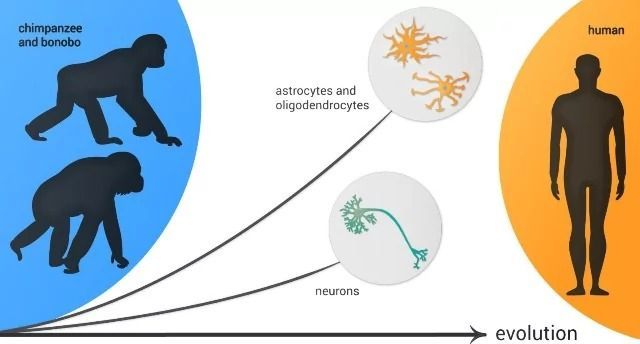
Oligodendrocytes and astrocytes displayed more differences in the human evolutionary lineage than neurons as compared to similar cells in other primates. Credit: Pavel Odinev/ Skoltech.

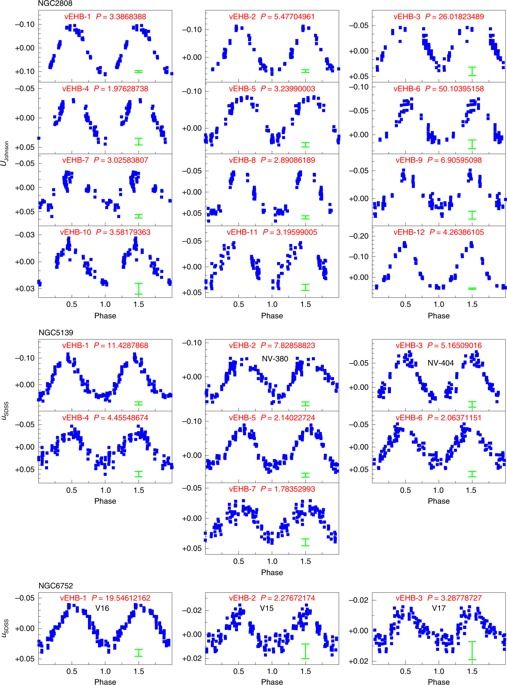
For more than six decades, the quest to understand the formation of hot (about 20,000−30,000 K) extreme horizontal branch (EHB) stars in Galactic globular clusters has remained one of the most elusive in stellar evolutionary theory. Here we report on two discoveries that challenge the idea of the stable luminosity of EHB stars. The first mode of EHB variability is periodic and cannot be ascribed to either binary evolution or pulsation. Instead, we attribute it here to the presence of magnetic spots: superficial chemical inhomogeneities whose projected rotation induces the variability. The second mode of EHB variability is aperiodic and manifests itself on timescales of years. In two cases, six-year-long light curves display superflare events that are several million times more energetic than solar analogues. We advocate a scenario in which the two EHB variability phenomena are different manifestations of diffuse, dynamo-generated, weak magnetic fields. Magnetism is therefore a key player driving the formation and evolution of EHB clusters stars and, likewise, operating in the Galactic field counterparts. Our conclusions bridge similar variability/magnetism phenomena in all radiative-enveloped hot-stars: young main-sequence stars, old EHBs and defunct white dwarfs.
How do we know what to do in life? How do we know where to go, where to start, where we are, what it’s all made of, why it matters? Why don’t we know? Can we know? Why am I alive? What is alive? Why is this place here? What is going on?
In his collection of papers and notes posthumously published as a book in 1969, titled On Certainty, Ludwig Wittgenstein writes, “How does someone judge which is his right and which his left hand?” We are certain that we know, but we really don’t know the answer. “At the foundation of well-founded belief lies belief that is not founded.” He serendipitously illustrated his point from beyond the grave when he wrote: “‘But is there then no objective truth? Isn’t it true, or false, that someone has been on the moon?’ If we are thinking within our system, then it is certain that no one has ever been on the moon. Not merely is nothing of the sort ever seriously reported to us by reasonable people, but our whole system of physics forbids us to believe it.“ We only have the ability to examine a minuscule fraction of the information available in the big picture of it all. We cannot escape uncertainty yet, even though we routinely pretend that we have.
