Circa 2018
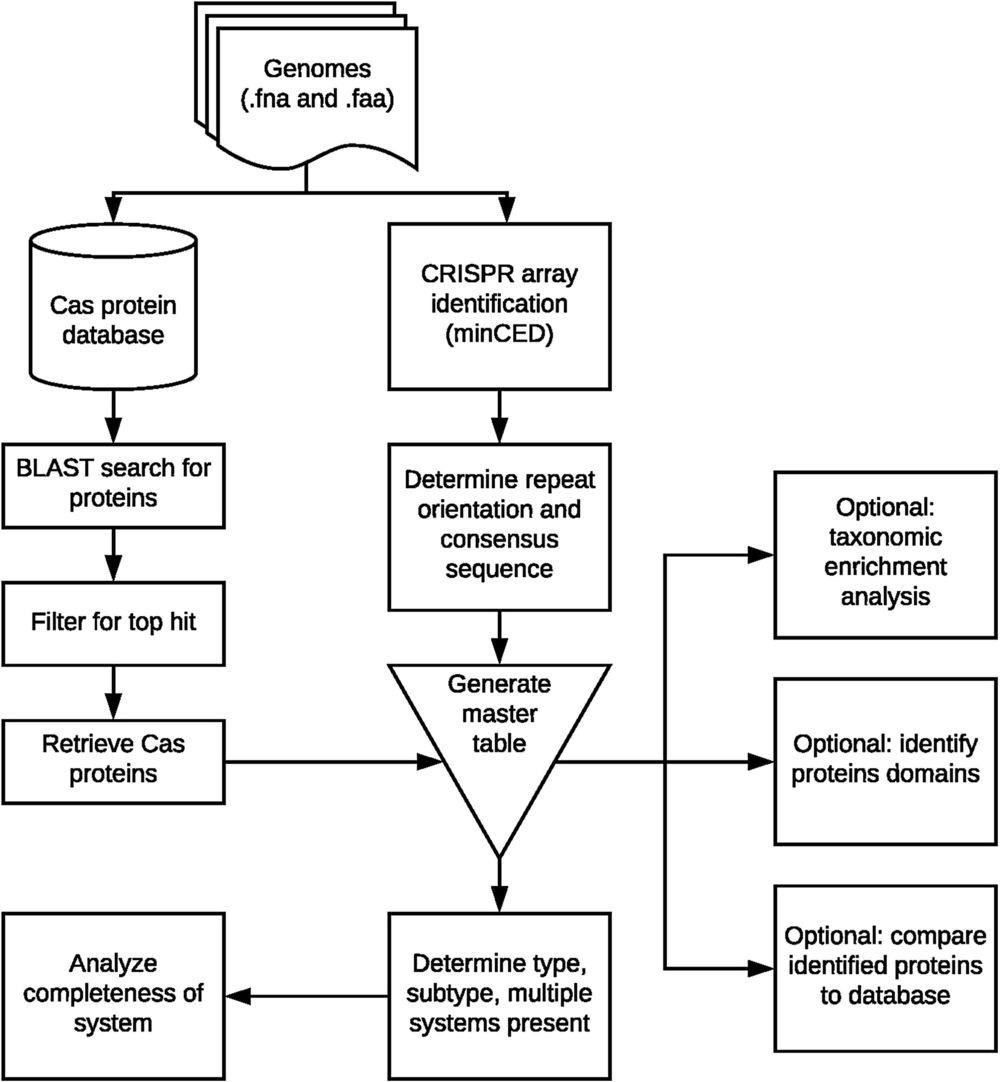
CRISPR-Cas adaptive immune systems of bacteria and archaea have catapulted into the scientific spotlight as genome editing tools. To aid researchers in the field, we have developed an automated pipeline, named CRISPRdisco (CRISPR discovery), to identify CRISPR repeats and cas genes in genome assemblies, determine type and subtype, and describe system completeness. All six major types and 23 currently recognized subtypes and novel putative V-U types are detected. Here, we use the pipeline to identify and classify putative CRISPR-Cas systems in 2,777 complete genomes from the NCBI RefSeq database. This allows comparison to previous publications and investigation of the occurrence and size of CRISPR-Cas systems. Software available at http://github.com/crisprlab/CRISPRdisco provides reproducible, standardized, accessible, transparent, and high-throughput analysis methods available to all researchers in and beyond the CRISPR-Cas research community. This tool opens new avenues to enable classification within a complex nomenclature and provides analytical methods in a field that has evolved rapidly.
CRISPR-Cas* bacterial and archaeal immune systems remain of high interest across many domains of the life sciences, including food science, molecular biology, prokaryotic evolution, and as a technology from pharma to next-generation crops.1–4 The unifying interest in CRISPR is the tremendous wealth of applications this technology affords. While application and tool development using a handful of characterized CRISPR-Cas systems has exploded, the annotation and discovery of systems remains an ongoing challenge for microbiologists and bioinformaticians to solve. The ability to identify CRISPR-Cas systems can benefit the greater scientific community, from microbiologists attempting to learn about adaptive immunity in prokaryotes, to molecular biologists interested in harnessing the nucleic acid-targeting functions of various Cas proteins.