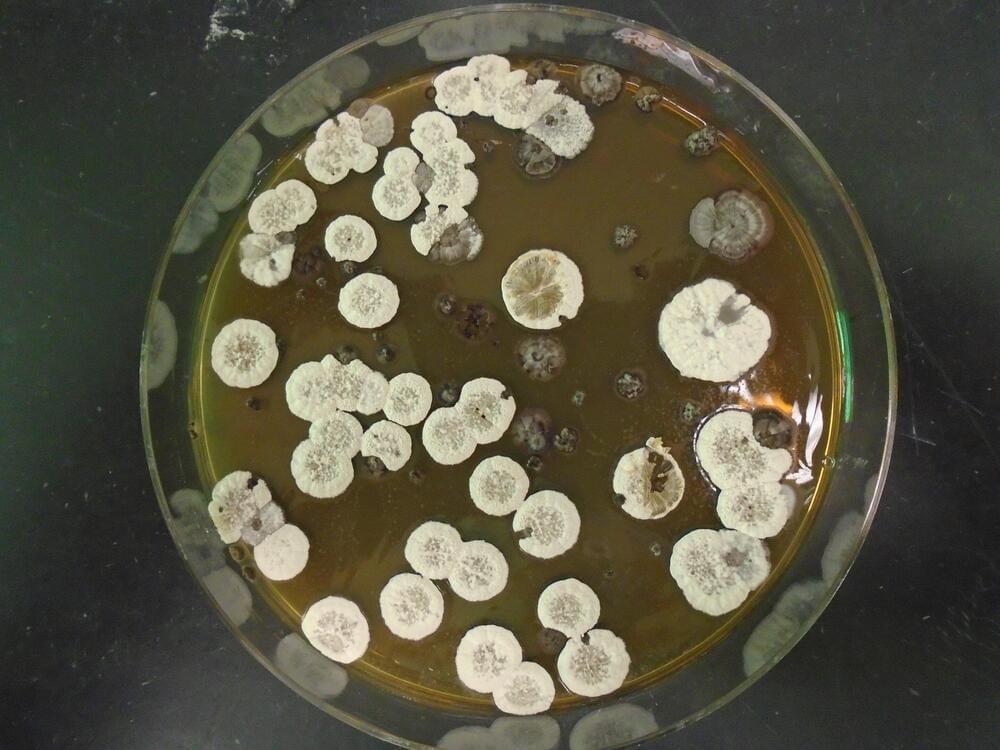
Aircrafts transport people, ship goods, and perform military operations, but the petroleum-based fuels that power them are in short supply. In research publishing on June 30 in the journal Joule, researchers at the Lawrence Berkeley Lab have found a way to generate an alternative jet fuel by harvesting an unusual carbon molecule produced by the metabolic process of bacteria commonly found in soil.
“In chemistry, everything that requires energy to make will release energy when it’s broken,” says lead author Pablo Cruz-Morales, a microbiologist at DTU Biosustain, part of the Technical University of Denmark. When petroleum jet fuel is ignited, it releases a tremendous amount of energy, and the scientists at the Keasling Lab at the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory thought there must be a way to replicate this without waiting millions of years for new fossil fuels to form.
Jay Keasling, a chemical engineer at University of California, Berkeley, approached Cruz-Morales, who was a postdoc in his lab at the time, to see if he could synthesize a tricky molecule that has the potential to produce a lot of energy. “Keasling told me: it’s gonna be an explosive idea,” says Cruz-Morales.