Any future colonization efforts directed at the Mars all share one problem in common; their reliance on a non-existent magnetic field. Mars’ magnetosphere went dark about 4 billion years ago when it’s core solidified due to its inability to retain heat because of its small mass. We now know that Mars was quite Earth-like in its history. Deep oceans once filled the now arid Martian valleys and a thick atmosphere once retained gasses which may have allowed for the development of simple life. This was all shielded by Mars’ prehistoric magnetic field.
When Mars’ magnetic line of defense fell, much of its atmosphere was ripped away into space, its oceans froze deep into the red regolith, and any chance for life to thrive there was suffocated. The reduction of greenhouse gasses caused Mars’ temperature to plummet, freezing any remaining atmosphere to the poles. Today, Mars is all but dead. Without a magnetic field, a lethal array of charged particles from the Sun bombards Mars’ surface every day threatening the potential of hosting electronic systems as well as biological life. The lack of a magnetic field also makes it impossible for Mars to retain an atmosphere or an ozone layer, which are detrimental in filtering out UV and high energy light. This would seem to make the basic principles behind terraforming the planet completely obsolete.
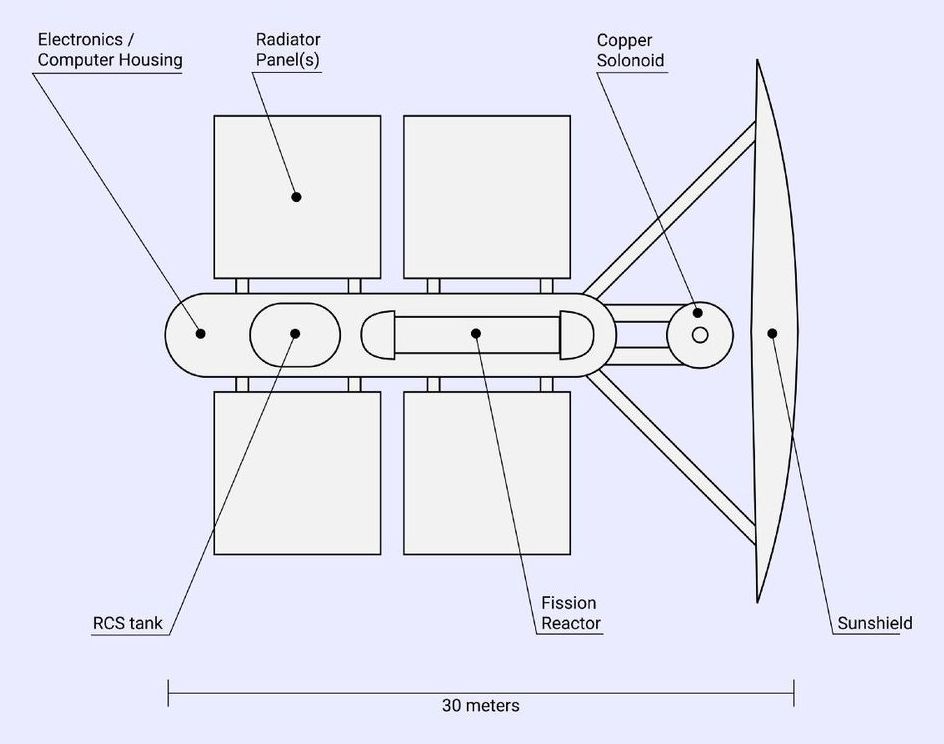
I’ve read a lot of articles about the potential of supplying Mars with an artificial magnetic field. By placing a satellite equipped with technology to produce a powerful magnetic field at Mars L1 (a far orbit around Mars where gravity from the Sun balances gravity from Mars, so that the satellite always remains between Mars and the Sun), we could encompass Mars in the resulting magnetic sheath. However, even though the idea is well understood and written about, I couldn’t find a solid mathematical proof of the concept to study for actual feasibility. So I made one!