Guys! I’m so thrilled to present to you my debut work in documentary filmmaking! You can now watch my new film Consciousness: Evolution of the Mind in its entirety on major networks, such as Vimeo on demand, worldwide.
Category: evolution – Page 135
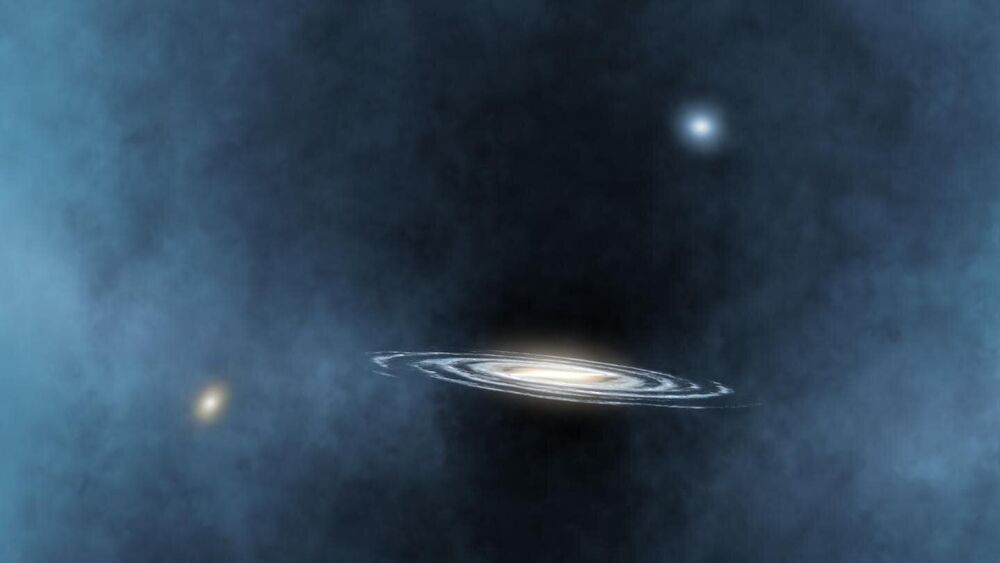

A study shows the unexpected effect of black holes beyond their own galaxies
At the heart of almost every sufficiently massive galaxy there is a black hole whose gravitational field, although very intense, affects only a small region around the center of the galaxy. Even though these objects are thousands of millions of times smaller than their host galaxies, our current view is that the Universe can be understood only if the evolution of galaxies is regulated by the activity of these black holes, because without them the observed properties of the galaxies cannot be explained.
Theoretical predictions suggest that as these black holes grow they generate sufficient energy to heat up and drive out the gas within galaxies to great distances. Observing and describing the mechanism by which this energy interacts with galaxies and modifies their evolution is therefore a basic question in present day Astrophysics.
With this aim in mind, a study led by Ignacio Martín Navarro, a researcher at the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), has gone a step further and has tried to see whether the matter and energy emitted from around these black holes can alter the evolution, not only of the host galaxy, but also of the satellite galaxies around it, at even greater distances. To do this, the team has used the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, which allowed them to analyze the properties of the galaxies in thousands of groups and clusters. The conclusions of this study, started during Navarro’s stay at the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics, are published today in Nature magazine.
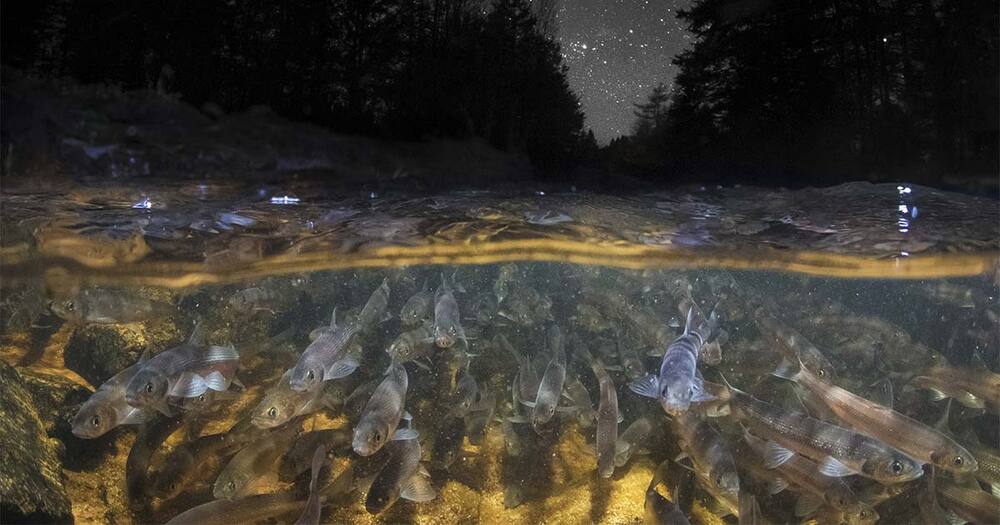

DNA Jumps Between Animal Species. No One Knows How Often
Laurie Graham, a molecular biologist at Queen’s University in Ontario and lead author on the paper, knows she’s making a bold claim in arguing for the direct transfer of a gene from one fish to another. That kind of horizontal DNA movement once wasn’t imagined to happen in any animals, let alone vertebrates. Still, the more she and her colleagues study the smelt, the clearer the evidence becomes.