The book talks about “language games”. It’s a concept that Wittgenstein developed earlier in his life to explain how people inherit and subconsciously create unspoken rules of communication that gloss over or emphasize certain words and ideas. He writes, “It’s not a matter of [philosopher G.E.] Moore’s knowing that there’s a hand there, but rather we should not understand him if he were to say ‘Of course I may be wrong about this.’ ” We don’t say we know that our religious, political or even sports affiliations are true, the assumptions are built right into our languaging. What better example is there than the wide-eyed sports fan who is unquestionably convinced that their random group of players is the best that there ever was and will be? Many of them are not bluffing, their language game has programmed them. The word structure that they know will not allow them to see it any other way. People’s various language games assume what they want, often from habit, usually based on subconscious tradition.
“Suppose now I say ‘I’m incapable of being wrong about this: that is a book’ while I point to an object. What would a mistake here be like? And have I any clear idea of it?” There are fake books, tricks are played, there are mind altering substances, coincidences happen, there could be a secret society of magicians controlling public perceptions, or our world could be some kind of solipsistic melting pot of dreams and hallucinations. We could list things like these all day. There are simpler examples for common situations as well, like, somebody might be unquestionably convinced they are seeing a magazine when it is a zine, or a cow when it is in fact a bull. It’s also pretty common for people to think that they know a person made a mistake that they did not actually make. Consider that the way the future is headed, there is a good chance we will all have 3d printers that run on practically free energy and make everything out of basic materials like sand and vegetation, be free to travel around the universe with access to trillions of planets, and so forth. In that reality, theme planets are all but inevitable. There will be planets for specific ecological niches and time periods. People will be able to set up Plato’s Cave, Truman Show style planets, and countless other scenarios. Being that this seems so inevitable (read The Singularity is Near if you are not convinced), why would we assume that we are not in a scenario like that right now?
What happens though, is if we were to take the groundlessness of surety into account in our day to day communication, we wouldn’t be able to say anything. It seems we might almost be cornered into adopting language games. “This game proves its worth. That may be the cause of its being played, but it is not the ground.” The temptation to stay locked into them is almost irresistible, especially the hereditary ones. “[W]ould it be unthinkable that I should stay in the saddle however much the facts bucked?” It isn’t unthinkable because the entire purpose of the game is to ride unreasonable broncos and we have been training since we were born. Wittgenstein goes on to ponder, “Certain events would [put] me into a position in which I could not go on with the old language-game any further. In which I was torn away from the sureness of the game. Indeed, doesn’t it seem obvious that the possibility of a language-game is conditioned by certain facts?” It’s possible but usually very difficult because safeguards and defense mechanisms are built into them too. When a person does something detrimental, “it is what it is” — when evidence bucks, faith grips tighter — another team might have won the super bowl, but their quarterback threw for more yards in the season.
There are a lot of incompatible language games being played around the world. If you tell a person embedded in another one that they are wrong, it’s almost as if they cannot know it because if they were to consider that they should doubt parts of it, it would open the door to the slippery slope leading to the “annihilation of all yardsticks”, and it is difficult, maybe nearly impossible, to live in a world without them. “If something happened calculated to make me doubtful of my own name, there would certainly also be something that made the grounds of these doubts themselves seem doubtful, and I could therefore decide to retain my old belief.” In order to take action, you have to make decisions, and in order to make decisions, some of the patterns in your mind need to win out over the others. If there aren’t any execute commands in the code, then the code is lifeless and goes nowhere.
Does this mean that we have to permit some unsubstantiated assertions? All of them? Do we have the right to dismiss any of them? If it turns out to be true that there is no foundation for knowledge or contemplation, then how could we draw such a line? I think a lot of it comes down to what I talk about in terms of how much we are willing to bet at a given time, and the use of words like “seems”. “We just do not see how very specialized the use of ‘I know’ is. For ‘I know’ seems to describe a state of affairs which guarantees what is known, guarantees it as a fact. One always forgets the expression ‘I thought I knew’ “.
