Researchers from the University of Cambridge developed the technique, which involves splitting water into oxygen and hydrogen in plants.


This video is the first in a two-part series discussing 5G. In this video, we’ll be discussing the many many aspects of current generation mobile networks that 5G is set to improve.
As well as the technologies and communication techniques that will be required to enable these upgrades in speed, latency, bandwidth, energy consumption and more!
[0:35–8:15] First we’ll take a look at the core technologies that 5G is composed of, how they work together and the benefits they will each bring.
[8:15–11:50] Following that, we’ll look at the upgrades 5G will bring to current mobile generation speeds, latency, bandwidth and energy consumption.
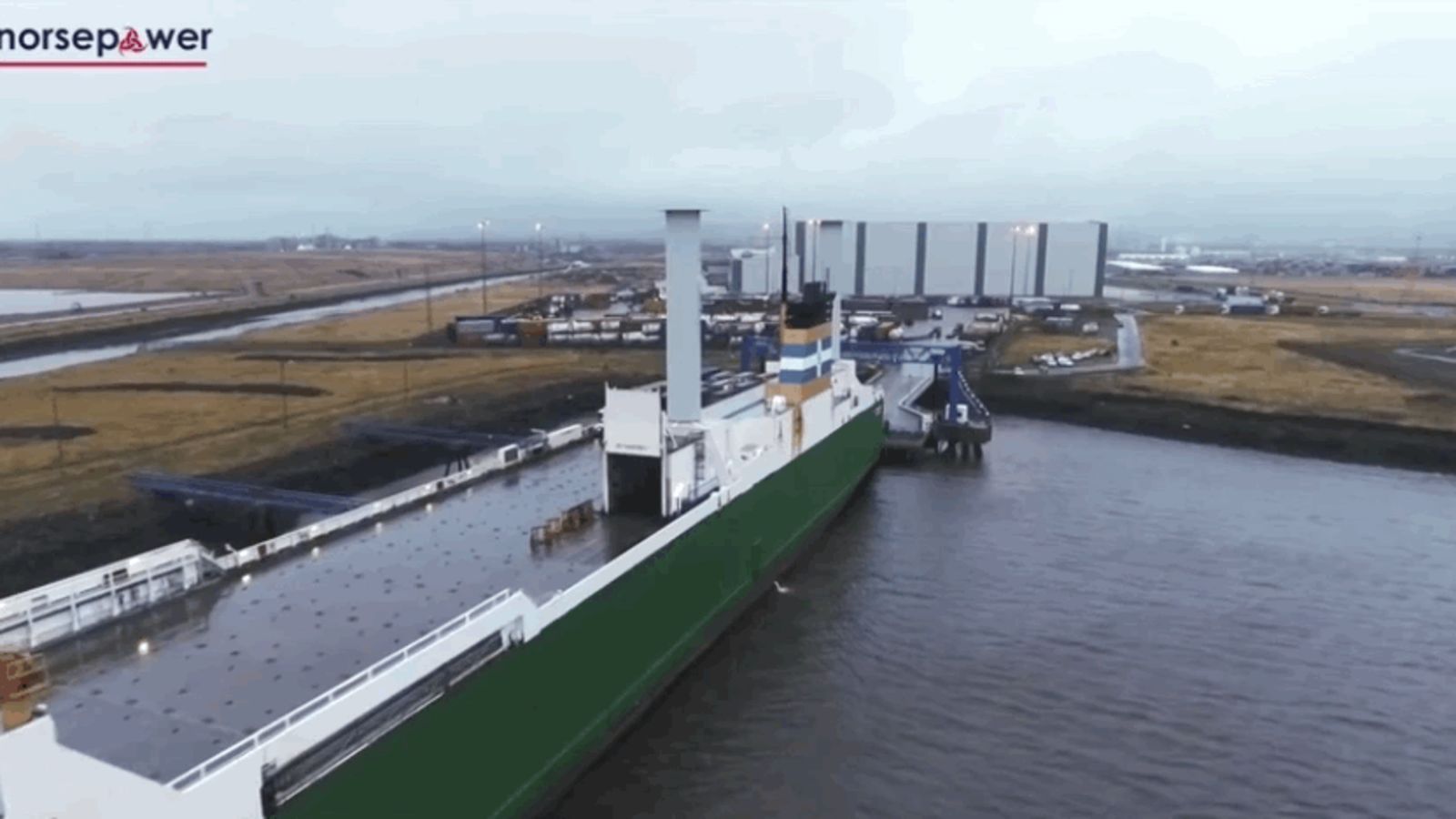