Nor are the smelt unique. Recent studies of a range of animals — other fish, reptiles, birds and mammals — point to a similar conclusion: The lateral inheritance of DNA, once thought to be exclusive to microbes, occurs on branches throughout the tree of life.
Sarah Schaack, an evolutionary genomicist at Reed College in Portland, Oregon, believes these cases of horizontal transfer still have “a pretty big wow factor” even among scientists, “because the conventional wisdom for so long was that it was less likely or impossible in eukaryotes.” But the smelt discovery and other recent examples all point to horizontal transfers playing an influential role in evolution.
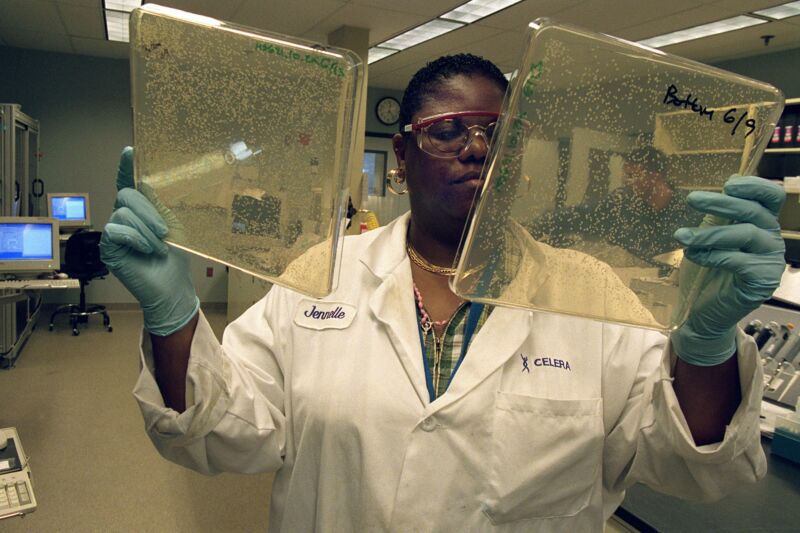

Researchers rewire the genetics of E. coli, make it virus-proof
Many of the fundamental features of life don’t necessarily have to be the way they are. Chance plays a major role in evolution, and there are always alternate paths that were never explored, simply because whatever evolved previously happened to be good enough. One instance of this idea is the genetic code, which converts the information carried by our DNA into the specific sequence of amino acids that form proteins. There are scores of potential amino acids, many of which can form spontaneously, but most life uses a genetic code that relies on just 20 of them.
Over the past couple of decades, scientists have shown that it doesn’t have to be that way. If you supply bacteria with the right enzyme and an alternative amino acid, they can use it. But bacteria won’t use the enzyme and amino acid very efficiently, as all the existing genetic code slots are already in use.
In a new work, researchers have managed to edit bacteria’s genetic code to free up a few new slots. They then filled those slots with unnatural amino acids, allowing the bacteria to produce proteins that would never be found in nature. One side effect of the reprogramming? No viruses could replicate in the modified bacteria.

Researchers: Culture drives human evolution more than genetics
PROCEEDINGS OF THE ROYAL SOCIETY • JUN 3, 2021
Culture drives human evolution more than genetics
I wonder about the thought that only humans do this, and perhaps that somehow culture is separate in some way from biological evolution enmeshed with the rest of the planet?
by University of Maine
Culture is an under-appreciated factor in human evolution, Waring says. Like genes, culture helps people adjust to their environment and meet the challenges of survival and reproduction. Culture, however, does so more effectively than genes because the transfer of knowledge is faster and more flexible than the inheritance of genes, according to Waring and Wood.
