caltech and lead author of the study. “Very little is known about what causes the formation of magnetars upon the death of massive stars. Our work helps to answer this question.”
For the study, the researchers used the Deep Synoptic Array (DSA-110) to analyze 30 galaxies where FRBs have been confirmed to exist with the goal of ascertaining comparing the properties of each galaxy to the FRBs they produce. While researchers have long hypothesized that FRBs are produced in galaxies of all sizes that are actively forming stars, the researchers discovered a higher number of FRBs were produced in larger galaxies as opposed to smaller galaxies. They concluded that this was likely due to larger galaxies being more metal-rich, also known as metallicity, whereas smaller galaxies tend to have smaller metallicities.