It’s not that we know, it’s that certain things look very likely to us from our current perspective, and we all know that our perspectives have changed, and therefore that more of them will likely change as well. We should learn to expect this, and if we are honest with ourselves, be proactive about it. I believe that is the common language game we can all play. It is like we are trying to play blackjack with people who are trying to play poker, war, concentration and rummy with us. If we all played poker, our individual bets would still range in scale depending on our hands at any given time but we would all be playing a compatible game.
When it comes to the concept of “seems”, I have found that there doesn’t seem to be a lot of alternatives, which sometimes makes it difficult to talk in terms of it in a stylistically appropriate way. Being that people are prone to asserting the uncertain so pervasively, it makes sense that we might end up with so few words for expressing variations and shades of doubt. Wittgenstein uses a variety of phrasing throughout the book that give us some ideas on how we might expand it. I pulled many of them together and summed them up:
“Suppose I replaced Moore’s ‘I know’ by ‘I am of the unshakeable conviction’?”
“It stands fast for me and many others…”
‘That’s how it is — rely upon it.’
“I learned it years and years ago”
“I am sure it is so.“
“is an irreversible belief.“
“it gives us a right to assume it.”
“Suppose it were forbidden to say ‘I know’ and only allowed to say ‘I believe I know’?”
“excludes a certain kind of failure”
“I can hardly be mistaken”
“That is the truth — so far as a human being can know it.“
That is not to say that every communication should necessarily be tentative. One of the main conclusions that Wittgenstein reaches is that our beliefs can be justified, but not certain. “[…] I find it quite correct for someone to say ‘Rubbish!’ and so brush aside the attempt to confuse him with doubts at bedrock, — nevertheless, I hold it to be incorrect if he seeks to defend himself (using, e.g., the words ‘I know’).” I think of that in terms of calculated risk. Sometimes you have to remove the language of doubt in order to favor the patterns in life that seem most important. That, though, is less like certainty and more like leadership. All confidence is either bluff or ignorance. If we have calculated the potential value in bluffing our certainty, that is one thing, but to do it blindly, unknowingly, is another.
Wittgenstein talks about how if existential certainty is there to be found, it would probably be in a form similar to a mathematical proposition and proof. “If the proposition 12×12=144 is exempt from doubt, then so too must non-mathematical propositions be.” “If” being a key word there. He reminds us that it seems as though they cannot be certain either but goes out on a short limb to humor that they are. In that process he makes what I find to be one of the most profound and rather Godel-esque insights of the book: ”there ought to be a proposition that is just as certain, and deals with the process of this calculation, but isn’t itself mathematical. I am thinking of such a proposition as: ‘The multiplication 12×12, when carried out by people who know how to calculate, will in the great majority of cases give the result 144.’ Nobody will contest this proposition, and naturally it is not a mathematical one.” That might be a key to extinguishing existential angst and establishing the foundation of common meaning.
It is true that the universe might be infinite and that even if it isn’t, the work to reach certainty might still end up being like trying to reach zero by continuously dividing by half, always inching closer, impossible to reach. In the meantime, we wait in suspense as patterns wind their way through the chaos like armies meandering through mine fields. Certainty is no more than the soldiers out ahead who haven’t been blown up yet, standing in the middle of the field with a universe of unknown mines ahead. Some evolutionary lineages successfully walk on for hundreds of millions of years before they are blown up and consumed by the blur. What choice do we have, what else might we do, use patterns we don’t understand or that are wrong more of the time? We don’t know if we will make it or not. Maybe it is too difficult. Maybe it will take a hundred million additional years. Maybe we are in the home stretch and artificial intelligence of the near future is the calculator of existential proofs. We just don’t know.
We don’t know how long it might take to get a better grip on the nature of certainty, and death is barreling down on us, hence the movement for indefinite life extension. It is tragic to be uncertain about everything, which includes our own wants and needs, when the stakes are so high. It is tragic to live and die as a captive in a dark basement. Earth is that basement and our lifespans are the walls. Some people don’t see that, like captives of Plato’s cave.