Waring and Wood say culture is also special in one important way: it is strongly group-oriented. Factors like conformity, social identity and shared norms and institutions—factors that have no genetic equivalent—make cultural evolution very group-oriented, according to researchers. Therefore, competition between culturally organized groups propels adaptations such as new cooperative norms and social systems that help groups survive better together.
According to researchers, “culturally organized groups appear to solve adaptive problems more readily than individuals, through the compounding value of social learning and cultural transmission in groups.” Cultural adaptations may also occur faster in larger groups than in small ones.
With groups primarily driving culture and culture now fueling human evolution more than genetics, Waring and Wood found that evolution itself has become more group-oriented.
“In the very long term, we suggest that humans are evolving from individual genetic organisms to cultural groups which function as superorganisms, similar to ant colonies and beehives,” Waring says. “The ‘society as organism’ metaphor is not so metaphorical after all.
Experimental vaccine forces bacteria down an evolutionary dead end
The team says that the technique could be used to develop new vaccines against antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and potentially even wipe out some dangerous strains in a similar way to how smallpox was eradicated.
Pathogens like bacteria and viruses are extremely good at evolving in response to drugs, which can render vaccines ineffective. But now, researchers at ETH Zurich have found a way to weaponize that ability against them, forcing the bugs down harmless evolutionary dead ends.
Microbes are living examples of evolution in action. Darwin’s classic theory says that when lifeforms are exposed to pressures from their environment, some of them will develop new genetic mutations that help them cope better. Since other individuals will be at a disadvantage, the mutations will eventually become the norm throughout a population.
In the world of bacteria and viruses, drugs and vaccines are the environmental pressures that they must overcome. And they do it with frustrating ease, quickly finding ways around the attacks and then swapping those genes like trading cards. The end result is the constant looming threat of antibiotic-resistant “superbugs” that render our best drugs ineffective.
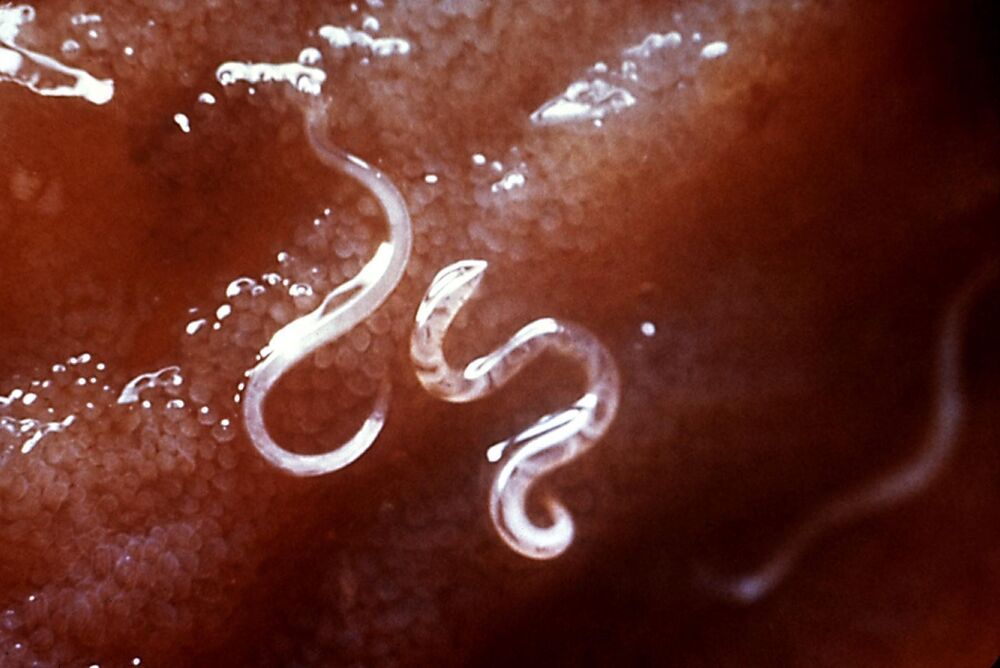
Parasitic worms: The helping hand of an unwanted friend
Full article available at: https://www.regenerativemedicinedaily.com/parasitic-worms… See More.
Humanity has a long and turbulent history with parasites, even today many parts of the world still struggle with rampant parasitic infections, with pathogens such as the malaria parasite claiming hundreds of thousands of lives every year. By their very nature parasites are harmful to our bodies, or at least that has been the prevailing opinion within the scientific community for as long as we have known of their existence. However, the malicious evolution of parasites might very well have produced a positive side effect which we are only just starting to notice.