We are undeniably using up what little remains of Earth’s petroleum, and because of that, it’s getting expensive. To reduce fuel costs, shipping companies are turning back to sailboats. Yes, seriously. Sailboats. But they don’t look like any sails you’ve seen before.
You know sails – most of the time big rectangle things, sometimes big triangle things, almost always (but not always-always) made out of cloth. But while those things in the top gif don’t look like your normal sails, that’s what they are. They just don’t work like any sail you’ve ever seen before.
Most sails you’ve seen rely on the wind directly acting against them to provide propulsion. But these new types of sails, known as “rotor sails” rely on a physics principle called the Magnus Effect. Here, I’ll let the people with delightfully thick Finnish accents from Norsepower, the company that makes them, explain it:
A sapphire-colored dye called methylene blue is a common ingredient in wastewater from textile mills.
But University at Buffalo scientists think it may be possible to give this industrial pollutant a second life. In a new study, they show that the dye, when dissolved in water, is good at storing and releasing energy on cue.
This makes the compound a promising candidate material for redox flow batteries—large, rechargeable liquid-based batteries that could enable future wind farms and solar homes to stockpile electricity for calm or rainy days.
Scotrenewables Tidal Power, a Scottish engineering company, is focused on an energy source they call “tidal energy generation.” A video promoting their solution: They have plenty to show for their efforts, namely, the world’s most powerful operational tidal turbine, the SR2000 2MW.
A reduction in manufacturing and installation costs plus simple, quick and low cost maintenance strategies will be key to success.
The company release said, “Scotrenewables Tidal Power has set another record with its first 2MW floating tidal stream turbine with the unit clocking up over 3GWh of renewable electricity in its first year of testing at the European Marine Energy Centre (EMEC) in Orkney, Scotland.”
How 5G Will Change The World! https://www.facebook.com/singularityprosperity/videos/438504459964467/
In this video, we’ll be discussing 5G – more specifically, what it is and its ability to change our world!
5G is a core technology in establishing the digital infrastructure of the future and will be essential in how all of the over 50 billion mobile and connected devices by 2020 will communicate together!
[0:25–2:55] First we’ll take a quick look at the history of mobile networks, and how they have evolved over the years to present day.
[2:55–14:20] Following that, we’ll focus on the technologies a 5G network is composed of and the improvements in speed, latency, bandwidth and energy consumption they will bring.

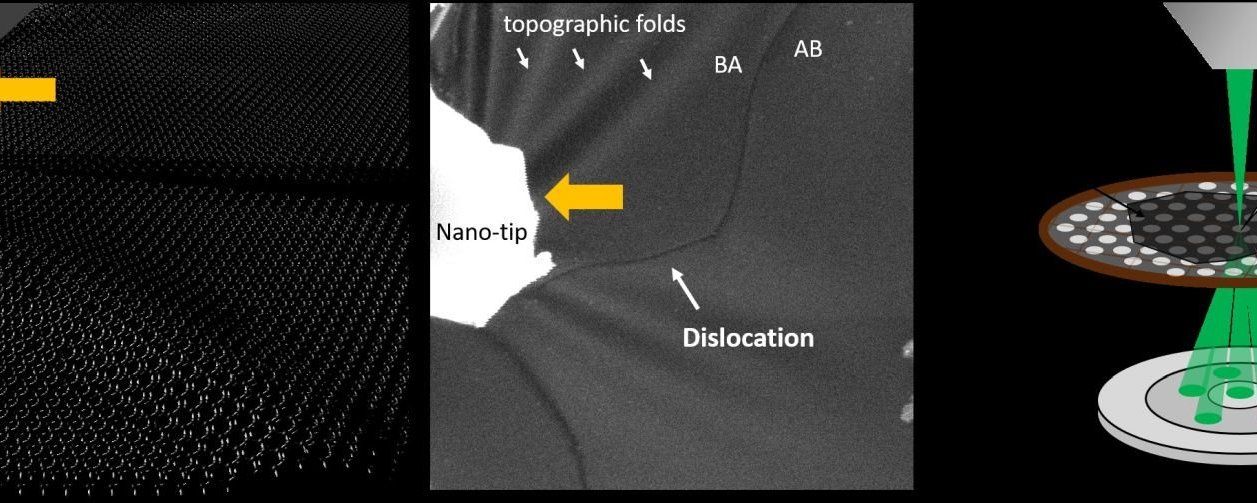
Materials can deform plastically along atomic-scale line defects called dislocations. Many technical applications such as forging are based on this fundamental process, but the power of dislocations is also exploited in the crumple zones of cars, for instance, where dislocations protect lives by transforming energy into plastic deformation. FAU researchers have now found a way of manipulating individual dislocations directly on the atomic scale.
Using advanced in situ electron microscopy, the researchers in Prof. Erdmann Spiecker’s group have opened up new ways to explore the fundamentals of plasticity. They have published their findings in Science Advances.
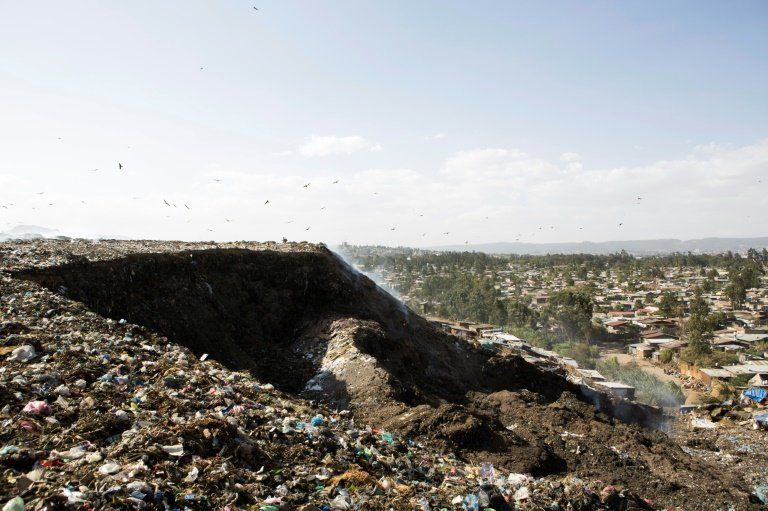

Ethiopia on Sunday inaugurated a power plant which converts waste into energy, next to a filthy open-air dump in Addis Ababa where a landslide last year killed more than 110 people.
Named Reppie, the facility is the first of its kind in Africa, according to the government and the British company Cambridge Industries behind the project, and will turn 1,400 tons of waste per day into energy.
Ethiopian President Mulatu Teshome said at the ceremony that the country “has been investing extensively in hydro power, geothermal, wind energy and now biomass to boost the manufacturing sector with a supply of clean, renewable energy.”
Our freeways and highways could really use this. What do you think?