As things stand, the best we can do is be willing to make educated bets at any given time. The only thing we know for sure is that we don’t know anything for sure. We don’t even know if we don’t know. That is good news though, therein sneaks the foundation that begins to unravel the absurd. If the only thing we know is that nothing makes sense until we know, and that by working to figure stuff out, we could end up knowing, that small patch of philosophical ground in the quicksands of uncertainty becomes the launchpad upon which we begin stringing lines of certainty together. Anything else would be illogical, against our nature, detrimental to our fitness. Standing on this platform is a stage in our evolutionary trajectory.
“We all believe that it isn’t possible to get to the moon; but there might be people who believe that that is possible and that it sometimes happens. We say: these people do not know a lot that we know. And, let them be never so sure of their belief — they are wrong and we know it. If we compare our system of knowledge with theirs then theirs is evidently the poorer one by far.”

Summary: Study reports SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, was well suited to making the jump from animals to humans by shapeshifting as it gained the ability to infect human cells. The virus’s ability to infect humans occurred via exchanging gene fragments from a coronavirus that infected pangolins. The species-to-species transmission was a result of the ability of SARS-CoV-2 to bind to host cells through alterations to its genetic material.
Source: Duke University
A team of scientists studying the origin of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that has caused the COVID-19 pandemic, found that it was especially well-suited to jump from animals to humans by shapeshifting as it gained the ability to infect human cells.

In the local (redshift z ≈ 0) Universe, collisional ring galaxies make up only ~0.01% of galaxies1 and are formed by head-on galactic collisions that trigger radially propagating density waves2,3,4. These striking systems provide key snapshots for dissecting galactic disks and are studied extensively in the local Universe5,6,7,8,9. However, not much is known about distant (z 0.1) collisional rings10,11,12,13,14. Here we present a detailed study of a ring galaxy at a look-back time of 10.8 Gyr (z = 2.19). Compared with our Milky Way, this galaxy has a similar stellar mass, but has a stellar half-light radius that is 1.5–2.2 times larger and is forming stars 50 times faster. The extended, diffuse stellar light outside the star-forming ring, combined with a radial velocity on the ring and an intruder galaxy nearby, provides evidence for this galaxy hosting a collisional ring. If the ring is secularly evolved15,16, the implied large bar in a giant disk would be inconsistent with the current understanding of the earliest formation of barred spirals17,18,19,20,21. Contrary to previous predictions10,11,12, this work suggests that massive collisional rings were as rare 11 Gyr ago as they are today. Our discovery offers a unique pathway for studying density waves in young galaxies, as well as constraining the cosmic evolution of spiral disks and galaxy groups.
Dr. Michael R. Rose is Professor at Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at University Of California, Irvine. His main area of work has been the evolution of aging.
“Our task is to make nature, the blind force of nature, into an instrument of universal resuscitation and to become a union of immortal beings.“
- Nikolai F. Fedorov
We hold faith in the technologies & discoveries of humanity to END AGING and Defeat involuntary Death within our lifetime.
Working to Save Lives with Age Reversal Education.
========== Perpetual Life Creed ==========
We believe that all of life is sacred and that we have been given this one life to make unlimited. We believe in our Creator’s divine plan for all of humanity to have infinite lifespans in perfect health and eternal joy, rendering death to be optional.
By following our Gospel we achieve eternal life creating a heaven here on earth.

Transhumanism is a form of “Humanism” (atheism or naturalism). The word and concept was coined by Julian Huxley back in the day. I was a student of A.J. Ayer who suceeded Huxley as head of British Humanism. https://humanism.org.uk/humanism/the-humanist-tradition/20th…an-huxley/ We must nowadays include “Christian Transhumanism” and tolerate all religions and superstitions (however daft), without right to criticise such “Holy” sanctified cows. And so the posthuman goddesses and gods 😉 have decreed it is a good idea to make MVT, FM-2030 and post/ “humanist” ideas available tor current religious self-IDers, I have kicked things off with Posthuman Buddhism https://www.facebook.com/groups/posthumanbuddhism/ and Posthuman Christianity https://www.facebook.com/groups/2164360640528843/
Perhaps we can update and reform such bastions of anachronism and conventionalism with the light of (actual, not gospel) truth?