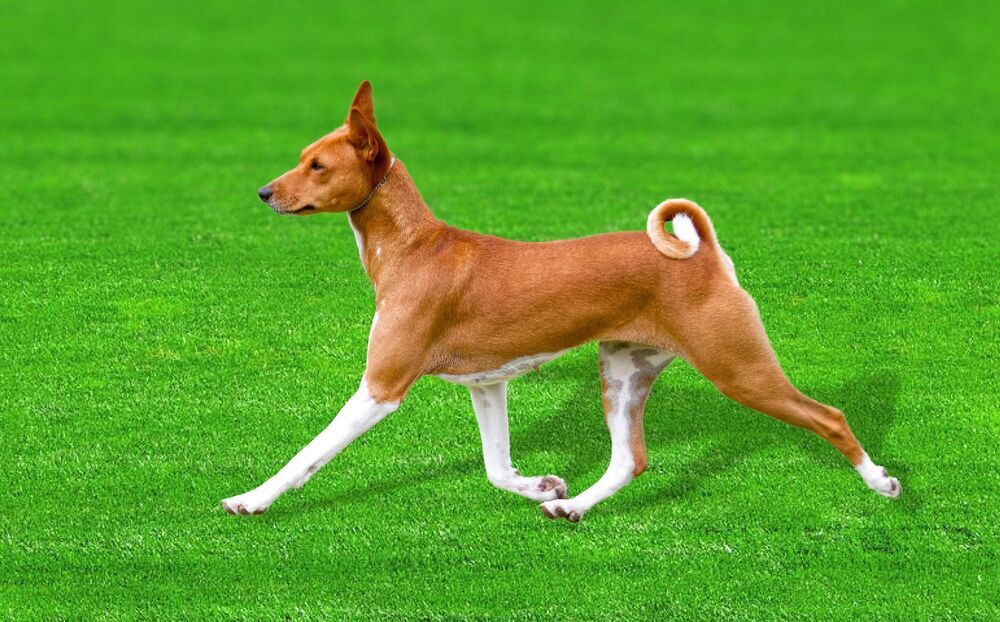

Ancient dog breed DNA helps unravel clues about evolution of man’s best friend
An international study led by UNSW researchers has mapped one of the most intact and complete dog genomes ever generated.
The genome sequence of the Basenji dog could have a big impact on the understanding of dog evolution, domestication and canine genetic diseases.
The Basenji—also known as the barkless dog—is an ancient African dog breed which still lives and hunts with tribesmen in the African Congo.
The Passage of Time and the Meaning of Life | Sean Carroll
What is time? What is humankind’s role in the universe? What is the meaning of life? For much of human history, these questions have been the province of religion and philosophy. What answers can science provide?
In this talk, Sean Carroll will share what physicists know, and don’t yet know, about the nature of time. He’ll argue that while the universe might not have purpose, we can create meaning and purpose through how we approach reality, and how we live our lives.
Sean Carroll is a Research Professor of theoretical physics at the California Institute of Technology, and an External Professor at the Santa Fe Institute. His research has focused on fundamental physics and cosmology, especially issues of dark matter, dark energy, spacetime symmetries, and the origin of the universe.
Recently, Carroll has worked on the foundations of quantum mechanics, the emergence of spacetime, and the evolution of entropy and complexity. Carroll is the author of Something Deeply Hidden, The Big Picture, The Particle at the End of the Universe amongst other books and hosts the Mindscape podcast.
“The Passage of Time and the Meaning of Life” was given on May 4, 02021 as part of Long Now’s Seminar series. The series was started in 02003 to build a compelling body of ideas about long-term thinking from some of the world’s leading thinkers. The Seminars take place in San Francisco and are curated and hosted by Stewart Brand. To follow the talks, you can:
Explore the full series: http://longnow.org/seminars.
Episode 52 — The Unexpected Origins of Life’s Genetic Code
Great new episode with guest Ben K.D. Pearce on how and why our own genetic code was able to form in Earth’s warm little ponds as early as 4.5 billion years ago. Please have a listen.
Guest Ben K.D. Pearce, a Ph.D student in astrophysics and astrobiology at McMaster University in Toronto, and an expert on the origins of life’s building blocks here on Earth. We discuss the idea that all the genetic components from which life emerged were incredibly readily available biogenically very early in Earth’s evolution. As early as 4.5 billion years ago. Pearce is part of a group making great strides in learning how this all may have happened in Earth’s very ancient warm little ponds.