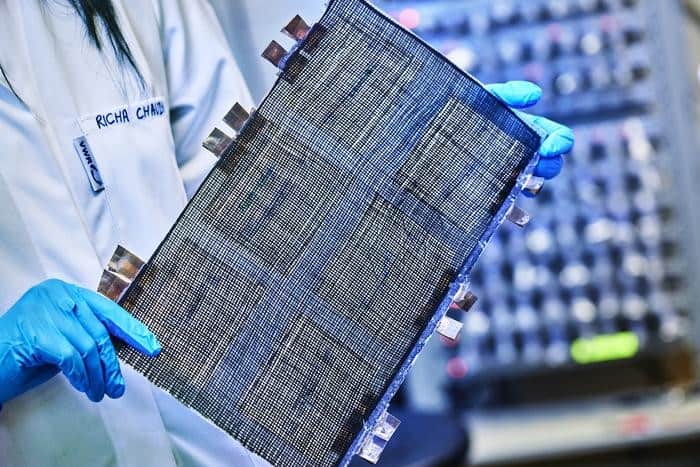
A prototype described as the world’s strongest functional structural battery has been unveiled by researchers in Sweden.
By 2023, Asp’s team had improved on this approach with a second-generation structural battery that used the same constituents, but employed an improved manufacturing method. This time, the team used an infusion technique to ensure the resin was distributed more evenly throughout the carbon fibre network.
In this incarnation, the team enhanced the battery’s negative electrode by using ultra-thin spread tow carbon fibre, where the fibres are spread into thin sheets. This approach improved both the mechanical strength and the electrical conductivity of the battery. At that stage, however, the mechanical strength of the battery was still limited by the LFP positive electrode.
Now, the team has addressed this challenge by using a carbon fibre-based positive electrode. Asp says, “This is the third generation, and is the first all-fibre structural battery, as has always been desired. Using carbon fibres in both electrodes, we could boost the battery’s elastic modulus, without suffering from reduced energy density.”