Julian Huxley was the grandson of T H Huxley (staunch supporter of Charles Darwin and creator of the term “agnostic”). He continued his grandfather’s valuable work – in 1927, he joined H G Wells and his son in producing a comprehensive book called The Science of Life, which helped to spread a general understanding of evolution and to promote Biology in the school curriculum. He believed that the study of evolution could help us to understand our own nature and behaviour. He was a professor at King’s College, London, and a pioneer in the study of animal behaviour (ethology) and conservation.
His wife wrote of him: “Julian had a gift of enhancing the moment, making a memorable event of an ordinary walk. He was intensely aware of the moods and treasures of the natural world, knew mountains and their geological structures, feeling their bones under the skin of earth and trees. I loved his all-embracing recognition – knitting together the earth and the animal world, including human beings…”
In 1935 he became one of the first directors of London Zoo. In the early sixties, he wrote articles about hunted and endangered species in Africa, which contributed to the founding of the World Wildlife Fund.

Maximizing the protection of life on Earth requires knowledge of the global patterns of biodiversity at multiple dimensions, from genetic diversity within species, to species and ecosystem diversity. Yet, the lack of genetic sequences with geographic information at global scale has so far hindered our ability to map genetic diversity, an important, but hard to detect, biodiversity dimension.
In a new study, researchers from the Universities of Copenhagen and Adelaide have collected and georeferenced a massive amount of genetic data for terrestrial mammals and evaluated long-standing theories that could explain the global distribution of genetic diversity. They found that regions of the world rich in deep evolutionary history, such as Northern Andes, the Eastern Arc Mountains, Amazonia, the Brazilian Atlantic forest, the central America jungles, sub-Saharan Africa and south-eastern Asia are also strongholds of genetic diversity. They also show that the relatively stable climate in these regions during the past 21’000 years contributes significantly to this intraspecific richness.
“Genetic diversity within species is a critical component of biodiversity, playing two important roles at the same time. It reflects species evolutionary history and defines their capacity to adapt under future environmental change. However, and despite the predictions of major biodiversity theories, the actual global distribution of genetic diversity remained, so far, a mystery. Recent collective efforts to populate public databases with genetic sequences and their localities allowed us to evaluate these theories and generate the first global maps of genetic diversity in terrestrial mammal assemblages”, says Spyros Theodoridis, Postdoctoral Researcher at the Center for Macroecology, Evolution and Climate, GLOBE Institute, and lead author of the study.
I always enjoy the perspective of David Wood, and in this session of the London Futurists there is a panel discussion about genetic engineering in the future.
Our DNA is becoming as readable, writable, and hackable as our information technology. The resulting genetic revolution is poised to transform our healthcare, our choices for the characteristics of the next generation, and our evolution as a species. The future could bring breathtaking advances in human well-being, but it could also descend into a dangerous genetic arms race.
These claims are made in the recent book “Hacking Darwin: Genetic Engineering and the Future of Humanity”, https://hackingdarwin.com/ by Technology Futurist Jamie Metzl, https://jamiemetzl.com/
Jamie’s view is that society isn’t at all ready for the fast-approaching future of widespread genetic hacking.
