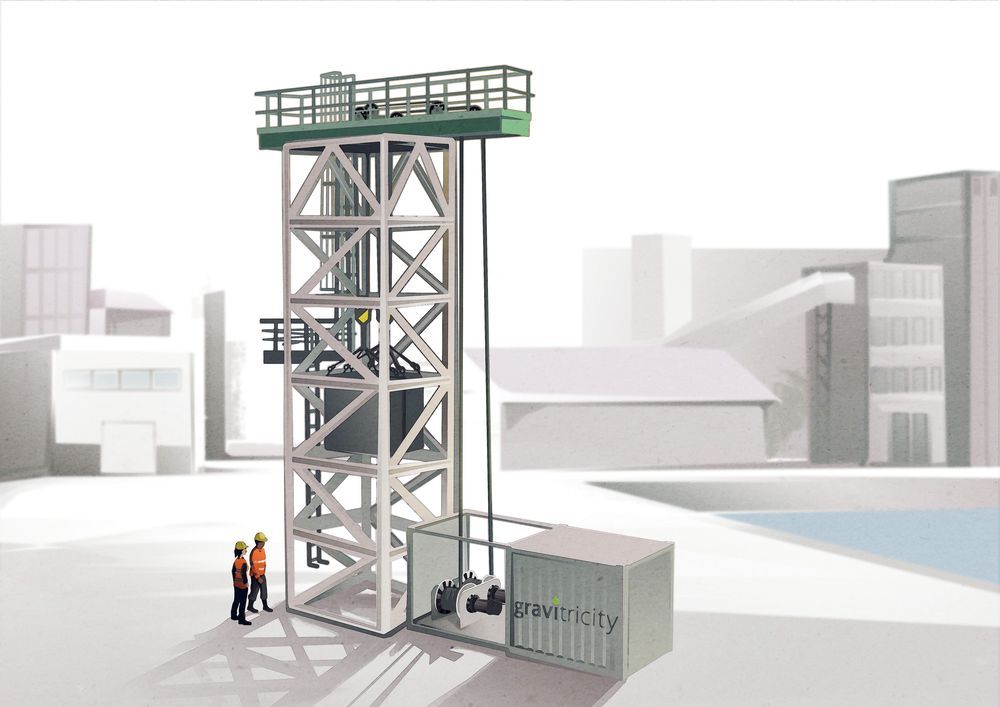
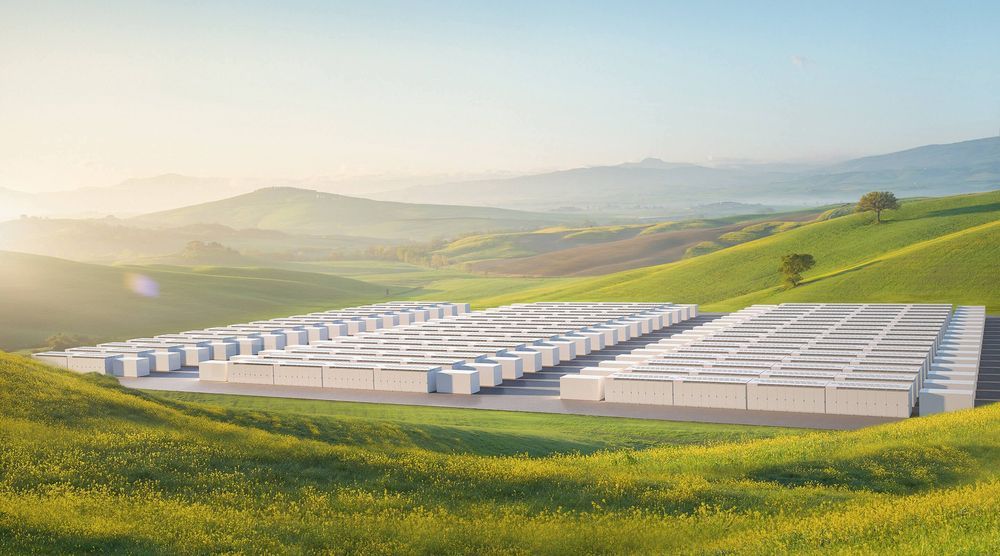
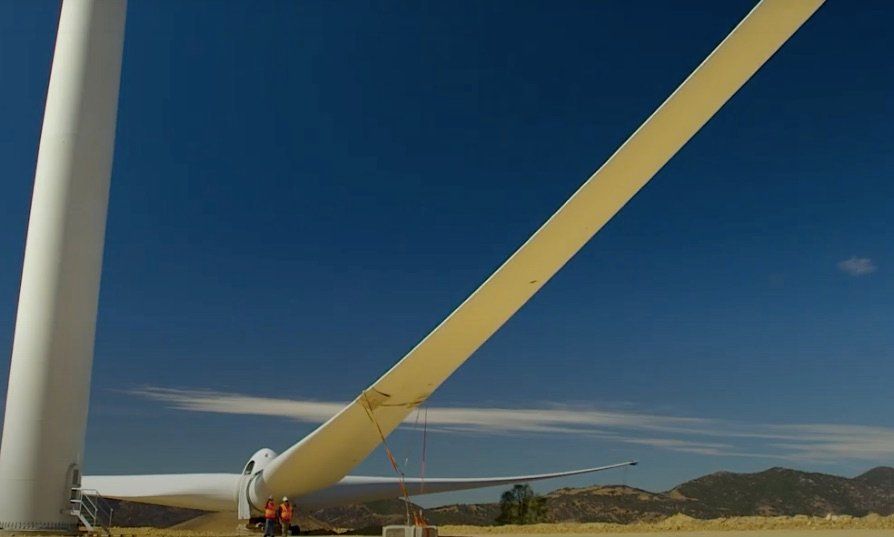
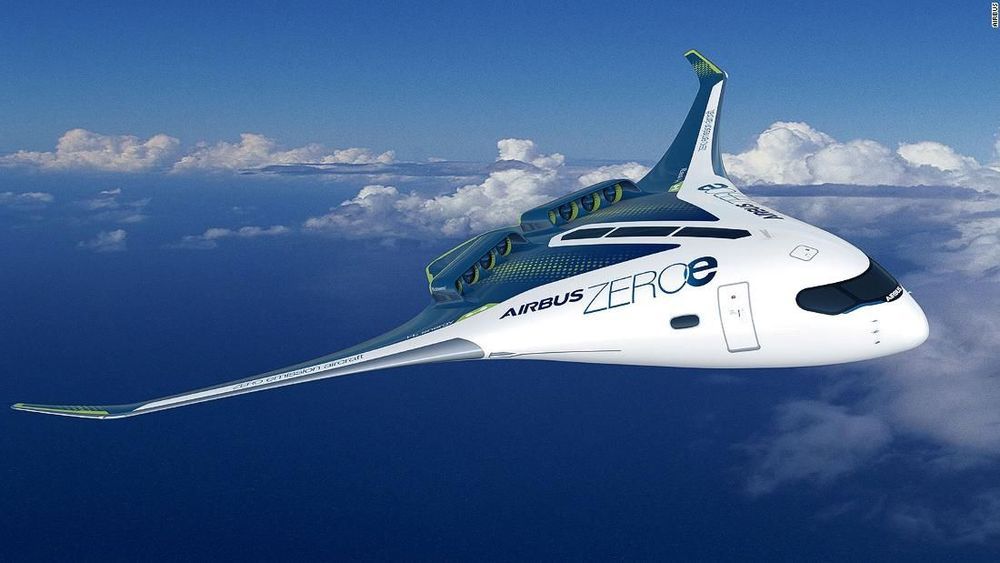
Renewable energy is now richer than the Oil industry.
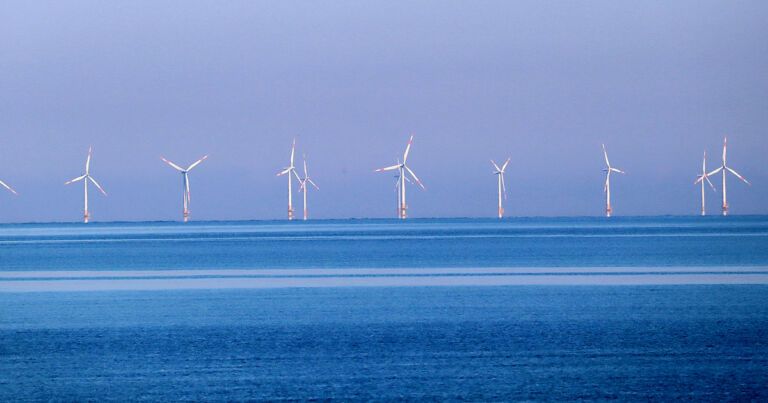
In yet another sign of the pace of the global energy transition – and the massive switch taking place in the investment community – the market value of company that describes itself as the world’s biggest producer of wind and solar power, US utility NextEra, has overtaken that of what used to be the world’s most valuable company, oil major ExxonMobil.
The flip occurred last last week, when NextEra overtook ExxonMobil to become the largest energy company in the US by market value. As Forbes reported, an investment in NextEra a decade ago would have delivered to return of 600 per cent, while an investment in ExxonMobil would have returned minus 25 per cent.
The shift is as significant as the one the world has seen in the auto industry, with electric vehicle maker Tesla overtaking the biggest car companies in the world in the last year, to the point where it is now valued at more than the next five biggest global car makers combined, despite producing just a fraction of the number of cars.