Here is some feedback for his book:
Circa 2018
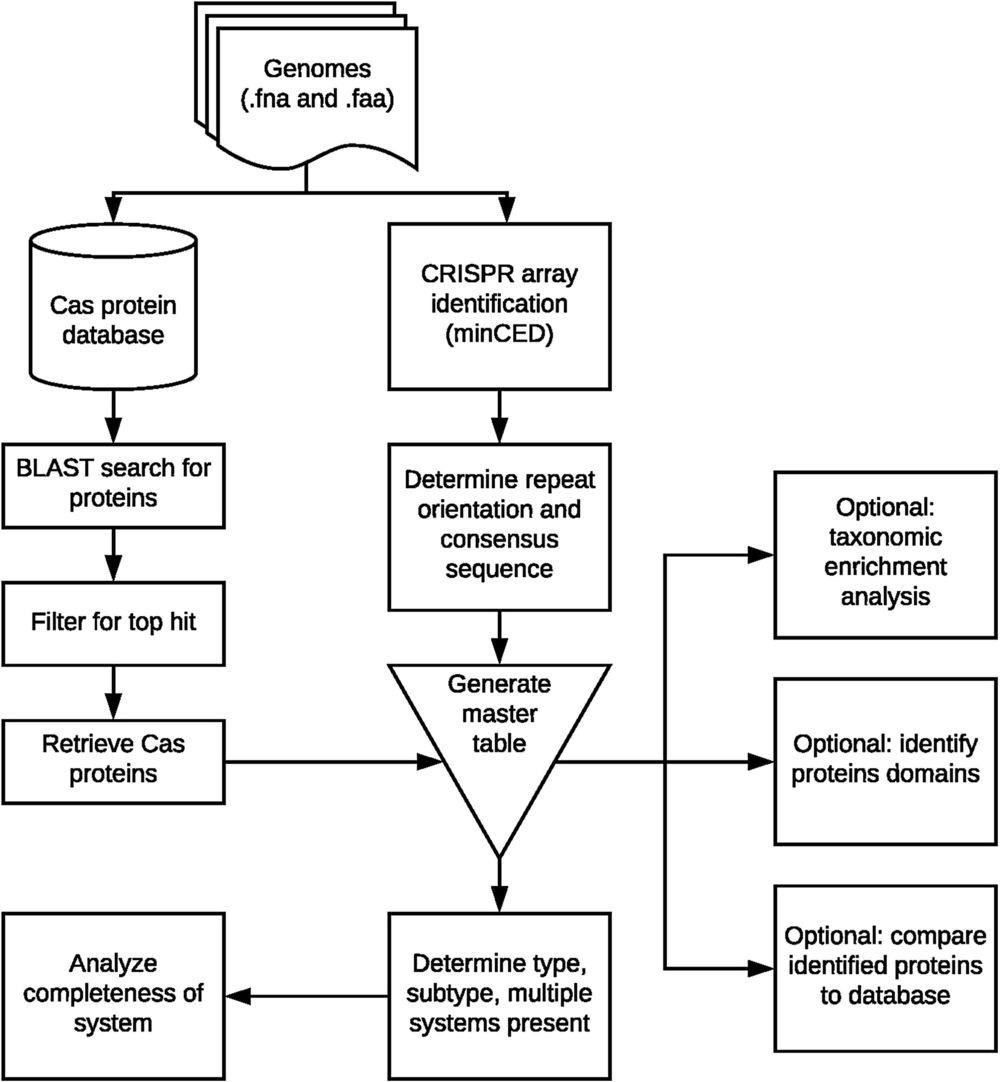
CRISPR-Cas adaptive immune systems of bacteria and archaea have catapulted into the scientific spotlight as genome editing tools. To aid researchers in the field, we have developed an automated pipeline, named CRISPRdisco (CRISPR discovery), to identify CRISPR repeats and cas genes in genome assemblies, determine type and subtype, and describe system completeness. All six major types and 23 currently recognized subtypes and novel putative V-U types are detected. Here, we use the pipeline to identify and classify putative CRISPR-Cas systems in 2,777 complete genomes from the NCBI RefSeq database. This allows comparison to previous publications and investigation of the occurrence and size of CRISPR-Cas systems. Software available at http://github.com/crisprlab/CRISPRdisco provides reproducible, standardized, accessible, transparent, and high-throughput analysis methods available to all researchers in and beyond the CRISPR-Cas research community. This tool opens new avenues to enable classification within a complex nomenclature and provides analytical methods in a field that has evolved rapidly.
CRISPR-Cas* bacterial and archaeal immune systems remain of high interest across many domains of the life sciences, including food science, molecular biology, prokaryotic evolution, and as a technology from pharma to next-generation crops.1–4 The unifying interest in CRISPR is the tremendous wealth of applications this technology affords. While application and tool development using a handful of characterized CRISPR-Cas systems has exploded, the annotation and discovery of systems remains an ongoing challenge for microbiologists and bioinformaticians to solve. The ability to identify CRISPR-Cas systems can benefit the greater scientific community, from microbiologists attempting to learn about adaptive immunity in prokaryotes, to molecular biologists interested in harnessing the nucleic acid-targeting functions of various Cas proteins.